Citratzyklus einfach erklärt - Ablauf, Phasen, Eigenschaften & Beispiel - Zellatmung - Stoffwechsel
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into why bananas are a favorite energy source for athletes, as they are rich in carbohydrates that provide chemically stored energy. It explains the process of energy release from glucose through cellular respiration, including glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain, ultimately converting energy into ATP. The script also touches on the role of enzymes and coenzymes in energy transfer and storage, offering an insightful look into the biochemical processes that power physical activity.
Takeaways
- 🏃♂️ Athletes love bananas because they are a popular source of energy due to their high carbohydrate content.
- 🔋 Carbohydrates in bananas are broken down by the body into simpler components, releasing energy stored in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
- 🚀 ATP is the universal energy storage in cells and can be used for various forms of work, such as cycling.
- 🔬 There are two main ways the body frees energy from nutrients and stores it in ATP: fermentation and cellular respiration.
- 🧬 Cellular respiration involves three steps: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle), and the electron transport chain.
- 🍌 When you eat a banana, your digestive system breaks down the carbohydrates into simpler compounds like glucose.
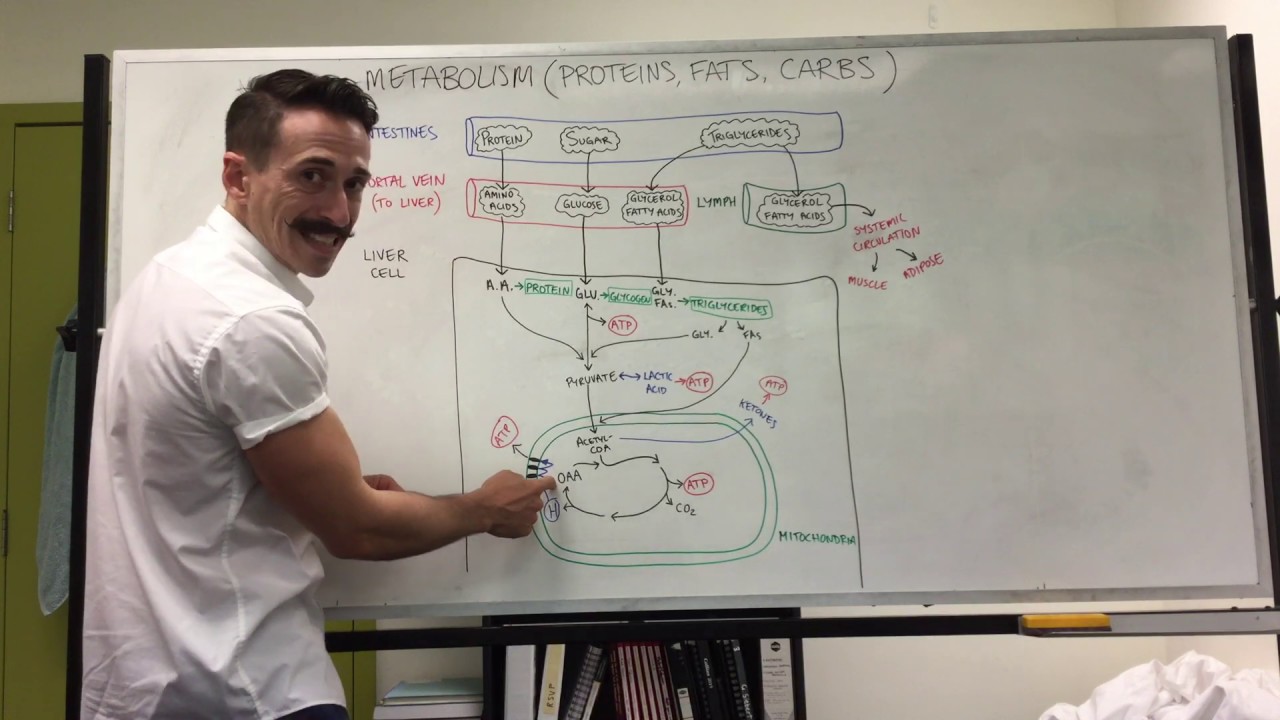
- 🔄 Glucose is then split into two molecules of pyruvate in the cytoplasm of the cell, which can then be transported into the mitochondria for further energy extraction.
- 🌀 The citric acid cycle consists of eight steps, each catalyzed by a different enzyme, and it is where most of the energy from pyruvate is released and stored as ATP.
- 🔋 The cycle involves redox reactions, where electrons are transferred along with protons to electron acceptors, such as NAD+ and FAD, which are important energy carriers.
- ♻️ The citric acid cycle oxidizes the acetyl group from pyruvate through several steps, storing the energy in the form of high-energy electrons in NADH and FADH2.
- 🔌 NADH and FADH2 act as the link between the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain, transferring their high-energy electrons to the enzymes of the electron transport chain.
Q & A
Why are bananas popular among athletes?
-Bananas are popular among athletes because they are a rich source of carbohydrates, which are a form of stored chemical energy that can be easily converted into ATP for various forms of work, such as cycling.
What is the role of carbohydrates in the body after consuming a banana?
-Carbohydrates from bananas are broken down by the body's cells with the help of enzymes into simpler components, releasing part of the contained energy that is stored in the form of ATP, the universal energy storage in cells.
What is ATP and why is it important for athletes?
-ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the universal energy currency in cells and is crucial for athletes as it provides the energy needed for physical activities.
What are the two main processes for energy release from nutrients?
-The two main processes for energy release from nutrients are fermentation and cellular respiration.
What is the role of glucose in cellular respiration?
-Glucose is broken down into simpler compounds, such as pyruvate, during cellular respiration. Pyruvate is then transported into the mitochondria where most of the energy is released and stored in the form of ATP.
What is the citric acid cycle and why is it important?
-The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria and is crucial for converting the energy from pyruvate into ATP.
What happens to the carbon dioxide produced during the citric acid cycle?
-The carbon dioxide produced during the citric acid cycle is released as a waste product and appears on the right side of the chemical equation for cellular respiration.
What are the electron acceptors in the citric acid cycle and what is their role?
-The electron acceptors in the citric acid cycle are NAD+ and FAD. They accept electrons along with protons, forming NADH and FADH2, which are important energy carriers in the cycle.
How is the energy from the citric acid cycle transferred to the electron transport chain?
-The high-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred to the enzymes of the electron transport chain, where they are used to generate ATP through a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the final product of the electron transport chain and how is it related to ATP production?
-The final product of the electron transport chain is ATP, which is generated through the transfer of electrons and the pumping of protons across the mitochondrial membrane, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
Why is water a product of cellular respiration?
-Water is a product of cellular respiration because it is formed when oxygen combines with protons during the final steps of the electron transport chain.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

How The Body Uses Food - You Are What You Eat - How Are Carbohydrates, Protein, Fat Used In The Body

Carbohydrates

Sumber Energi Bagi Tubuh Manusia #biologi #energi #makanan
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrate, Protein, and Fat Metabolism | Metabolism

Carbohydrates | A type of biological molecule | Functions and Classification
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
