Jenis Media Transmisi Dalam Dunia Telekomunikasi
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Ken Dhil explains the different transmission media used in telecommunications. He covers two primary types: cables and wireless. Cables include electrical cables, commonly used for LAN connections with a maximum distance of 100 meters, and optical cables that transmit light signals and can cover up to 70 kilometers. Wireless transmission uses radio microwave signals and offers varying ranges depending on antenna type, with a maximum distance of 64 kilometers. The video also touches on satellite communication, highlighting its role in remote areas, and the challenges of interference and latency due to long distances and external factors.
Takeaways
- 😀 Transmission media in telecommunications can be broadly divided into two categories: cable and wireless.
- 😀 Cables are considered stable media, with two types: electrical cables (like LAN) using electrical signals and fiber optic cables using light signals.
- 😀 Electrical cables (LAN) use copper as the core material and have a maximum distance of 100 meters. Beyond that, hubs or switches are needed.
- 😀 Fiber optic cables use optical fibers to transmit light signals, offering a maximum distance of up to 70 km, depending on the SFP type.
- 😀 Wireless transmission uses radio microwave signals, and its range is affected by power and antenna design.
- 😀 Antennas in towers come in two types: one for communication between BTS and mobile phones with shorter but wider coverage, and another for point-to-point communication over longer distances.
- 😀 Point-to-point antennas can have a maximum range of 64 km, with a bandwidth of up to 200 Mbps per channel.
- 😀 Regulations control the use of radio frequencies to prevent interference, and these are monitored by Balmon (regulatory authority).
- 😀 Microwave radio signals are influenced by external conditions, such as line of sight and obstructions like trees or poor weather.
- 😀 For remote areas, such as mountains or isolated islands, satellites are used for communication, involving a ground station on Earth and a satellite in geostationary orbit (about 36,000 km from Earth).
- 😀 Satellites act as repeaters, retransmitting signals from one ground station to another, although this comes with higher latency due to the long distance and potential disruptions like sun outages or radiation interference.
Q & A
What are the two main types of transmission media in telecommunications?
-The two main types of transmission media in telecommunications are cables and wireless media.
What is the difference between electrical cables and optical cables?
-Electrical cables, such as LAN cables, use electrical signals to communicate and are made of copper. They have a maximum range of 100 meters, and beyond that, a hub or switch is required. Optical cables use light signals for communication and are made of optical fiber, offering a maximum range of up to 70 km, depending on the type of SFP.
What is the maximum bandwidth capacity for optical cables as mentioned in the script?
-The maximum bandwidth capacity for optical cables, as mentioned in the script, is 100 GBps.
How does wireless communication work, and what factors affect its range?
-Wireless communication works by using radio microwave signals. The range of these signals is affected by the power of the signal and the shape of the antennas. The two types of antennas mentioned are used for different purposes: one for communication between BTS and mobile phones with a wider but shorter range, and the other for long-distance point-to-point connections.
What is the maximum range for point-to-point wireless communication?
-The maximum range for point-to-point wireless communication is around 64 km.
What is the bandwidth capacity of wireless communication as mentioned in the script?
-The bandwidth capacity of wireless communication is up to 200 Mbps per channel.
What regulatory body oversees the use of radio frequencies to prevent interference?
-The regulatory body that oversees the use of radio frequencies is Balmon, which ensures frequencies are used properly and without interference.
What external factors can affect the quality of microwave radio signals?
-The quality of microwave radio signals can be affected by external factors such as line of sight and physical obstructions like trees, as well as adverse weather conditions.
What is the solution for providing communication in remote areas like mountains or isolated islands?
-The solution for providing communication in remote areas is the use of satellites. Satellites in geostationary orbit, approximately 36,000 km from Earth, can help bridge the communication gap.
How do ground stations and satellites work together in telecommunications?
-Ground stations on Earth send signals to satellites in geostationary orbit, which act as repeaters to send the signals back to Earth. The signals are then received by other ground stations. However, this process results in high latency due to the long distance, and potential disruptions may occur due to factors like weather or solar radiation.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

CS601_Topic102
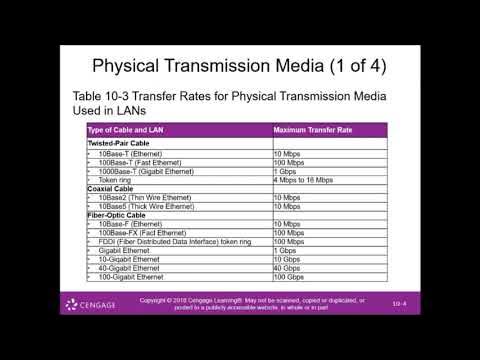
Module 10 Communicating Digital Content Wired and Wireless Networks and Devices PART5

JARINGAN KOMPONEN - DASAR-DASAR TEKNIK JARINGAN KOMPUTER DAN TELEKOMUNIKASI - PORTAL KAWAN BELAJAR

CN 5 : Transmission Media | Guided & Unguided Media with Examples | Computer Network

How does an Antenna work? | ICT #4

KUASAI MATERI "MEDIA TRANSMISI DATA" dalam 5 MENIT
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
