Komponen Ekosistem dan Jenis Jenis Ekosistem, Materi Pembelajaran Ekosistem SMA Kelas 10.
Summary
TLDRThis biology lesson explains the concept of ecosystems, beginning with their position in the hierarchy of life. The video covers the basic components of ecosystems, such as biotic (living organisms) and abiotic (non-living factors) elements, and the interactions between species like competition, predation, and symbiosis. It also distinguishes between natural ecosystems (like forests and oceans) and artificial ones (like rice fields and gardens). The video aims to help viewers understand the delicate balance in ecosystems and the crucial role of both living organisms and their environment in maintaining life on Earth.
Takeaways
- 😀 Ecosystems are defined by interactions between living organisms and their environment, including both biotic and abiotic components.
- 😀 Organisms are the smallest units in the ecological hierarchy, referring to individual living beings, like a single deer.
- 😀 Populations consist of individuals of the same species living in the same area at the same time, like a herd of deer.
- 😀 Communities refer to different populations of species living together, such as deer, insects, and plants coexisting in a habitat.
- 😀 An ecosystem involves both living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) elements that interact with each other, like deer with soil or water.
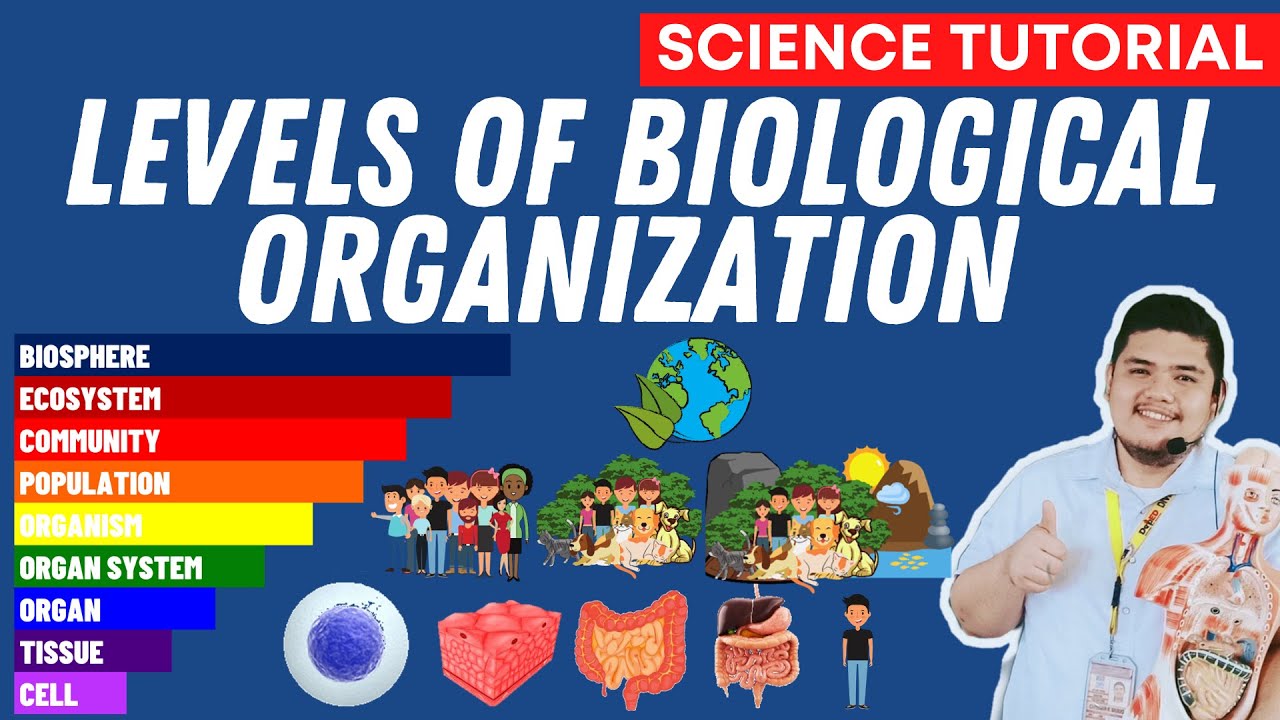
- 😀 Biomes are large-scale ecological areas that contain multiple ecosystems, and the biosphere encompasses all ecosystems on Earth.
- 😀 Biotic components include all living organisms, such as animals, plants, and microorganisms, while abiotic components are non-living elements like water, soil, and air.
- 😀 Key types of biotic interactions in ecosystems include neutral (no impact), competition (for resources), predation (one eats another), and symbiosis (mutual or beneficial relationships).
- 😀 Symbiosis is categorized into three types: mutualism (both benefit), commensalism (one benefits, the other is unaffected), and parasitism (one benefits at the other's expense).
- 😀 Ecosystems can be natural (e.g., forests, oceans) or artificial (e.g., rice fields, gardens), with natural ecosystems typically showing higher biodiversity.
Q & A
What is an ecosystem?
-An ecosystem is the interaction between living organisms (biotic components) and non-living components (abiotic components) in an environment. It includes both the interactions among living organisms and between them and their environment.
What are the basic levels of organization in the hierarchy of life?
-The basic levels of organization in the hierarchy of life include organisms (individuals), populations (groups of the same species), communities (different species living together), ecosystems (biotic and abiotic components), biomes, and the biosphere (the entire Earth).
What is the difference between a population and a community?
-A population refers to a group of individuals of the same species living in a particular area, whereas a community consists of multiple populations of different species living together in the same area.
How do biotic and abiotic components interact in an ecosystem?
-Biotic components, like animals, plants, and microorganisms, interact with each other and with abiotic components, such as water, air, and soil. These interactions can be beneficial, neutral, or harmful, and they help maintain balance in the ecosystem.
What are some examples of abiotic components in an ecosystem?
-Abiotic components include non-living factors such as water, air, soil, rocks, temperature, and sunlight, all of which influence the living organisms in the ecosystem.
What are the different types of species interactions in an ecosystem?
-The main types of species interactions are neutralism (no effect on each other), competition (competing for resources), predation (one organism preys on another), and symbiosis (close relationships between species), which can be mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic.
What is mutualism, and can you provide an example?
-Mutualism is a type of symbiotic relationship where both species benefit. An example is the relationship between clownfish and sea anemones, where clownfish receive protection from predators, and the anemones get food from the clownfish.
What is the difference between commensalism and parasitism?
-In commensalism, one organism benefits, and the other is neither helped nor harmed. For example, orchids growing on trees benefit from the tree's structure, while the tree is unaffected. In parasitism, one organism benefits at the expense of the other, like lice living on the skin of mammals.
What are the two main types of ecosystems based on their origin?
-Ecosystems can be classified into two main types: natural ecosystems, which form without human intervention and have high biodiversity, such as forests and oceans, and artificial ecosystems, which are created or modified by humans, such as agricultural fields or urban environments.
What is the primary difference between natural and artificial ecosystems?
-Natural ecosystems are formed by nature and typically have a high level of biodiversity, while artificial ecosystems are human-made and often have lower biodiversity due to human control over species and environmental conditions, such as in farms or gardens.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Biological Hierarchy with Dr. K. Sathasivan

Tingkat Organisasi Kehidupan | Biologi Kelas 10 - KHATULISTIWA MENGAJAR

SCIENCE 7: LEVELS OF BIOLOGICAL ORGANIZATIONS, THE SPECTRUM OF BIOLOGICAL ORGANIZATION
LEVELS OF BIOLOGICAL ORGANIZATION SCIENCE 7 QUARTER 2 MODULE 2 WEEK 3

Kingdom Fungi - Kelas X SMA

Introdução à ecologia - Conceitos básicos - Aula 01 - Módulo VIII: Ecologia | Prof. Gui
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
