Hukum Pascal kelas 8 SMP
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Heriana, an IPA teacher from SMP Negeri 3 Cikesal, introduces Pascal's Law by demonstrating a simple hydraulic car lift experiment. The video explains how pressure in a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions, using hydraulic systems like those in car lifts. Through practical examples and calculations, the viewers learn how to apply this principle to real-world tools such as hydraulic jacks, pumps, and brakes. The video also highlights how Pascal's Law enables the lifting of heavy objects, like cars, at car washes. A clear and engaging lesson on the power of fluid pressure!
Takeaways
- 😀 Pascal's Law is explained as the principle of pressure in liquids within a closed system being transmitted equally in all directions.
- 😀 The video introduces a simple experiment using syringes and a toy car to demonstrate Pascal's Law.
- 😀 In the experiment, pressing a small syringe raises a larger syringe, showcasing the principle of pressure transmission.
- 😀 The experiment mimics a hydraulic lift, demonstrating how small forces can lift larger objects, such as a toy car.
- 😀 Pascal's Law is applied to hydraulic systems, such as car lifts at car washes, where fluid pressure moves in all directions.
- 😀 The hydraulic lift works because of the difference in the area of pistons, where the smaller piston requires less force to lift a larger object.
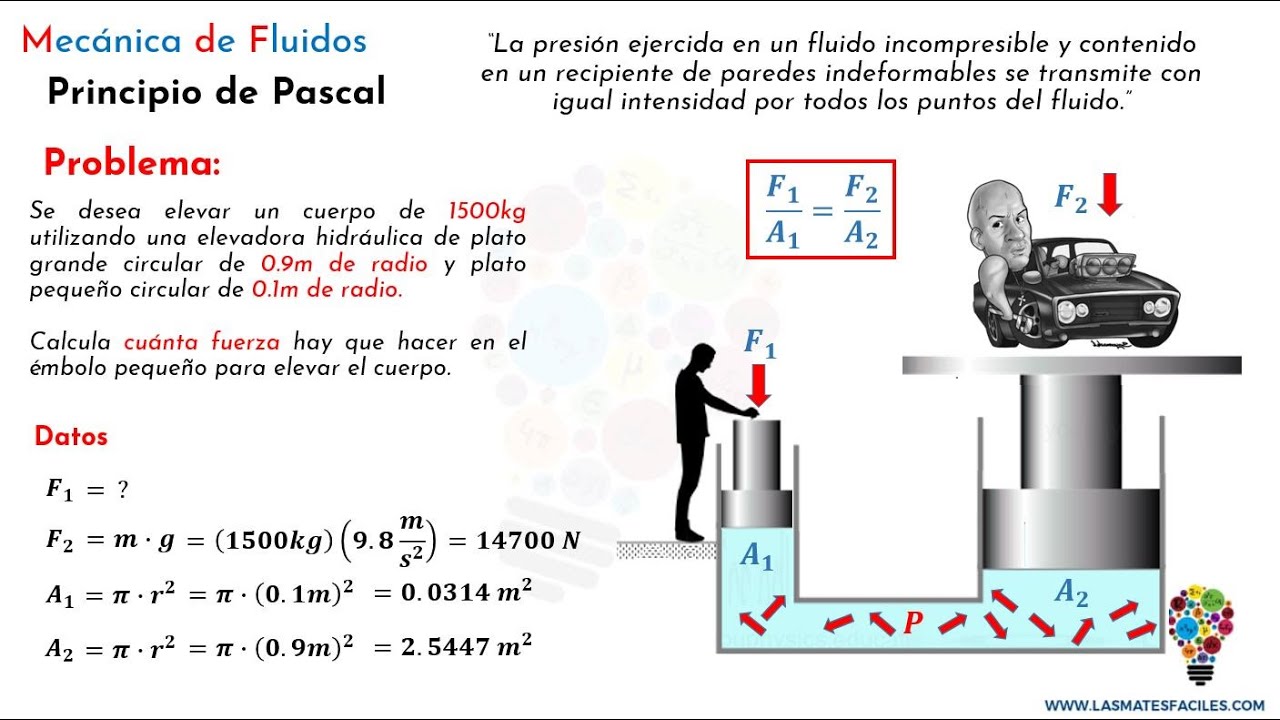
- 😀 The formula for Pascal's Law is explained: F1/A1 = F2/A2, where F is force and A is area of the pistons.
- 😀 The script uses an example problem where the forces and areas of pistons are calculated using Pascal's Law to lift a toy car.
- 😀 The second example involves calculating the weight of a car being lifted, given the force and area values, using the same Pascal's Law formula.
- 😀 Various tools that use Pascal's Law are highlighted, such as hydraulic lifts, hydraulic brakes, car jacks, and pressure gauges.
- 😀 The video concludes by acknowledging Blaise Pascal, the scientist who formulated Pascal's Law, and encourages students to appreciate the practical applications of the law.
Q & A
What is Pascal's Law, as discussed in the video?
-Pascal's Law states that the pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally and undiminished in all directions. This principle is used in various hydraulic systems like the car jack or hydraulic lifts.
How does the hydraulic lifting system for cars work according to the video?
-The hydraulic lifting system works by applying pressure to a smaller piston, which then lifts a larger piston. This principle, governed by Pascal's Law, allows a small force applied to a smaller piston to lift a heavier object, like a car, through the larger piston.
What materials are used in the hydraulic lift demonstration in the video?
-The demonstration uses simple tools: two syringes (a small one and a large one), a tube, and a toy car. Water is used as the fluid to apply pressure in the system.
What was the key observation when the smaller syringe was pressed in the experiment?
-When the smaller syringe was pressed, the larger syringe also moved, demonstrating that the pressure applied to the small syringe was transmitted to the large one, causing the toy car to lift.
How do you calculate the force required to lift an object using Pascal's Law?
-The force required to lift an object can be calculated using the formula: F1/A1 = F2/A2. F1 is the force applied to the smaller piston, A1 is its area, F2 is the force on the larger piston, and A2 is the area of the larger piston.
What is the significance of the areas of the pistons in the hydraulic system?
-The difference in the areas of the pistons (A1 and A2) determines how much force is needed to lift the object. A larger area (A2) on the larger piston allows a small force on the smaller piston (A1) to lift a heavier object.
How does Pascal's Law apply to real-world devices like hydraulic jacks?
-In hydraulic jacks, Pascal's Law is applied to generate the lifting force. A small force applied to the smaller piston is transmitted through the fluid and creates a much larger lifting force on the larger piston, which is used to lift heavy objects like cars.
Can you explain the relationship between force and area in Pascal's Law?
-In Pascal's Law, pressure is constant in a confined fluid. This means that the force applied to the smaller piston is proportional to its area. By increasing the area of the larger piston, the force can be amplified, making it possible to lift heavier objects with a smaller input force.
What was the example calculation shown in the video for finding the required force?
-In the video, the example calculation involved finding the force needed to lift a car. The known values were the areas of the small and large pistons (A1 = 50 cm² and A2 = 400 cm²), and the force on the large piston (F2 = 20,000 N). Using the formula F1/A1 = F2/A2, the required force on the small piston (F1) was calculated to be 2,500 N.
What other tools were mentioned that use Pascal's Law in the video?
-Other tools that utilize Pascal's Law, as mentioned in the video, include hydraulic pumps, hydraulic brakes, hydraulic jacks, and tensiometers. These devices rely on fluid pressure to perform tasks such as lifting, braking, or measuring tension.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)