Enzim pada Pencernaan Manusia
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Widyaningsih discusses the digestive enzymes in humans, explaining the two types of digestion: mechanical and chemical. She covers the various enzymes produced by organs such as the salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, and small intestine, detailing their roles in breaking down food. The video also explores the presence of digestive enzymes in fruits like papaya, pineapple, and apples. Viewers are invited to share their thoughts on the best time to consume fruits, followed by an upcoming lesson on digestion in ruminants.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses digestion, focusing on digestive enzymes in humans.
- 😀 There are two types of digestion: mechanical digestion and chemical digestion.
- 😀 Mechanical digestion involves breaking down food into smaller pieces for easier chemical digestion.
- 😀 Chemical digestion uses enzymes as catalysts to break down nutrients.
- 😀 Salivary glands produce the enzyme amylase (ptyalin) to break down starch into glucose.
- 😀 The stomach produces hydrochloric acid (HCL) and enzymes like pepsin to break protein bonds.
- 😀 The enzyme rennin in the stomach helps coagulate milk protein (casein).
- 😀 The pancreas produces enzymes like trypsin, amylase, maltase, sucrase, lactase, and lipase to digest proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
- 😀 The small intestine produces enzymes like erepsinogen and enterokinase to break down peptides and activate trypsinogen.
- 😀 Fruits like papaya, pineapple, and kiwi contain proteolytic enzymes, while fruits like tomatoes and apples contain carbohydrate-digesting enzymes.
- 😀 The script invites viewers to share their opinions on whether consuming fruit before or after meals is better for digestion, encouraging scientific explanations.
Q & A
What are the two main types of digestion discussed in the transcript?
-The two main types of digestion are mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. Mechanical digestion involves breaking down food into smaller pieces, while chemical digestion uses enzymes to break down food at a molecular level.
What is the role of mechanical digestion?
-Mechanical digestion's role is to physically break down food into smaller pieces, making it easier for the body to process it further in chemical digestion.
What enzyme does the salivary glands produce, and what is its function?
-The salivary glands produce the enzyme amylase (also called ptyalin), which helps digest starches (amilum) into simpler sugars like glucose.
What substances does the stomach produce to aid digestion?
-The stomach produces hydrochloric acid (HCl) and the enzyme pepsin. HCl helps break down food, while pepsin helps digest proteins by breaking peptide bonds.
What is the function of rennin in the stomach?
-Rennin is an enzyme produced in the stomach that helps precipitate casein, a protein found in milk, aiding in its digestion.
What enzymes does the pancreas secrete and what are their roles?
-The pancreas secretes enzymes such as trypsin, which breaks down proteins into amino acids, amylase, which converts starch into glucose, and lipase, which breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
What are the functions of disaccharidase enzymes like maltase, sucrase, and lactase?
-Disaccharidase enzymes, including maltase, sucrase, and lactase, break down disaccharides into monosaccharides. For example, maltase converts maltose to glucose, sucrase converts sucrose to fructose, and lactase converts lactose to galactose.
What enzymes are produced in the small intestine, and what do they do?
-The small intestine produces enzymes like erepsinogen, which helps break peptide bonds, and enterokinase, which activates trypsinogen into trypsin to further aid in protein digestion.
According to the transcript, which fruits contain enzymes that aid in digestion?
-Fruits such as papaya, pineapple, and kiwi contain proteolytic enzymes, which help in protein digestion. Apples and tomatoes contain enzymes that assist in carbohydrate digestion.
What is the suggested time for consuming fruits based on the transcript, and why?
-The transcript encourages viewers to think about whether consuming fruits before or after meals is better. The reasoning can be linked to the enzymatic activity of fruits, though it suggests that the answer varies and should be based on individual preferences.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
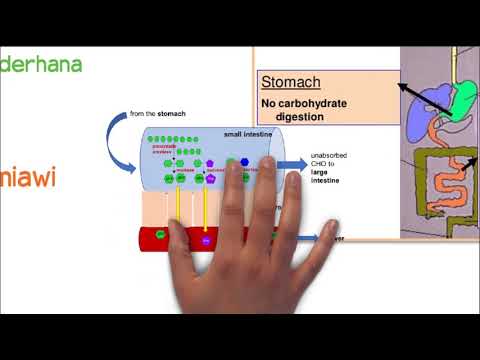
Sistem Pencernaan Makanan (karbohidrat, protein, lemak)

ระบบย่อยอาหาร 1/2 (ปาก-กระเพาะอาหาร)

Fisiologi Lengkap Sistem Pencernaan (Deglutisi, Propulsi, Digestasi, Abrosbsi, Defekasi)
SISTEM PENCERNAAN MANUSIA PART 2: IPA KELAS 8 SMP
Organ Percernaan Manusia - IPAS Bab 5 Topik B || Kurikulum Merdeka
MECHANICAL AND CHEMICAL DIGESTION | Easy to understand processes and enzyme actions
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
