Reti Lan-#2.I livelli della pila ISO/OSI
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the OSI model, a key framework in networking. It outlines the seven layers of the OSI model—from the application layer down to the physical layer—and their respective functions. The speaker discusses various network devices like switches, routers, and hubs, which operate at different layers, and how protocols like TCP/IP and UDP manage data transmission. The video emphasizes the concept of encapsulation and decapsulation as data moves through layers, and highlights the importance of service access points (SAP) in directing data between layers. Real-world examples like YouTube and Skype calls demonstrate the practical use of these concepts.
Takeaways
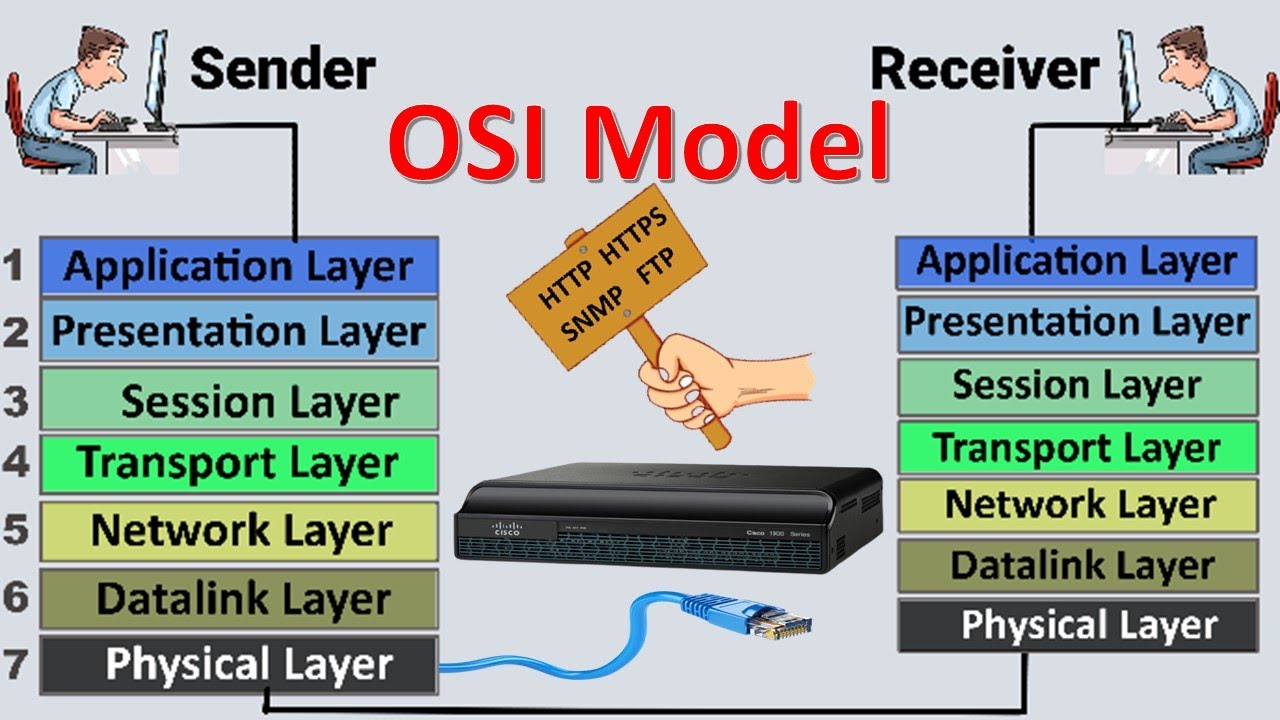
- 😀 The OSI model is a framework that defines 7 layers through which data travels in a network, from the Application layer down to the Physical layer.
- 😀 The OSI model was created by the ISO in 1984 to standardize how networks function and ensure interoperability between different systems.
- 😀 The 7 layers of the OSI model are: Application, Transport, Network, Data Link, and Physical, each playing a specific role in data transmission.
- 😀 The Transport layer handles data reliability, with TCP ensuring reliable communication and UDP prioritizing speed over accuracy.
- 😀 Routers operate at the Network layer (Layer 3), directing traffic between different networks using IP addresses.
- 😀 Switches function at the Data Link layer (Layer 2) and help route data within the same local network.
- 😀 The Physical layer deals with the transmission of raw data, like electrical signals or wireless waves, across physical media.
- 😀 Communication between systems involves the data moving from the highest layer (Application) down to the Physical layer for transmission and then back up to the Application layer on the receiving end.
- 😀 The concept of 'SAP' (Service Access Point) identifies the protocol to which the data should be passed, ensuring it reaches the correct layer for processing.
- 😀 Real-world applications like video streaming (YouTube) or calls (Skype) use different protocols at the Transport layer, depending on the need for speed or reliability.
Q & A
What is the OSI model and why is it important in networking?
-The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a seven-layer framework that defines how different network protocols interact. It is important because it standardizes network communication, enabling devices from different manufacturers to communicate seamlessly over networks.
What are the seven layers of the OSI model?
-The seven layers of the OSI model, from highest to lowest, are: Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, and Physical.
What role do Service Access Points (SAP) play in network communication?
-Service Access Points (SAP) serve as identifiers that allow different network layers to access and pass information. They help link the higher layers of the OSI model to the lower layers by indicating which protocol is being used.
What is the difference between TCP and UDP?
-TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a connection-oriented protocol, meaning it ensures reliable data transmission with error checking, but it can be slower due to its reliability. UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless protocol that is faster but does not guarantee data integrity or order.
Why is TCP considered slower than UDP?
-TCP is slower than UDP because it involves processes like error checking, data retransmission, and ensuring that the data is received in the correct order. This makes it reliable but adds latency, while UDP sacrifices these checks for faster delivery.
What is the role of a router in a network?
-A router operates at the Network Layer (Layer 3) and is responsible for forwarding data packets between different networks based on IP addresses. It ensures that data reaches its correct destination across networks.
What is the function of a switch in networking?
-A switch operates at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) and is used to connect devices within the same network, directing data frames to the correct destination based on MAC addresses.
What are hubs, and how do they differ from switches?
-Hubs are basic networking devices that operate at the Physical Layer (Layer 1). They broadcast data to all connected devices, whereas switches, operating at Layer 2, only send data to the specific device that needs it. Switches are more efficient and secure than hubs.
What is the significance of the Physical Layer in the OSI model?
-The Physical Layer is the lowest layer of the OSI model, responsible for transmitting raw electrical signals or bits over the network medium. It includes physical components like cables, connectors, and wireless transmission systems.
What happens when data is transmitted in a network using the OSI model?
-When data is transmitted, it starts from the highest layer (Application) and moves down the layers to the Physical Layer, where it is sent over the network medium. At the receiving end, the data moves back up the layers to the Application Layer, where it is presented to the user.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)