Comparação de mitose e meiose
Summary
TLDRThis video offers a side-by-side comparison of mitosis and meiosis, explaining the key processes and stages involved in each. Mitosis results in two identical diploid cells, crucial for growth and repair, while meiosis creates four non-identical haploid cells, essential for reproduction. The video highlights stages like prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, showing how they differ between mitosis and meiosis. With visual aids, the video clarifies concepts like crossing over in meiosis and the creation of gametes (sperm and eggs). It serves as an educational tool to better understand these vital cellular processes.
Takeaways
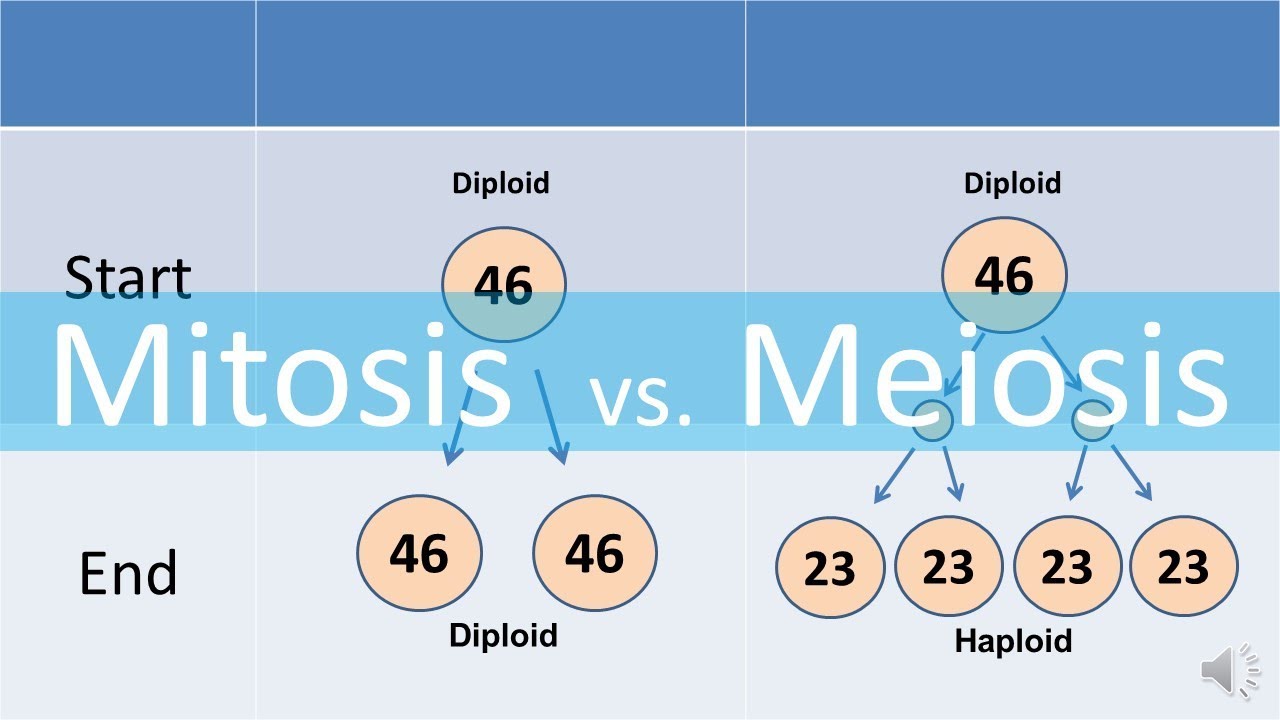
- 😀 Both mitosis and meiosis begin with a diploid cell (2m) containing 46 chromosomes in humans, 23 from each parent.
- 😀 Interphase is crucial for both processes, where chromosomes duplicate, resulting in 92 chromatids, though interphase isn't part of mitosis or meiosis.
- 😀 Mitosis and meiosis are differentiated by the number of divisions and the types of cells produced: mitosis results in two identical diploid cells, while meiosis results in four non-identical haploid gametes.
- 😀 Prophase in mitosis shows visible chromosomes, whereas prophase I in meiosis involves homologous chromosomes pairing up and crossing over, which introduces genetic diversity.
- 😀 Metaphase in mitosis sees chromosomes align in a single row, but in meiosis, the chromosomes align in pairs during metaphase I.
- 😀 During anaphase, mitosis pulls apart chromatids to opposite ends of the cell, whereas in meiosis I, entire chromosomes (not chromatids) are separated.
- 😀 Telophase in mitosis forms two identical diploid cells after cytokinesis, while in meiosis II, four haploid cells (gametes) are produced, each with half the chromosome number of the original cell.
- 😀 Cytokinesis occurs in both mitosis and meiosis, dividing the cytoplasm to complete the cell division process.
- 😀 Mitosis is important for growth, development, and cell repair, resulting in two genetically identical body cells.
- 😀 Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction, producing gametes (sperm or eggs) with half the chromosome number (haploid) for genetic diversity in offspring.
Q & A
What is the main difference between mitosis and meiosis?
-Mitosis results in two identical diploid cells, which are used for growth or cell replacement. Meiosis results in four non-identical haploid cells, which are gametes (sperm and eggs), each containing half the number of chromosomes of the original cell.
What is the starting cell for both mitosis and meiosis?
-The starting cell for both mitosis and meiosis is diploid, meaning it has two sets of chromosomes—one set from the mother and one from the father, totaling 46 chromosomes in humans.
What role does interphase play in mitosis and meiosis?
-Interphase is crucial as it duplicates the chromosomes before the start of mitosis and meiosis. While interphase is not technically part of mitosis or meiosis, it ensures that the chromosomes are ready for cell division.
How is crossing over important in meiosis?
-During prophase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over. This creates recombinant chromosomes, increasing genetic diversity in the resulting gametes.
What happens during metaphase in both mitosis and meiosis?
-In mitosis, chromosomes line up in a single row at the cell's center. In meiosis, during metaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs line up in the middle of the cell, while in metaphase II, individual chromosomes line up in a single row, similar to mitosis.
How do the processes of anaphase differ in mitosis and meiosis?
-In anaphase of mitosis, chromatids (identical copies of chromosomes) are pulled to opposite sides of the cell. In anaphase I of meiosis, whole chromosomes are separated to opposite sides. In anaphase II of meiosis, chromatids are pulled apart, similar to mitosis.
What occurs during cytokinesis after mitosis and meiosis?
-After mitosis, cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm, resulting in two identical diploid cells. After meiosis, cytokinesis also divides the cytoplasm, but the result is four non-identical haploid cells, which are gametes.
Why is meiosis necessary for sexual reproduction?
-Meiosis is necessary for sexual reproduction because it produces haploid gametes (sperm and eggs), which ensures that when fertilization occurs, the resulting zygote has a diploid number of chromosomes, maintaining the chromosome count in a species.
What is the significance of homologous chromosomes in meiosis?
-Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes, one from each parent, that have similar structure and genetic content. They undergo crossing over during meiosis, which increases genetic diversity in the offspring.
How does the number of resulting cells differ between mitosis and meiosis?
-Mitosis results in two identical diploid cells, whereas meiosis results in four non-identical haploid cells, which are gametes (sperm or eggs).
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)