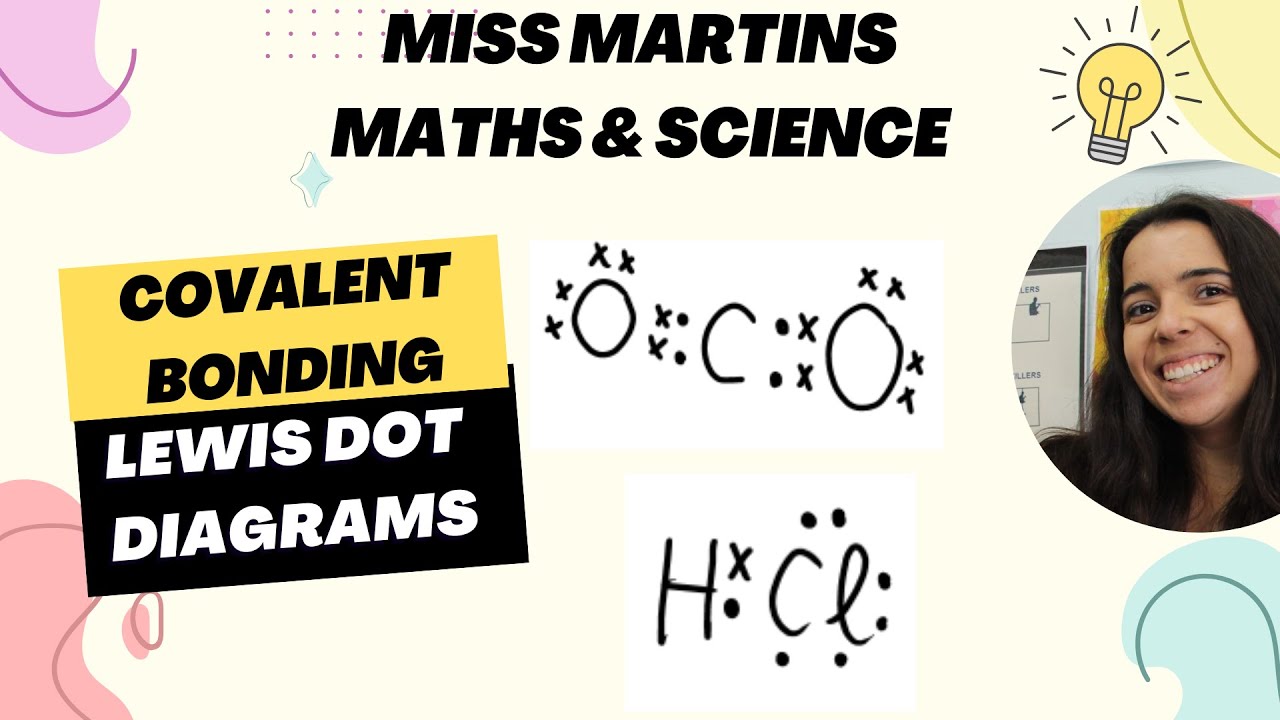Introduzione al legame chimico
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Michele introduces the concept of chemical bonding in a simple and accessible way, focusing on the role of valence electrons in atoms. He explains how atoms like magnesium, lithium, and fluorine interact to achieve stable configurations similar to noble gases. The video covers various bonding types, including electron sharing and transfer, and introduces the Lewis dot structure for visualizing valence electrons. Additionally, it touches on electronegativity, the ability of atoms to attract bonding electrons, and its trend in the periodic table. The video concludes by encouraging viewers to subscribe for future, more detailed discussions on chemical bonds.
Takeaways
- 😀 The channel 'Cinque Minuti di Chimica' is dedicated to chemistry lovers and students who might not enjoy studying it.
- 😀 Chemical bonding is introduced in a simplified manner, with further details on atomic and molecular orbitals to be presented in future videos.
- 😀 Chemical bonding refers to the interaction between the valence electrons of two atoms.
- 😀 Valence electrons are those in the outermost energy level of an atom and are responsible for the element's chemical properties.
- 😀 The noble gases are stable and typically do not form compounds, due to their full valence electron configurations.
- 😀 Helium, with only two valence electrons, is stable because its energy level can only hold two electrons.
- 😀 Other noble gases, like neon, have eight valence electrons, making them highly stable.
- 😀 Atoms tend to form bonds to achieve a stable electron configuration similar to that of noble gases.
- 😀 The lithium atom, with one valence electron, loses that electron to form a stable ion (Li+), resembling the electron configuration of helium.
- 😀 The fluorine atom, with seven valence electrons, gains an electron to form a fluoride ion (F-) and achieve a stable electron configuration like neon.
- 😀 Elements like carbon, with four valence electrons, share electrons with other atoms (like in diamond) to achieve a stable configuration, following the 'octet rule'.
- 😀 The concept of electronegativity, which describes an atom's ability to attract electrons in a bond, varies across the periodic table. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, while cesium is the least.
- 😀 Francium is a highly radioactive element and not commonly encountered in practical chemistry, despite being positioned near cesium in the periodic table.
Q & A
What is a chemical bond?
-A chemical bond is the interaction between two atoms that allows them to stay together. It can involve either the sharing or transfer of electrons between atoms.
What are valence electrons, and why are they important?
-Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. They are important because they determine how an atom will interact with others in chemical reactions, influencing the atom's chemical properties.
How does the electron configuration of magnesium relate to its chemical behavior?
-Magnesium has 12 electrons, with two in its first energy level, eight in the second, and two in the third. The two outermost electrons are its valence electrons and are responsible for its chemical properties. These electrons are involved in bonding with other atoms.
Why do noble gases typically not form chemical bonds?
-Noble gases are stable due to their full outer electron shell, which means they do not need to gain, lose, or share electrons. As a result, they are usually chemically inert and do not form bonds under normal conditions.
What is the significance of the electron configuration of helium compared to other noble gases?
-Helium is unique among noble gases because it has only two electrons in its outermost shell, which is the maximum it can hold. This configuration makes helium particularly stable, even though it doesn't follow the 'octet rule' seen in other noble gases, which have eight valence electrons.
How does the concept of noble gas configuration explain why atoms form bonds?
-Atoms form bonds in order to achieve a more stable electron configuration, similar to that of noble gases. This could mean filling their outer shell with electrons, either by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons with other atoms.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
-An ionic bond is formed when one atom transfers electrons to another, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other. A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
How does lithium form an ionic bond, and what happens to its electron configuration?
-Lithium, with one valence electron, will lose this electron to form a positive ion (Li+), achieving a stable electron configuration similar to helium. The electron transfer creates an ionic bond with an atom that gains the electron, such as fluorine.
Why does carbon form covalent bonds instead of ionic bonds?
-Carbon has four valence electrons, which is too many to lose in an ionic bond but too few to gain four more. Therefore, carbon atoms share electrons with other atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration, forming covalent bonds.
What is the 'octet rule,' and how does it relate to chemical bonding?
-The octet rule states that atoms tend to form bonds in such a way that they achieve eight electrons in their outermost shell, mimicking the stable electron configuration of noble gases. This rule helps explain why atoms bond to fill their valence shells.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)