Uji Normalitas Menggunakan SPSS
Summary
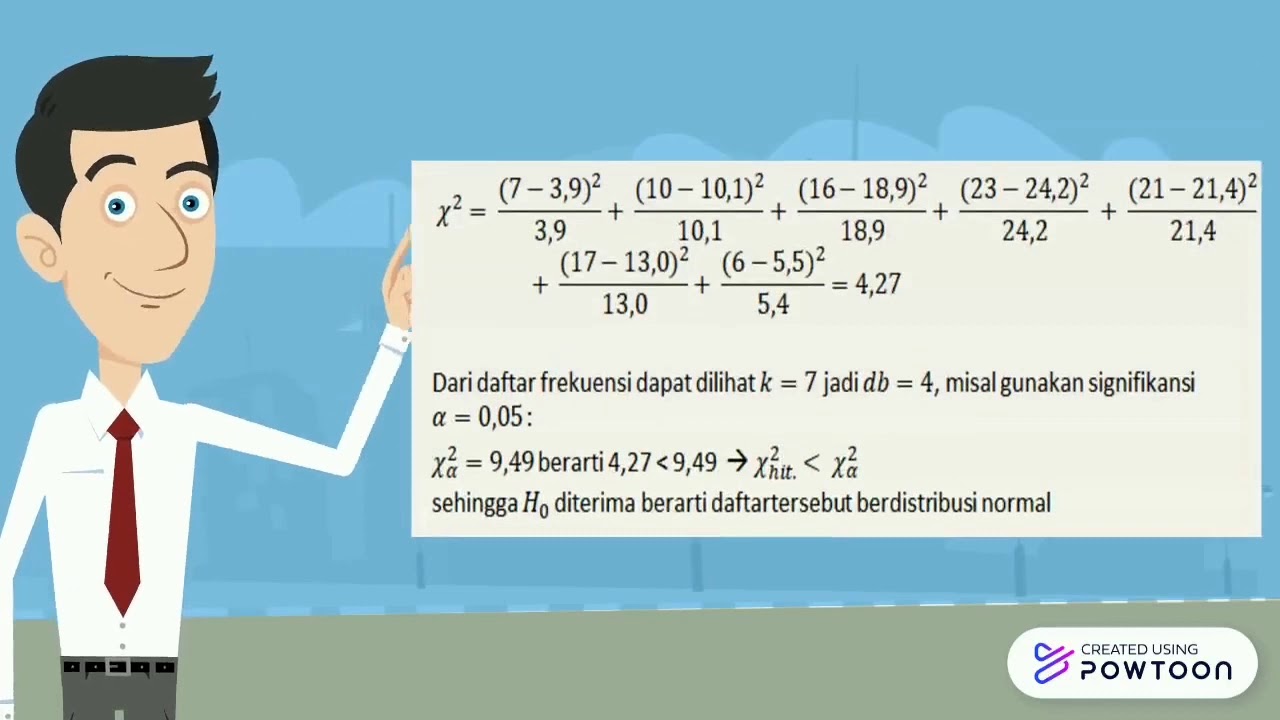
TLDRIn this video, Neli Elizah, an educator in Islamic Education from the University of UN, explains the concept of normality testing in statistical analysis. She discusses various methods of conducting normality tests, such as the Lilliefors test, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, C-Square test, and Kiklot test. The focus is on the use of SPSS software to perform normality tests, including interpreting the significance value (sig) to determine whether a sample comes from a normally distributed population. The tutorial demonstrates how to perform and interpret the normality test using SPSS, concluding with a practical example for students and researchers.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script discusses normality testing in the context of educational statistics, focusing on the use of SPSS software for this analysis.
- 😀 Normality testing helps determine whether a sample is from a normally distributed population or not.
- 😀 Key normality tests mentioned include the Liliefors test, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, C-square test, and the Shapiro-Wilk test.
- 😀 The null hypothesis (H0) in normality testing is that the sample comes from a normally distributed population.
- 😀 The alternative hypothesis (H1) is that the sample does not come from a normally distributed population.
- 😀 SPSS simplifies the process by allowing researchers to compare the significance value (Sig) directly to the alpha level (0.05).
- 😀 If the significance value (Sig) is greater than 0.05, H0 is accepted, indicating the sample comes from a normally distributed population.
- 😀 If the significance value (Sig) is less than 0.05, H0 is rejected, meaning the sample comes from a non-normally distributed population.
- 😀 SPSS enables the user to adjust data formats easily (such as changing decimal points) before performing the normality test.
- 😀 The video demonstrates a normality test using SPSS, with a sample size of 35, and shows that a Sig value of 0.225 supports the null hypothesis, indicating normality.
- 😀 The script emphasizes the practical benefits of using SPSS for statistical analysis, particularly in simplifying complex processes like hypothesis testing.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the script?
-The script discusses the concept of 'normality testing' in statistical analysis, specifically using SPSS software to perform normality tests on educational data.
What are the two main types of prerequisite tests mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of prerequisite tests mentioned are 'normality test' and 'homogeneity test'. However, the focus of the script is on the normality test.
What is the purpose of a normality test?
-The purpose of a normality test is to determine whether a sample comes from a population that follows a normal distribution.
Which statistical tests use normality tests as a prerequisite?
-Tests like the T-test, correlation test (r), and ANOVA (F-test) require a normality test to be performed as a prerequisite.
What are the four methods mentioned for conducting normality tests?
-The four methods mentioned are the Lilliefors test, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, Chi-square test, and the Q-Q plot method.
What is the null hypothesis (H0) in a normality test?
-The null hypothesis (H0) in a normality test states that the sample comes from a population that follows a normal distribution.
What happens if the significance value (Sig) is greater than 0.05?
-If the significance value (Sig) is greater than 0.05, the null hypothesis (H0) is accepted, meaning the sample is considered to come from a population that is normally distributed.
What happens if the significance value (Sig) is less than 0.05?
-If the significance value (Sig) is less than 0.05, the null hypothesis (H0) is rejected, and the alternative hypothesis (H1) is accepted, meaning the sample does not come from a normally distributed population.
How do you calculate normality using SPSS?
-To calculate normality using SPSS, you input the data into the software, check the descriptive statistics, and look for the significance value in the output. You also use the 'Plots' option to visualize the data distribution.
What is the specific significance value from the example in the script, and what does it indicate?
-In the example, the significance value is 0.225, which is greater than 0.05. This indicates that the null hypothesis is accepted, meaning the sample comes from a population that is normally distributed.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)