DETIK-DETIK INVASI JEPANG KE INDONESIA (1942) | Belanda Bertekuk Lutut
Summary
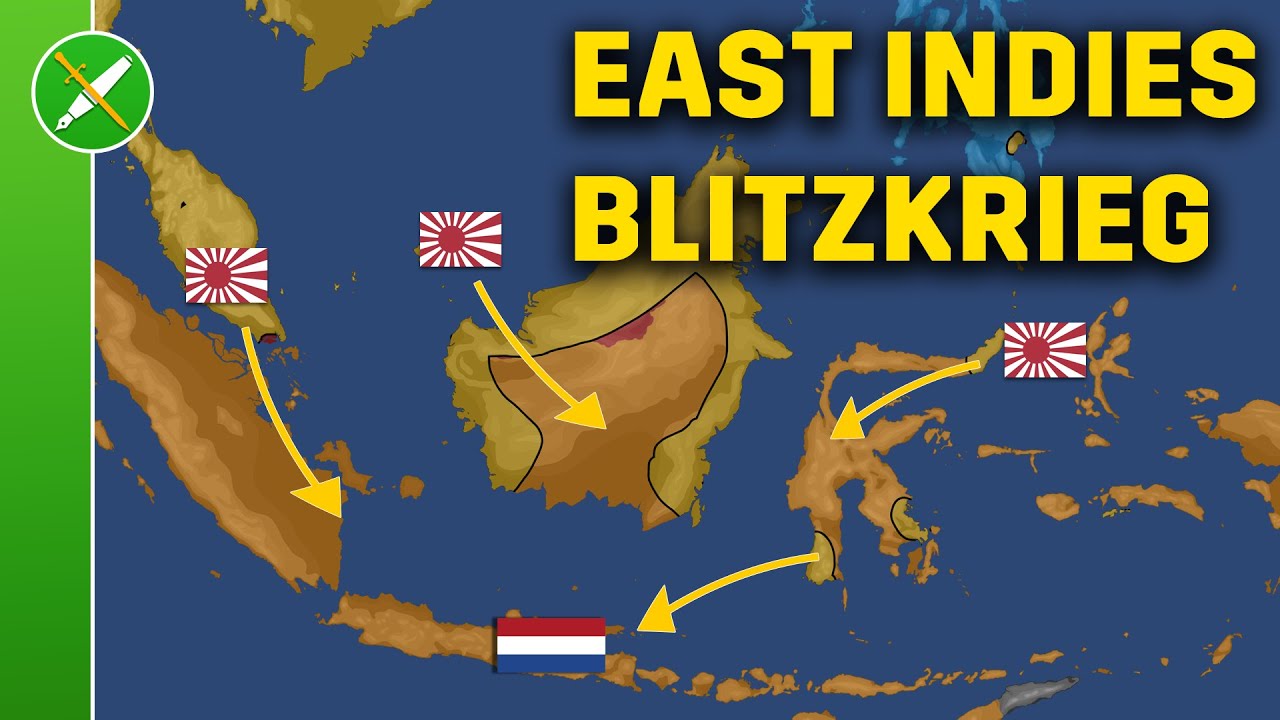
TLDRIn early 1942, the Japanese Empire launched a swift and strategic invasion of the Dutch East Indies, spanning multiple regions from January to March. The invasion targeted key locations across Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, and Maluku, with the aim of securing crucial oil fields, airbases, and military positions for the Pacific War. Despite the Dutch resistance, Japan rapidly secured territory, culminating in the signing of the Kalijati Agreement on March 8, marking the official surrender of the Dutch and the fall of their colonial empire in Indonesia.
Takeaways
- 😀 Japan's military invasion of the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia) occurred through three main routes in just three months, from January to March 1942.
- 😀 The Japanese Empire declared war on the Netherlands on January 10, 1942, and swiftly made advances, starting with the occupation of Manado in North Sulawesi the next day.
- 😀 The first invasion force attacked Southeast Sulawesi, including Kendari (January 24) and Makassar (February 10), while a second force targeted Maluku and East Nusa Tenggara.
- 😀 Japan aimed to control strategic locations like Tarakan in North Kalimantan for its oil fields and airbases, leading to an attack on January 10, 1942.
- 😀 Despite the Dutch destroying Tarakan's oil facilities before Japan took control, Japan continued its advance to Balikpapan for its oil complex on January 23, 1942.
- 😀 Japan issued an ultimatum to the Dutch to avoid destroying the oil industry in Balikpapan, but the Dutch refused, leading to further Japanese military action in Balikpapan and Samarinda in January 1942.
- 😀 On January 31, 1942, Japan captured Banjarmasin in South Kalimantan, securing airfields and preparing for an invasion of Java.
- 😀 Japanese forces continued their operations across Nusa Tenggara with invasions on Lombok (January 9) and Flores (May 9), while Java was also targeted from March 1, 1942.
- 😀 Japan's western invasion route began with the capture of Pontianak in West Kalimantan on January 19, followed by Palembang in Sumatra on February 6, aiming to control oil resources.
- 😀 Japan's complete dominance in Java was marked by the capture of Batavia (now Jakarta) on March 5, 1942, forcing Dutch forces to retreat to Lembang in West Java.
- 😀 The Netherlands officially surrendered to Japan on March 8, 1942, signing the Kalijati Agreement, marking the end of Dutch colonial rule in the East Indies.
Q & A
What was the main objective of the Japanese invasion in the Nusantara region during January to March 1942?
-The primary objective of the Japanese invasion was to occupy key strategic territories in the Nusantara region, which included capturing vital oil fields and military bases to strengthen Japan's position in the Pacific War.
How quickly did the Dutch colonial government surrender to Japan during the invasion?
-The Dutch colonial government surrendered to Japan within three months, from January to March 1942, after Japan successfully invaded key areas in the region.
What was Japan's first military action against Dutch territories in early January 1942?
-On January 10, 1942, Japan declared war on the Netherlands and began its invasion by attacking Manado in North Sulawesi, with the aim of securing the Manado Bay and Lake Tondano as bases for amphibious aircraft.
Why was Tarakan considered a strategic location for Japan?
-Tarakan was strategically important due to its 700 oil wells and air bases, which could significantly support Japan’s military operations in the Pacific. Despite the Dutch destroying the oil facilities before surrendering, Japan aimed to seize Tarakan for its vital resources.
What happened after Japan captured Balikpapan in January 1942?
-After capturing Balikpapan, which had a large oil tank complex, Japan gained direct access to oil fields in the interior of Borneo. Despite Japan’s threat, the Dutch destroyed the oil facilities before surrendering.
Which key cities did Japan invade on the island of Java during the invasion?
-Japan launched invasions on Java starting from March 1, 1942, with landings in Kragan, Rembang (Central Java), Surabaya (East Java), and Cilacap (Central Java). They eventually captured Batavia (now Jakarta) on March 5, 1942.
What was the significance of the Kalijati Agreement on March 8, 1942?
-The Kalijati Agreement marked the unconditional surrender of the Dutch colonial government to Japan, transferring control over the Dutch East Indies (Hindia Belanda) to Japan.
How did the Japanese military continue to expand its influence in Sumatra after the surrender of the Dutch?
-After the Dutch surrender, Japan continued to expand its control over Sumatra by launching military operations, including invasions of Jambi (March 4), Medan (March 12), and Padang (March 19), along with other key areas in Sumatra.
What was the strategic purpose of Japan's invasion of Palembang in Sumatra?
-Palembang was targeted for its oil refineries, which were crucial for Japan's war effort. Japan executed a rapid aerial assault on February 6, followed by a naval landing to secure the area.
Why was the Japanese attack on Balikpapan in late January 1942 particularly significant?
-The attack on Balikpapan was significant because the region contained one of the largest oil tank complexes in the area, providing Japan with access to substantial oil reserves vital for their military operations.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Blitzkrieg in South East Asia - Japan's Conquest of Indonesia Animated

Serangan Kilat Tentara Jepang Menggulung Belanda Di Kalijati (1942)

Bagaimana Strategi Jepang Menguasai Indonesia? Part 2

Tahun 1942, Belanda dan Sekutu Menyerah kepada Jepang di Hindia-Belanda (Indonesia)

Hitoshi Imamura, Jenderal Jepang yang Berbeda dari yang Lain - Sejarah Indonesia

Masuknya Jepang Ke Indonesia Dan Jatuhnya Hindia Belanda | Sejarah
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
