Memahami Arus Bolak-Balik
Summary
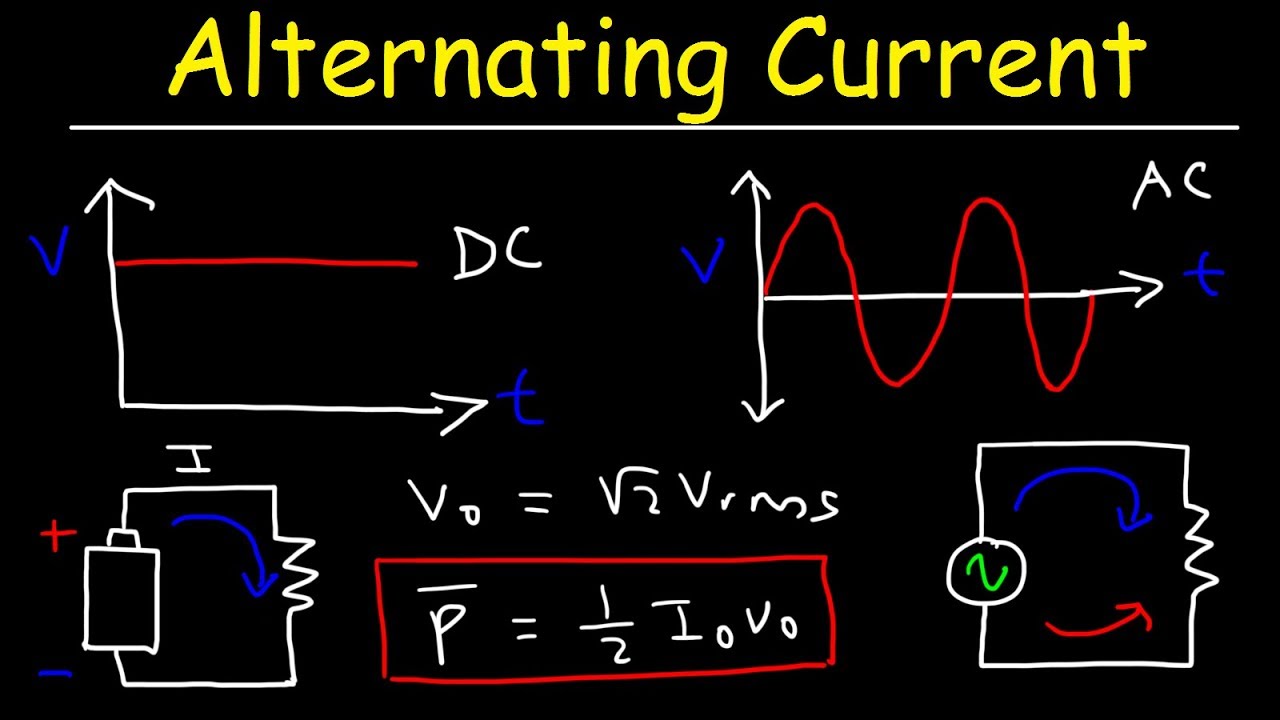
TLDRThis video explains the difference between Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC), focusing on how electricity from PLN (Perusahaan Listrik Negara) powers everyday devices. The speaker introduces the concept of DC, where voltage remains constant, and contrasts it with AC, where voltage fluctuates sinusoidally between positive and negative values. Visual aids, such as graphs, demonstrate the behavior of both types of currents. The video wraps up with a teaser about calculating voltage or current at specific moments, encouraging viewers to stay tuned for more insights on electrical principles.
Takeaways
- 😀 AC (Alternating Current) is the type of electrical current used in household appliances powered by PLN (Indonesian State Electricity Company).
- 😀 AC's voltage alternates between positive and negative values, resulting in a back-and-forth flow of current.
- 😀 DC (Direct Current) flows in a single direction and has a constant voltage, typically used in batteries.
- 😀 The key difference between AC and DC is how their voltages behave over time—AC fluctuates, while DC remains constant.
- 😀 AC is also known as 'alternating current' because its direction of flow changes periodically.
- 😀 In AC, the current first flows in the positive direction (forward), then switches to the negative direction (reverse).
- 😀 The flow of current in AC is represented in two phases: 'forward' (positive) and 'reverse' (negative).
- 😀 The voltage of AC changes sinusoidally, making it cyclical—positive, negative, and back to positive in regular intervals.
- 😀 DC's graphical representation is a straight, constant line, while AC shows a sinusoidal wave that fluctuates over time.
- 😀 Understanding the difference between AC and DC is crucial for understanding how electricity powers various devices and systems.
Q & A
What is the main difference between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current)?
-The main difference is in how the electrical current behaves. DC flows in one direction only, maintaining a constant polarity, while AC alternates between positive and negative directions periodically.
What is the type of electricity used in most homes and businesses?
-The type of electricity used in most homes and businesses is AC (Alternating Current), supplied by the national grid (PLN in Indonesia).
Why is AC electricity referred to as 'alternating'?
-AC is called 'alternating' because its voltage and current values change periodically, oscillating between positive and negative directions over time.
How does the behavior of current in a battery differ from AC?
-In a battery, the current flows in a constant direction, providing a steady voltage. In contrast, AC changes direction periodically, causing the voltage to fluctuate.
What happens to the current when there are additional components like capacitors or inductors in a circuit?
-When components like capacitors or inductors are added, the current will fluctuate over time, but it will eventually stabilize at a certain value in the long term.
How is the current in a DC circuit different from the current in an AC circuit?
-In a DC circuit, the current flows in one direction only, while in an AC circuit, the current alternates between positive and negative directions, effectively switching directions back and forth.
What does a graph of current versus time look like for AC and DC circuits?
-For DC, the graph shows a constant current over time. For AC, the graph fluctuates in a sinusoidal wave pattern, alternating between positive and negative values.
Why does the direction of current in AC circuits switch periodically?
-The current switches direction in AC circuits because the voltage supplied by the grid alternates, causing the current to reverse direction at regular intervals.
What is meant by 'arus maju' and 'arus mundur' in the context of AC?
-'Arus maju' refers to the positive current direction (forward current), while 'arus mundur' refers to the negative direction (reverse current) during different phases of the AC cycle.
Can we measure the voltage or current of an AC circuit at a specific moment?
-Yes, the voltage or current of an AC circuit can be measured at a specific moment, but it will vary over time due to its alternating nature. The exact value depends on the phase of the cycle.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

AC and DC Electricity basics

AC and DC Current Explained | DC and AC current Explained | AC and DC Current |

Hati-Hati jangan asal colok arus listrik! bisa meledak...(Pengertian Arus AC dan DC)

What is Electronics? || Electronics Terminology Course Preview
Alternating Current vs Direct Current - Rms Voltage, Peak Current & Average Power of AC Circuits

AC vs. DC
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
