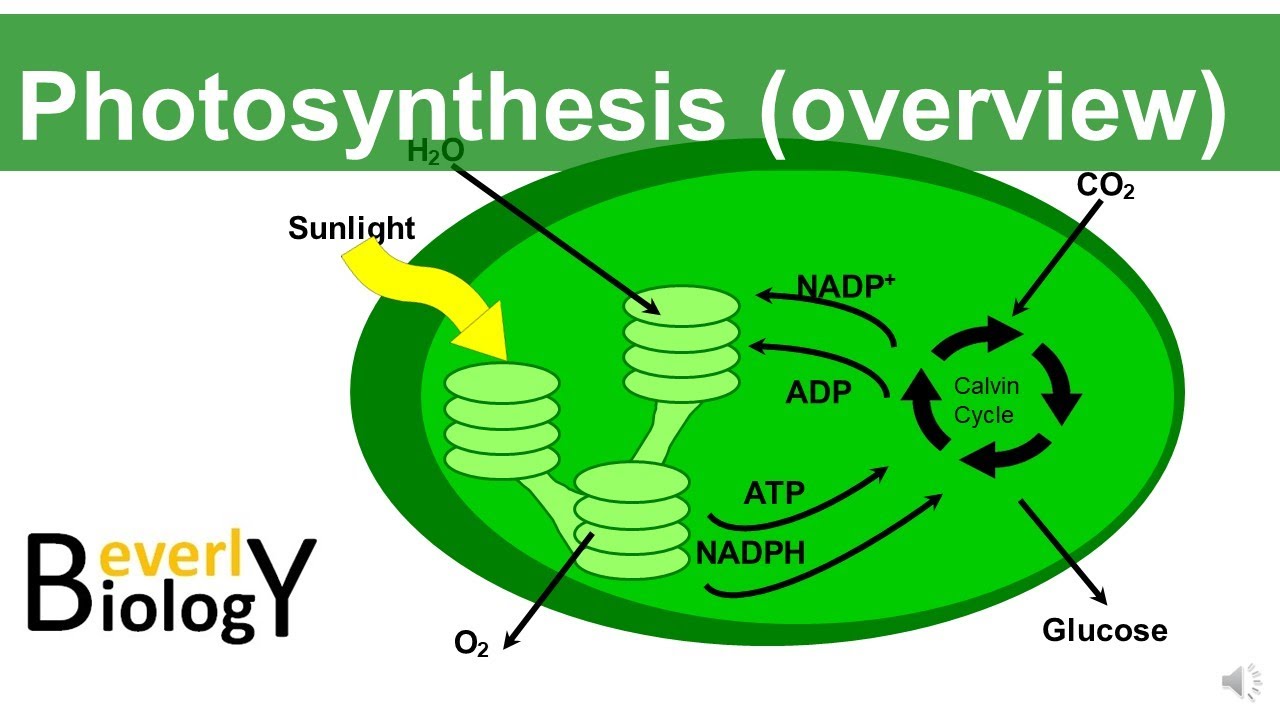
Light Reactions | Cell Biology | Photosynthesis
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun, with a focus on visible light and its role in photosynthesis. It explains how light is absorbed, reflected, or transmitted by leaves, contributing to their color. The transcript highlights the importance of pigments like chlorophyll, carotenoids, and ficocyanin, which capture light and drive biological processes. The changing colors of leaves in fall are explained by the loss of chlorophyll, revealing other pigments. Finally, the video introduces photosystems 1 and 2, the cellular structures responsible for converting light into chemical energy.
Takeaways
- 😀 The sun emits a wide spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet waves, visible light, infrared, micro, and radio waves.
- 😀 Visible light, which is what we see from the sun, consists of many different colors corresponding to different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation.
- 😀 The light reflected or transmitted by a leaf produces its color, while absorbed light heats up the leaf or drives processes like photosynthesis.
- 😀 Chlorophyll is the key molecule responsible for the green color of plants, as it absorbs violet, blue, and red light but reflects green.
- 😀 Carotenoids and ficoin are accessory pigments that capture light energy and transfer it to chlorophyll molecules.
- 😀 Carotenoids absorb blue and green light, reflecting yellow and red, while ficoin absorbs green and yellow light and reflects blue or purple.
- 😀 In the fall, the colors of carotenoids and ficoin become more visible as chlorophyll disappears, revealing yellow, orange, red, and purple hues.
- 😀 Photosynthesis can be driven by light from all wavelengths, but the peak wavelengths are in the blue and red regions of the visible light spectrum.
- 😀 Pigments, like chlorophyll, carotenoids, and ficoin, each absorb and reflect different wavelengths of light, playing key roles in photosynthesis.
- 😀 Photosystems 1 and 2 in plant cells convert light captured by pigments into chemical energy, starting the process of photosynthesis.
Q & A
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
-The electromagnetic spectrum is a wide range of electromagnetic radiation, varying in energy and wavelength. It includes high-energy gamma rays, X-rays, and ultraviolet waves at one end, and longer wavelength, lower energy infrared, micro, and radio waves at the other end.
What types of light make up visible light from the sun?
-Visible light from the sun is made up of various colors corresponding to different wavelengths. These colors range from ultraviolet and blue at one end to green, yellow, and red, extending up to the edge of the infrared range.
How does light interact with a leaf?
-Light striking a leaf can be reflected, transmitted through the leaf, or absorbed. The light that is reflected or transmitted affects the color of the leaf, while the absorbed light either heats up the leaf or drives biological processes like photosynthesis.
What are pigments and their role in plants?
-Pigments are natural substances in organisms that color their tissues. In plants, chlorophyll is the main pigment responsible for capturing light during photosynthesis, giving most plants their green color.
What other pigments are found in plants besides chlorophyll?
-In addition to chlorophyll, plants contain accessory pigments such as carotenoids and ficoin. These pigments capture light energy and transfer it to chlorophyll molecules to aid in photosynthesis.
What are accessory pigments, and how do they work?
-Accessory pigments, such as carotenoids and ficoin, absorb different wavelengths of light and transfer the energy to chlorophyll for photosynthesis. They help capture a wider range of light for energy conversion.
What wavelengths of light are absorbed by chlorophyll?
-Chlorophyll absorbs light primarily in the violet, blue, and red regions of the light spectrum but reflects green light, which is why leaves typically appear green.
How do carotenoids and ficoin differ from chlorophyll in terms of light absorption?
-Carotenoids absorb blue and green light and reflect yellow and red light, while ficoin absorbs green and yellow light and reflects blue or purple light.
Why do leaves change color in the fall?
-During fall, chlorophyll breaks down, revealing the colors of carotenoids and ficoin, which produce the dramatic yellow, orange, red, and purple hues commonly seen in autumn foliage.
How does light absorption by pigments affect photosynthesis?
-All wavelengths of light are absorbed to some degree by pigments like chlorophyll, carotenoids, and ficoin. The absorption of light, especially in the blue and red regions, drives the process of photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)