ALGORITMA AES (Advance Encryption Standard)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker explains the AES encryption and decryption process, starting with the concept of plain-text and how it is transformed using mathematical operations. Using their own name as an example, the speaker demonstrates how to set up the plain-text and generate key values based on specific formulas. The video also highlights the step-by-step procedure of using an encryption key, applying it to columns, and calculating encrypted and decrypted values through a series of logical functions. The speaker concludes with a reminder of the potential for error and expresses gratitude for the audience's understanding.
Takeaways
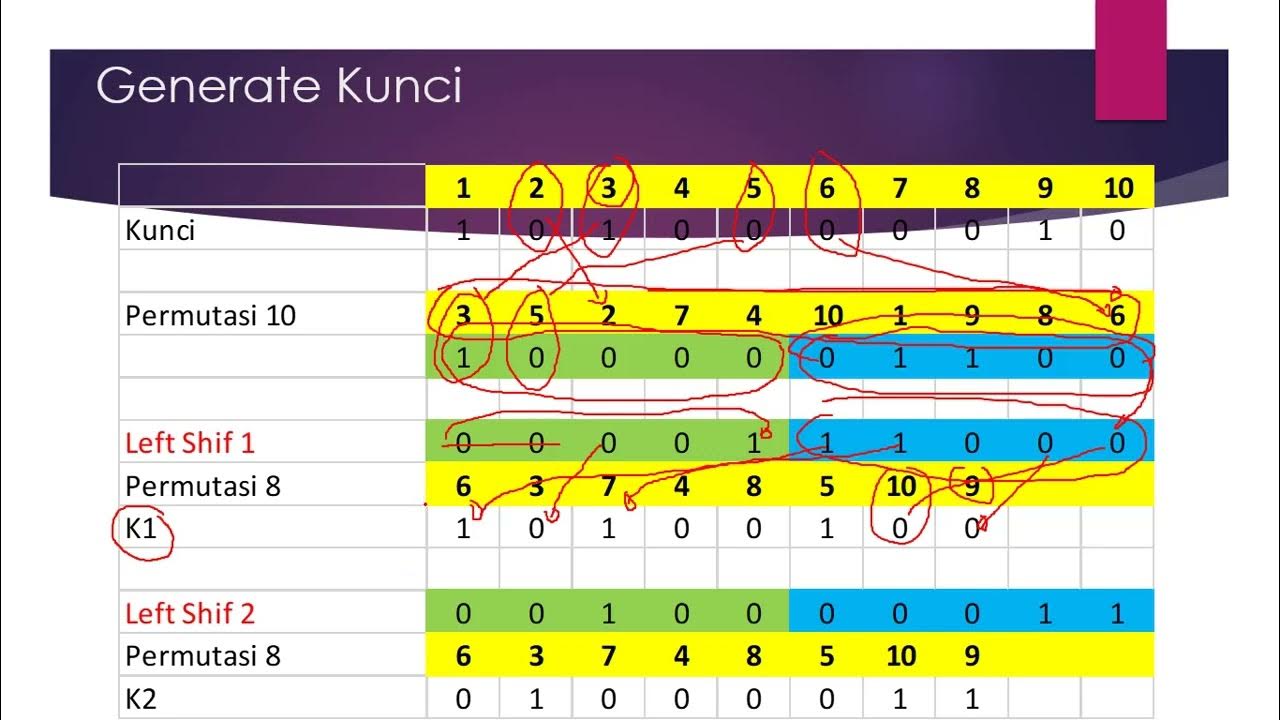
- 😀 Understanding plain-text: The script begins by explaining what plain-text is and how it is represented using 4 columns with values.
- 😀 AES Encryption Process: The encryption process involves applying mathematical formulas to the given plain-text and key values.
- 😀 Key Requirement: The key must be 25 characters long and is derived from something personal (like the speaker’s university name).
- 😀 Formula Application: The process uses the Chord b85 method for generating values for encryption, which involves applying specific formulas in Excel.
- 😀 Excel Functions: The speaker demonstrates how to use Excel formulas to automatically calculate the necessary values for AES encryption and decryption.
- 😀 Dropping Values: The calculated values are 'dropped' to the next row to proceed with further operations, ensuring the process is automated.
- 😀 Column Interactions: Values interact across multiple columns in the Excel sheet, with each column playing a crucial role in encryption or decryption.
- 😀 Key Generation Steps: The key is inputted in the form of a campus name (Budi Darma), and Excel is used to map and calculate corresponding encryption values.
- 😀 AES Transformation: The values are transformed according to AES encryption standards to produce the final ciphertext.
- 😀 Decryption and Roadworks: The process of decryption is explained, including the 'roadworks' step, where the original values are reversed to retrieve plain-text.
- 😀 Acknowledgment of Possible Errors: The speaker concludes by acknowledging potential mistakes in their explanation, suggesting a learning approach.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video script?
-The video script focuses on explaining the process of encryption and decryption using the AES algorithm.
What is 'plain-text' in the context of the AES encryption process?
-In the AES encryption process, plain-text refers to the original, unencrypted data that is processed during encryption.
How are the values for encryption derived from the 'plain-text'?
-The values for encryption are derived by applying a formula (referred to as 'chord') to the plain-text. In the example, the plain-text consists of four columns, with each column containing specific character values.
What is the purpose of the 'key' in the AES encryption process?
-The 'key' serves as a secret value used in the encryption and decryption processes. It is necessary to ensure that only authorized parties can decrypt the data.
What does the term 'key' refer to in the provided transcript?
-In the transcript, the 'key' refers to a value used in the AES algorithm, represented as a 25-character string based on a specific example, such as the name of the presenter’s university.
What is meant by 'channel' in the AES encryption explanation?
-The 'channel' refers to a step in the AES process where the values from the key are combined with the corresponding plain-text values using a specified formula to generate encrypted data.
How is the AES encryption formula applied in the example?
-The AES encryption formula is applied by combining values from the plain-text with values derived from the key. This involves mathematical operations such as 'X' (multiplication) and using the 'chord' formula to generate new values for encryption.
What does the 'drop' operation signify in the encryption process?
-The 'drop' operation refers to the action of moving values from one position to another in the calculation process, often used to align the correct data for further operations.
What are the values of 'subtext' in the encryption process?
-The 'subtext' values are intermediate data derived from the calculated results during the AES encryption process, used in further operations to finalize the encrypted result.
How is the final 'export' value calculated in AES encryption?
-The final 'export' value is calculated using a specific formula that involves multiplying values from the plain-text and key, with operations like 'X' (multiplication) and the use of the formula to derive the encrypted data.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Video 4.23 EDT

How prime numbers protect your privacy #SoME2
Algoritma S DES

CRYPTOGRAPHY | Encrypting & Decrypting | Caesar Cipher | Modulo Operator | TAGALOG-ENGLISH

What Is Hashing? | What Is Hashing With Example | Hashing Explained Simply | Simplilearn

Cryptography: Caesar Cipher and Modulo Operator| Encryption and Decryption
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
