Biopotential Amplifiers
Summary
TLDRThis lecture focuses on biopotential amplifiers, essential components in medical instrumentation used to amplify weak bioelectric signals from the body. Key topics include the importance of signal fidelity, high input impedance, and safety features to protect both patients and equipment. The script explains the workings of these amplifiers, including the use of filters, pre-amplifiers, and isolation stages to eliminate noise and interference. It also covers their wide applications in ECG, EMG, and other diagnostic tools. While biopotential amplifiers are scalable and reliable, they can suffer from noise and signal distortion. The lecture concludes with an overview of their advantages and disadvantages.
Takeaways
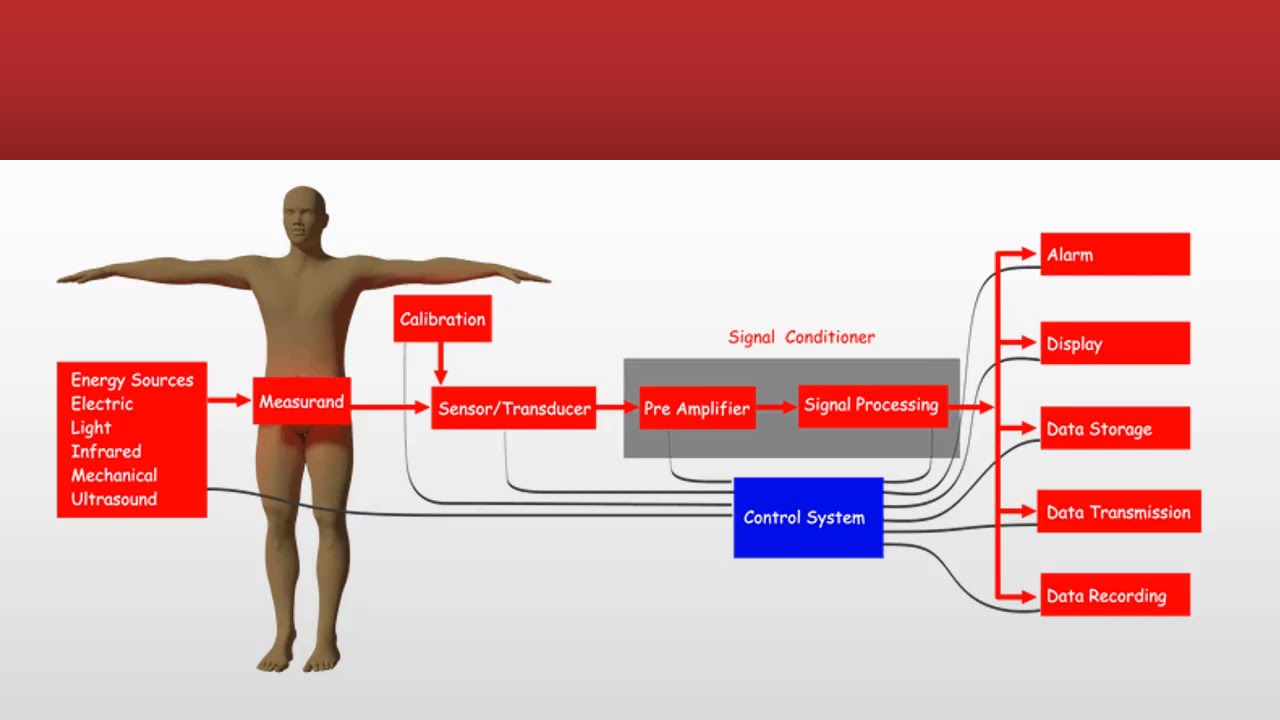
- 😀 Biopotential amplifiers are essential in medical instrumentation to amplify weak biological signals from the body with high source impedance.
- 😀 The amplifier should not interfere with the physiological processes being monitored and must maintain signal fidelity.
- 😀 High input impedance (greater than 10 MΩ) is required to avoid loading effects and ensure accurate measurements.
- 😀 Safety is crucial, and the amplifier must protect both the patient and the equipment from electrical hazards.
- 😀 The amplifier should have low output impedance to minimize distortion when driving external loads.
- 😀 Biopotential amplifiers must be free from noise and distortion to ensure accurate signal transmission.
- 😀 Isolation protection is important to safeguard the patient from electrical shocks and to maintain signal quality.
- 😀 Electrode offset potentials and tissue impedance variations can generate interference, which must be filtered during the amplification process.
- 😀 The signal from the electrodes is passed through a pre-amplifier stage to reduce noise and interference.
- 😀 Filters, including high-pass and low-pass, are used to eliminate unwanted noise and interference from the biosignals.
- 😀 Biopotential amplifiers are widely used in medical applications like ECG, EMG, CT scans, and patient monitoring systems.
Q & A
What is the primary function of biopotential amplifiers?
-The primary function of biopotential amplifiers is to amplify the low-level biopotentials generated in the body, while maintaining signal fidelity and minimizing interference.
What are the basic requirements for biopotential amplifiers?
-Biopotential amplifiers must not influence the physiological processes being monitored, provide excellent separation of signals and interference, and prevent distortion or noise in the signal.
Why is high input impedance important in biopotential amplifiers?
-High input impedance (greater than 10 mega ohms) is important to avoid loading the source and to preserve the accuracy of the biopotential signal without influencing the source.
How does safety play a role in the design of biopotential amplifiers?
-Safety in biopotential amplifiers is crucial to protect the patient from electrical shocks. The amplifier must be carefully designed to prevent any electrical hazard to the organism being studied.
What is the significance of the amplifier’s low output impedance?
-Low output impedance is significant because it allows the amplifier to drive external loads with minimal distortion, ensuring the integrity of the signal.
What types of interference signals can affect biopotential measurements?
-Interference signals such as electrode offset potential, tissue impedance, and external noise can affect biopotential measurements. These are typically minimized using filters and pre-amplifiers.
How do high-pass and low-pass filters help in biopotential amplification?
-High-pass and low-pass filters help eliminate interference signals like electrode half-cell potentials and pre-amplifier offset potentials, while also reducing noise amplitude in the measured biosignal.
What is galvanic decoupling in the isolation amplifier stage, and why is it important?
-Galvanic decoupling prevents the transmission of electrical currents between the patient and the measuring equipment, improving the signal-to-noise ratio and ensuring the safety of the patient.
What are the key applications of biopotential amplifiers in medical instrumentation?
-Biopotential amplifiers are used in medical devices such as ECG machines, EMG systems, patient monitors, electromyogram integrators, cardio tachometers, and vector cardiographs to monitor various health conditions.
What are the advantages of biopotential amplifiers?
-Biopotential amplifiers are scalable, easy to use, stable, and ideal for long-term use. They can amplify small input signals significantly and maintain consistent output even with varying influencing factors.
What are the disadvantages of biopotential amplifiers?
-Disadvantages include reliance on special cables to minimize noise, potential for minor distortion or noise in the output, and concerns with superimposing noise over the original signal when transmitted over long distances.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
ELEKTROMEDIS kebidanan
Instrumentation Amplifier Explained (with Derivation)

Analog Circuits | Introduction of Analog Circuits | AKTU Digital Education

How does an Amplifier Work? (Class-A)

Cara Membuat Penguat Input Amplifier Non Inverting + Rumus Penjelasannya

Origin of Bioelectric Signals | Basic Concepts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
