Angiotensin 2 Receptor Blockers (ARBS) Pharmacology Nursing NCLEX Quick Review
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses Angiotensin 2 Receptor Blockers (ARBs), a class of medications that block the effects of Angiotensin 2, leading to vasodilation and lower blood pressure. ARBs are commonly used to treat hypertension, diabetic nephropathy, heart failure, and peripheral arterial disease. They also protect kidney function, reduce aldosterone secretion, and help regulate blood volume. While effective, ARBs may cause side effects such as dizziness, hypotension, elevated potassium levels, and GI upset. Nurses need to monitor kidney function, blood pressure, and potassium levels to ensure patient safety, as rare cases of angioedema may also occur.
Takeaways
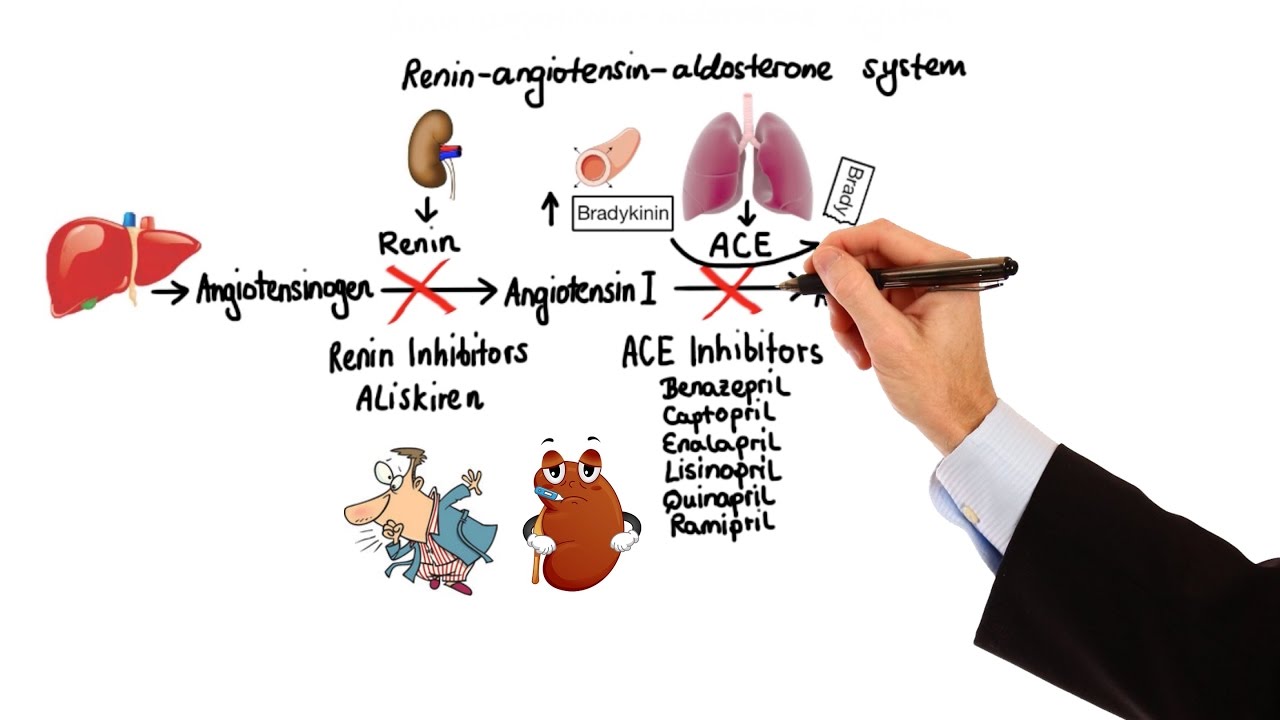
- 😀 Angiotensin 2 receptor blockers (ARBs) block the effects of Angiotensin 2, leading to vasodilation instead of vasoconstriction.
- 😀 ARBs are useful in treating hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetic nephropathy (chronic kidney disease from diabetes), heart failure, and peripheral arterial disease.
- 😀 Common ARB medications include Omartin, Valsartan, and Losartan, with the suffix '-stin' indicating they're ARBs.
- 😀 ARBs help protect kidney function by reducing blood pressure to the kidneys, decreasing inflammation, and preventing damage and scarring.
- 😀 ARBs work by blocking Angiotensin 2 from binding to type 1 receptors, leading to vessel dilation and decreased aldosterone secretion.
- 😀 Decreased aldosterone secretion helps reduce blood volume by excreting extra water and sodium while preserving potassium.
- 😀 Side effects of ARBs include dizziness, hypotension (low blood pressure), increased potassium levels, and GI upset.
- 😀 Nurses should monitor potassium levels closely since ARBs can cause hyperkalemia (elevated potassium).
- 😀 It’s important to monitor renal function (BUN and creatinine) and blood pressure, especially in patients with diabetes or kidney issues.
- 😀 A rare but serious side effect of ARBs is angioedema, which involves swelling of the face, lips, mouth, and throat, potentially compromising the airway.
Q & A
What is the role of Angiotensin 2 in the body?
-Angiotensin 2 is a substance that causes vasoconstriction throughout the body. This constriction raises blood pressure and can affect kidney function.
What do Angiotensin 2 receptor blockers (ARBs) do?
-ARBs block the activation of Angiotensin 2 receptors, which leads to vasodilation, a reduction in blood pressure, and a decrease in aldosterone secretion.
How do ARBs help in treating hypertension?
-ARBs lower blood pressure by blocking Angiotensin 2's effects, preventing vasoconstriction and promoting vasodilation, which in turn helps treat hypertension.
What is diabetic nephropathy and how do ARBs help?
-Diabetic nephropathy is a form of chronic kidney disease in people with diabetes. ARBs help by reducing blood pressure to the kidneys, decreasing inflammation, and preventing kidney damage.
How do ARBs impact kidney function?
-ARBs help protect kidney function by lowering blood pressure to the kidneys, which can reduce inflammation, prevent scarring, and protect from further kidney damage.
What other conditions can ARBs be helpful in treating?
-ARBs are also helpful in treating heart failure, peripheral arterial disease, and conditions that benefit from reduced workload on the heart.
What effect do ARBs have on aldosterone secretion?
-ARBs decrease the secretion of aldosterone, which normally helps regulate blood volume by retaining sodium and water and excreting potassium. As a result, ARBs help reduce blood volume and retain potassium.
What side effects should be monitored when taking ARBs?
-Common side effects include dizziness, hypotension (low blood pressure), increased potassium levels, and gastrointestinal upset. Kidney function should also be monitored.
Why is monitoring potassium levels important for ARB patients?
-ARBs can increase potassium levels due to the decrease in aldosterone secretion. Elevated potassium can be dangerous, so it is important to monitor levels, especially in patients at risk for kidney disease.
What is angioedema and why is it a concern with ARBs?
-Angioedema is a rare but serious side effect of ARBs, causing swelling of the face, lips, mouth, and throat. This swelling can block airflow, posing a risk to the airway and breathing.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

How do ACE & ARB's Work? (+ Pharmacology)

A Step-By-Step Guide to Blood Pressure Medication Management

Hypertension medications that affect the RAAS system - Pharmacology - Cardiovascular | @LevelUpRN

The Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System, RAAS, Animation

Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System | RAAS | Juxtaglomerular Apparatus | JGA | Renal Physiology
Pharmacology - HYPERTENSION & ANTIHYPERTENSIVES (MADE EASY)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
