Lamelar earing
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the intricacies of basic Wildan Mythology, focusing on structural steel flaws, particularly the issue of lamellar tearing. It discusses the causes, such as non-metallic inclusions during the rolling process, and the potential for cracks in the steel's thickness direction. The script offers solutions, including design modifications and controlling hydrogen content to prevent such defects. It also touches on inspection techniques and the importance of full penetration welding to mitigate stress concentration and the risk of lamellar tearing.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is a continuation of a learning series on Basic Wildan Mythology, focusing on structural issues in materials.
- 🔍 The speaker emphasizes the importance of understanding previous material and encourages questions in the YouTube comments section.
- 🛠️ Lamellar tearing is a significant topic discussed, which is a defect caused by non-metallic inclusions in steel materials.
- 💧 Non-metallic inclusions can flatten out during the rolling process, leading to a reduction in toughness in the thickness direction of the material.
- 🚫 Lamellar tearing can potentially cause cracks to open up in the material, especially near welds, due to the presence of these inclusions.
- 🔑 The likelihood of lamellar tearing is higher in the last web of a structure, where the material thickness is reduced and the risk of defects increases.
- 🔨 The type of joint and the rolling direction are critical factors that can lead to the occurrence of lamellar tearing.
- 🛡️ Hydrogen content can be a contributing factor to the development of lamellar tearing, highlighting the importance of material quality control.
- 🔧 Design considerations and changes in joint configurations can help mitigate the risk of lamellar tearing in critical applications.
- 🔄 The script suggests techniques such as full penetration welding and proper post-weld heat treatment to reduce stress concentrations and the risk of lamellar tearing.
- 🔬 Technical inspections and the use of non-destructive testing methods are recommended to ensure the quality and integrity of the material.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is about the basic Wildan Mythology of structural steel, specifically discussing the issue of lamellar tearing in steel materials.
What does 'lamellar tearing' refer to in the context of the script?
-Lamellar tearing refers to a defect in steel materials caused by non-metallic inclusions, which can lead to cracks opening up in the steel, especially in the thick direction of the material.
Why are non-metallic inclusions a problem in steel materials?
-Non-metallic inclusions are a problem because they can cause inhomogeneities in the steel, leading to a reduction in toughness and an increased risk of cracks or tearing, particularly during the rolling process.
What is the significance of the direction of rolling in relation to lamellar tearing?
-The direction of rolling is significant because non-metallic inclusions can flatten out during the process, making the steel less resistant to tearing in the direction of thickness compared to other directions.
What factors can contribute to the occurrence of lamellar tearing?
-Factors contributing to lamellar tearing include the type of joint in the steel, the presence of hydrogen, and the rolling process itself, which can cause non-metallic inclusions to become more pronounced.
How can the design of steel structures help in preventing lamellar tearing?
-The design of steel structures can help prevent lamellar tearing by considering the type of joint used, avoiding critical applications where high restraint of the joint cannot be avoided, and using premium steel with tight tolerances.
What is the role of hydrogen in the context of lamellar tearing?
-Hydrogen can be a contributing factor to lamellar tearing as it can cause hydrogen-induced cracking, which is a form of cracking that occurs due to the presence of hydrogen in the steel.
What are some techniques mentioned in the script to minimize the risk of lamellar tearing?
-Techniques mentioned include controlling hydrogen content, using premium steel with good toughness properties, modifying the design of corner joints, and applying full penetration welding to reduce stress concentration.
How can the quality of steel be improved to reduce the risk of lamellar tearing?
-The quality of steel can be improved by using high-quality steel with better toughness properties, ensuring proper rolling and welding techniques are applied, and controlling the hydrogen content during production.
What is the importance of post-weld heat treatment in the context of lamellar tearing?
-Post-weld heat treatment is important as it can help to relieve stress concentrations that may initiate cracking, thus reducing the risk of lamellar tearing in the welded joints.
What is the significance of the term 'block weld sequence' mentioned in the script?
-The term 'block weld sequence' refers to a specific technique used in welding to minimize the risk of lamellar tearing by controlling the sequence in which welds are applied to reduce stress concentrations and the potential for tearing.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Mekanika Statis Tentu: Struktur dan Elemen Bangunan

weld metal microstructure

Form, Lift, Drag and Propulsion

Structural Theory 1 Chapter 1 Part III (with Subtitles)
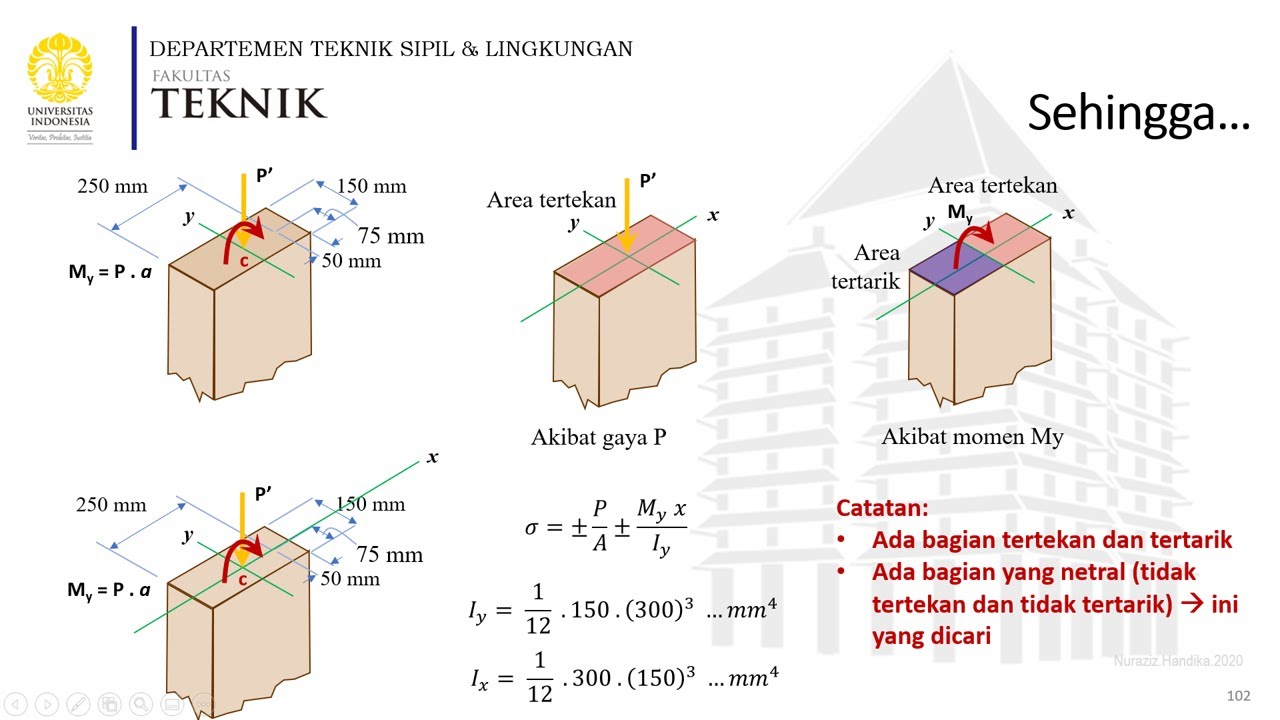
Normal stress due to axial and bending moment - Tegangan normal akibat gaya dalam momen lentur - 7

Dano à honra x liberdade de narrar fatos
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
