Magnetostatika bagian 1
Summary
TLDRThis lecture delves into the fascinating world of magnetism and the Lorentz force, explaining fundamental concepts such as magnetic fields, their effects, and their applications in everyday life. The speaker covers historical uses of magnetism, from navigation with compasses to modern technologies like wireless charging and maglev trains. Key scientific principles are explored, including the Lorentz force and how magnetic fields influence moving charged particles. Practical examples, such as the deflection of electrons in a magnetic field, are used to illustrate these concepts, highlighting their importance in various fields of study and technology.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script introduces the concept of magnetism and magnetostatics, emphasizing its importance in daily life, from ancient navigation using magnets to modern wireless charging and high-speed transportation.
- 😀 Magnetism is explained as a phenomenon where magnetic fields can attract certain materials like iron and other metals. The magnetic force is generated by magnetic poles, with similar poles repelling and opposite poles attracting.
- 😀 The word 'magnet' originates from the term 'Magnesia stone,' a naturally occurring stone that has magnetic properties. The behavior of magnetic fields can be visualized using magnetic field lines.
- 😀 The script highlights how magnets can influence nearby objects and how magnetic properties can be altered or weakened. One way to create a magnet is by aligning the magnetic dipoles within a material.
- 😀 Hans Christian Oersted’s 1826 experiment is mentioned, where he demonstrated that an electric current generates a magnetic field, which can affect the orientation of a compass.
- 😀 The force between a current-carrying wire and a magnetic field is described by the Lorentz force law. This force depends on the strength of the current, the length of the wire, and the magnetic field in the vicinity.
- 😀 The relationship between electric current and the generated magnetic field is mathematically expressed using the formula involving a cross product, reflecting the directional nature of the force.
- 😀 The script explains the use of the right-hand rule for determining the direction of magnetic force. The direction of the force is perpendicular to both the direction of current and the magnetic field.
- 😀 Several practical applications of the Lorentz force law are discussed, including the operation of cathode ray tubes in older TVs, where magnetic fields are used to bend the path of electrons.
- 😀 The script outlines different cases involving charged particles in magnetic fields, including scenarios involving positive and negative charges and their respective trajectories in the presence of magnetic fields.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The main focus of the video is on magnetism, specifically on magnetostatics and the Lorentz force law, explaining phenomena related to magnetic fields, their effects, and applications.
How is magnetism used in daily life, as mentioned in the script?
-Magnetism is used in daily life for navigation with a compass, in wireless charging, and in transportation systems like high-speed trains.
What is the origin of the word 'magnet'?
-The word 'magnet' originates from the Greek term 'magnes,' referring to magnesia, a type of stone that exhibits magnetic properties.
What are the key characteristics of magnetic poles?
-Magnetic poles have two types: the north and south poles. Like poles repel each other, while opposite poles attract. The magnetic field also forms lines of force that represent the direction of the magnetic force.
What experiment did Hans Christian Ørsted conduct, and what did it prove?
-Hans Christian Ørsted demonstrated that an electric current could generate a magnetic field. His experiment showed that when current flows through a wire, it deflects a compass needle, indicating the presence of a magnetic field around the wire.
What is the Lorentz force, and how is it defined?
-The Lorentz force is the force experienced by a charged particle moving through a magnetic field. It is defined as the combination of electric force and magnetic force acting on the particle, and its direction can be determined using the right-hand rule for positive charges and the left-hand rule for negative charges.
How does the direction of the magnetic field affect the movement of charged particles?
-The direction of the magnetic field affects the movement of charged particles by exerting a force that is perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and the magnetic field. This causes the particle to move in a circular or spiral path.
What is the right-hand rule used for in the context of magnetism?
-The right-hand rule is used to determine the direction of the magnetic force on a positive moving charge. The thumb points in the direction of the velocity (or current), the fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field, and the palm faces the direction of the magnetic force.
What are some applications of the Lorentz force law, as mentioned in the video?
-Applications of the Lorentz force law include devices such as cathode ray tubes (CRT) used in older TVs and technologies like motors and dynamos, where magnetic fields interact with moving charges to produce motion or energy conversion.
How does the interaction between electric and magnetic fields influence the movement of particles in a system?
-The interaction between electric and magnetic fields can either accelerate or deflect charged particles. The forces due to the electric and magnetic fields may counteract each other, influence the trajectory of the particles, or work together depending on the magnitude and direction of the fields.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Materi Kemagnetan Kelas 9 (Part-3) Induksi Magnet dan Gaya Lorentz
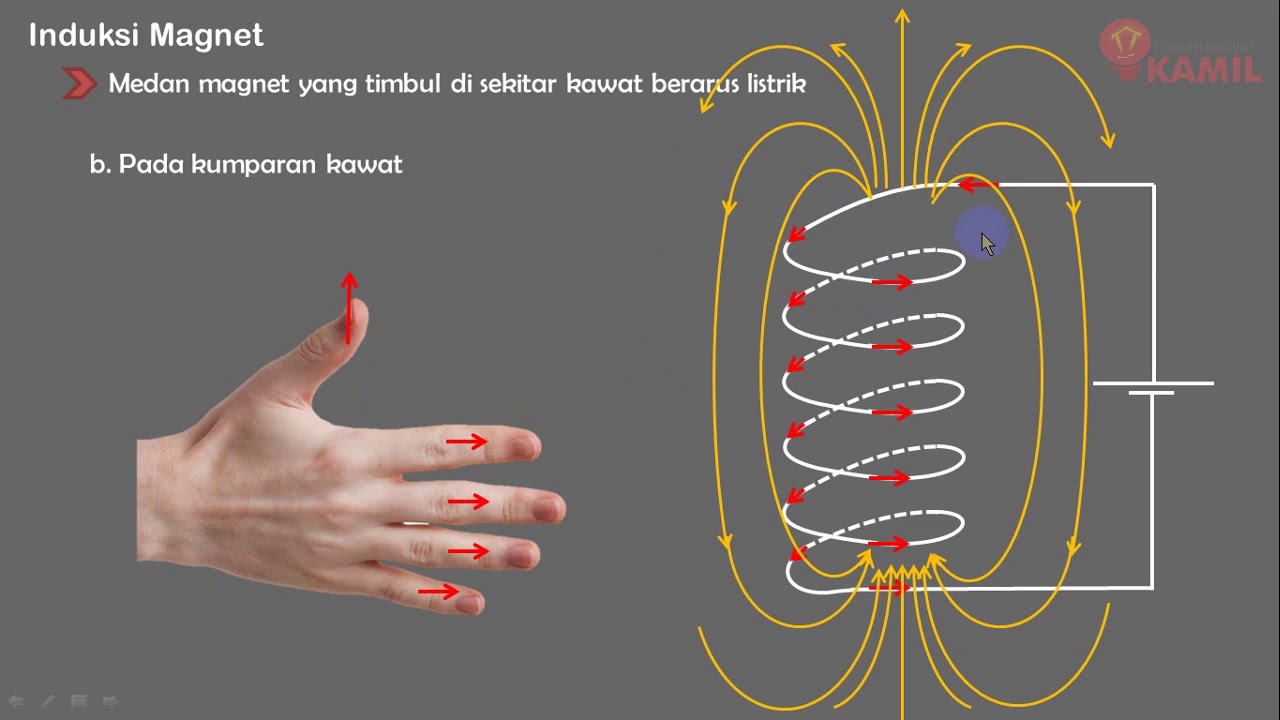
IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (Part 3 : Induksi Magnet dan Gaya Lorentz)

GAYA LORENTZ KELAS 9 (MEMBUKTIKAN ADANYA GAYA LORENTZ)

BAB 4: LISTRIK, MAGNET DAN SUMBER ENERGI ALTERNATIF | Part 3: MAGNET | IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka

KEMAGNETAN KELAS 9 part 2 - MEDAN MAGNET DAN MAGNET BUMI

ELECTROMAGNETISM-TAGLISH
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
