PlantEd Digital Learning Library - Gram Stain Procedure
Summary
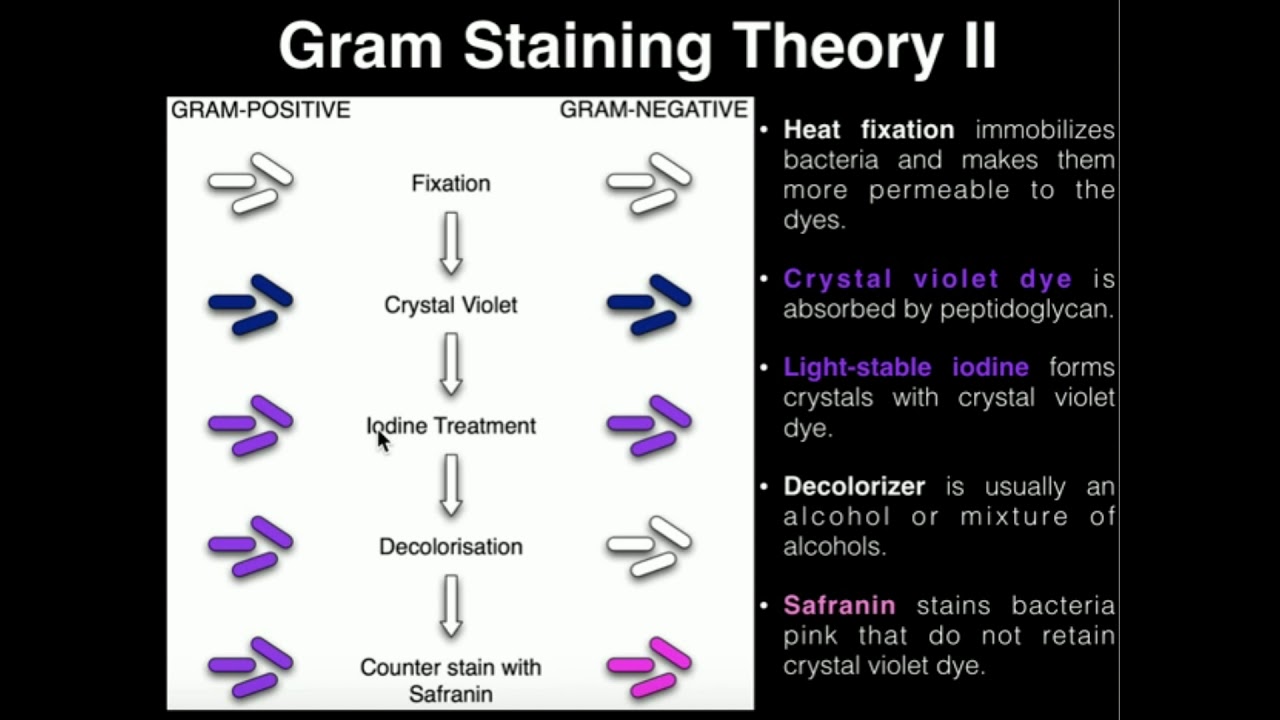
TLDRThe Gram Stain is a microbiological technique used to differentiate between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria based on their cell wall structure. The process involves preparing a bacterial smear on a slide, staining it with Crystal Violet, and applying Gram's Iodine, followed by decolorization with ethanol. Safranin is used as a counterstain. The key difference between the two types of bacteria is the thickness of their peptidoglycan layer. Gram-positive bacteria retain the Crystal Violet stain, appearing purple, while Gram-negative bacteria lose it and appear pink due to the Safranin counterstain.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Gram Stain is a microbiology technique used to differentiate between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria based on staining patterns.
- 😀 Proper sterilization of the workspace and tools, including flaming the loop and the glass tube openings, is essential when working with microbes.
- 😀 A small drop of water is placed on a slide, and the loop is used to transfer bacteria from a culture tube to the slide.
- 😀 A thin bacterial smear is made on the slide to ensure even drying and avoid clumping of bacteria.
- 😀 The slide is air-dried until no water droplets are visible before heat fixing the bacteria to the slide by passing it through a flame.
- 😀 The staining process begins by flooding the slide with Crystal Violet, which stains all bacteria.
- 😀 After staining with Crystal Violet, the slide is rinsed until the water runs clear, and then flooded with Gram's Iodine to form a complex with the Crystal Violet.
- 😀 Ethanol is used to decolorize the slide, which removes Crystal Violet from Gram-negative bacteria while leaving Gram-positive bacteria stained.
- 😀 The decolorization step should be performed quickly to avoid over-decolorizing Gram-positive bacteria.
- 😀 The slide is counterstained with Safranin to stain Gram-negative bacteria pink, allowing differentiation between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
- 😀 After staining and rinsing, the slide is dried using Bibulous Paper, and the bacteria can be viewed under oil immersion for detailed examination.
Q & A
What is the Gram Stain technique used for?
-The Gram Stain technique is used to differentiate between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria based on how their cells stain.
Why is it important to sanitize the bench before beginning the Gram Stain procedure?
-Sanitizing the bench is essential to maintain sterile conditions when working with microbes, preventing contamination of the samples.
What is the purpose of labeling the slide with the sample name or organism?
-Labeling the slide ensures that the correct sample or organism is identified and linked to the slide, preventing confusion during the procedure.
Why is the loop flamed before and after transferring the sample?
-Flaming the loop before and after transferring the sample sterilizes the loop, preventing contamination of the sample or culture.
What is the purpose of creating a thin bacterial smear on the slide?
-Creating a thin bacterial smear helps the sample dry faster and reduces clumping of bacteria, making it easier to observe under a microscope.
Why is heat fixing the slide important in the Gram Staining procedure?
-Heat fixing ensures that bacteria adhere to the slide, preventing them from washing off during the staining process.
What happens during the decolorization step, and why is it critical to perform it quickly?
-During decolorization, ethanol dissolves the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, removing the Crystal Violet stain. It is critical to perform quickly to avoid decolorizing Gram-positive bacteria, which would affect the results.
What role does Safranin play in the Gram Staining process?
-Safranin is a counterstain used to stain decolorized Gram-negative bacteria pink, making them visible under the microscope.
How can you distinguish between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria under a microscope after staining?
-Gram-positive bacteria appear purple due to their thick peptidoglycan layer, while Gram-negative bacteria appear pink due to the Safranin counterstain.
What are the main structural differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria?
-Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan outside their cell membrane, whereas Gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan surrounded by an outer membrane.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)