Come funziona una Centrale Termoelettrica? Ciclo di Rankine e Secondo Principio della Termodinamica
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the functioning of a coal-fired thermal power plant, which converts thermal energy into electricity using water as the working fluid. It describes the process of generating steam, driving turbines, and converting mechanical energy into electrical power. The video also explores efficiency improvements like superheating steam and dealing with issues such as air infiltration. It highlights environmental concerns, including CO2 emissions, and the methods used to mitigate pollution. The need for a shift towards renewable energy sources is emphasized, with a brief mention of other energy technologies like solar panels.
Takeaways
- 😀 A thermoelectric power plant is a large facility that converts thermal energy into electrical energy, using water as the working fluid.
- 😀 The first thermoelectric power plant was built in New York in 1882 during the Second Industrial Revolution to supply the first public lighting network.
- 😀 Thermoelectric plants play a crucial role in providing electricity worldwide, powering homes, businesses, and public infrastructure.
- 😀 Different types of fuels, such as natural gas, nuclear fission, coal, and renewable sources like geothermal energy and solar irradiation, are used to heat water in thermoelectric plants.
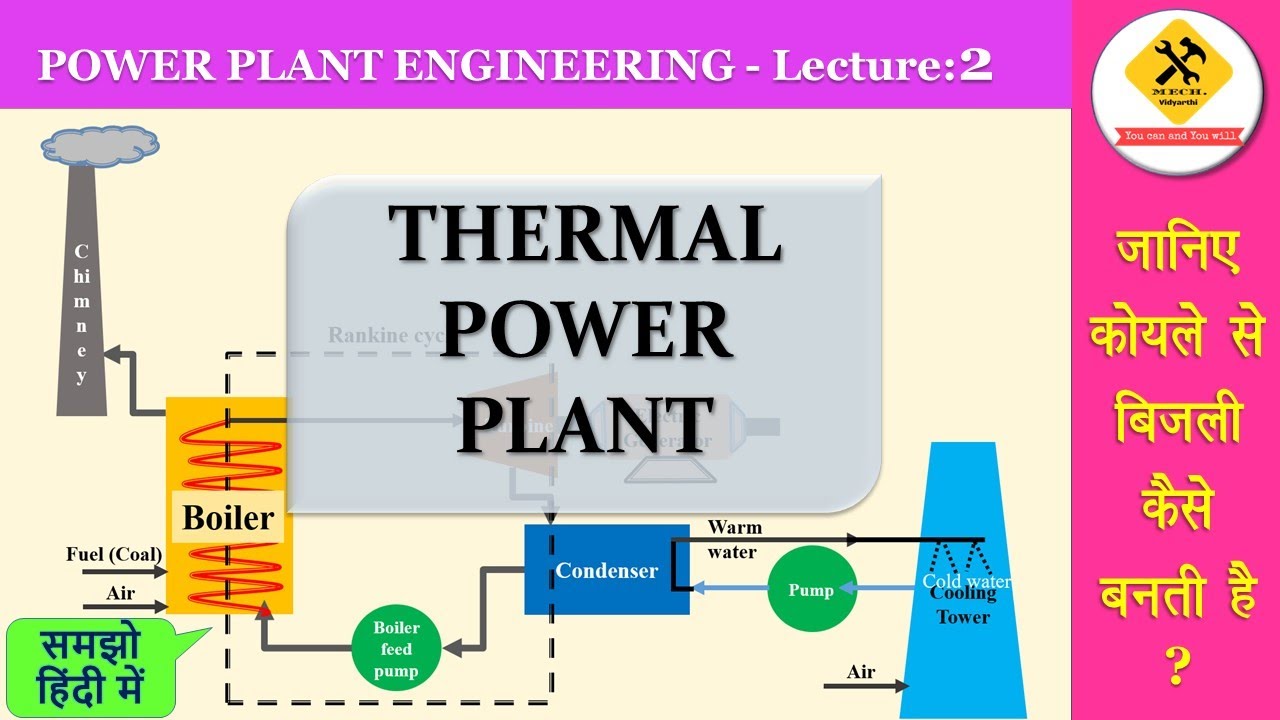
- 😀 In the plant's operation, pulverized coal is burned inside a boiler, and the heat generated turns water into steam.
- 😀 The high-pressure steam drives turbines that convert the mechanical energy into electrical energy, which is then distributed through the power grid.
- 😀 The used steam is cooled in a condenser, usually using water from a lake, river, or even the atmosphere through cooling towers, and then it is converted back into liquid water.
- 😀 The process of heating and cooling the water is part of the Rankine cycle, which is repeated to maintain a continuous supply of electricity.
- 😀 Efficiency improvements in thermoelectric plants are achieved by superheating the steam and by reheating it within the turbine using additional energy.
- 😀 One key challenge for these plants is the infiltration of atmospheric air, which can damage the boilers, so part of the steam and water is sent to a degasser to remove gases.
- 😀 The environmental impact of fossil fuel-based plants is significant due to emissions of carbon dioxide and other pollutants, but technologies like electrostatic precipitators help reduce the release of harmful particles into the atmosphere.
- 😀 Moving forward, a shift toward renewable energy sources is encouraged to mitigate the negative environmental effects of fossil fuels.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a thermal power plant?
-A thermal power plant transforms thermal energy into electrical energy using water as the working fluid. This energy allows us to power lights and household appliances.
When and where was the first thermal power plant built?
-The first thermal power plant was built in 1882 in New York during the Second Industrial Revolution to supply the world's first public lighting network.
What are the main types of fuels used to generate thermal energy in power plants?
-Fuels such as natural gas, nuclear fission, fossil coal, and even renewable energy sources like geothermal heat and solar radiation are used.
How does the water in the power plant's boiler receive energy?
-In a coal-fired power plant, pulverized coal is burned inside a water tube boiler. The water absorbs energy from the combustion gases as it moves through an economizer and then through the boiler’s serpentine pipes, turning into steam.
What happens to the steam after it leaves the boiler?
-The steam is sent to a turbine, where it loses pressure and temperature while spinning the turbine blades, converting thermal energy into mechanical energy.
How is mechanical energy from the turbine converted into electrical energy?
-The mechanical energy from the spinning turbine is transmitted to a shaft connected to a generator, which then converts it into electrical energy. This is distributed via transformers to the electrical grid.
What happens to the steam after it passes through the turbine?
-The exhaust steam is sent to a condenser, where it is cooled by a flow of water, often from a nearby lake or river, to convert it back into liquid water.
What is the Rankine cycle, and why is it important?
-The Rankine cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that describes how steam is used to generate energy. It includes processes of heating, expanding in a turbine, and cooling, and it ensures continuous energy production in thermal power plants.
What is the purpose of superheating steam in a thermal power plant?
-Superheating steam further in the boiler increases the efficiency of the cycle by raising the temperature of the steam, which leads to more efficient energy conversion, as per the second law of thermodynamics.
How do thermal power plants manage the issue of air infiltration?
-Air infiltration into the system is managed by sending the steam exiting the turbine and water from the hydraulic pump through a degasser, where gases are removed to prevent damage to the boiler and improve efficiency.
What environmental issues are associated with fossil fuel-powered thermal plants?
-Fossil fuel power plants release large amounts of CO2, greenhouse gases, acid gases, and particulate matter into the atmosphere, contributing to environmental pollution and climate change.
How do power plants reduce environmental pollution from exhaust gases?
-Exhaust gases pass through an electrostatic precipitator, which uses high-voltage static electricity to capture and remove harmful particulate pollutants before the gases are released into the atmosphere.
What is the recommended long-term solution for power generation?
-The long-term solution is to transition away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources to reduce environmental impacts and reliance on non-renewable resources.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

How does a Steam Turbine Work?

Materi Pelatihan Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Uap (PLTU).
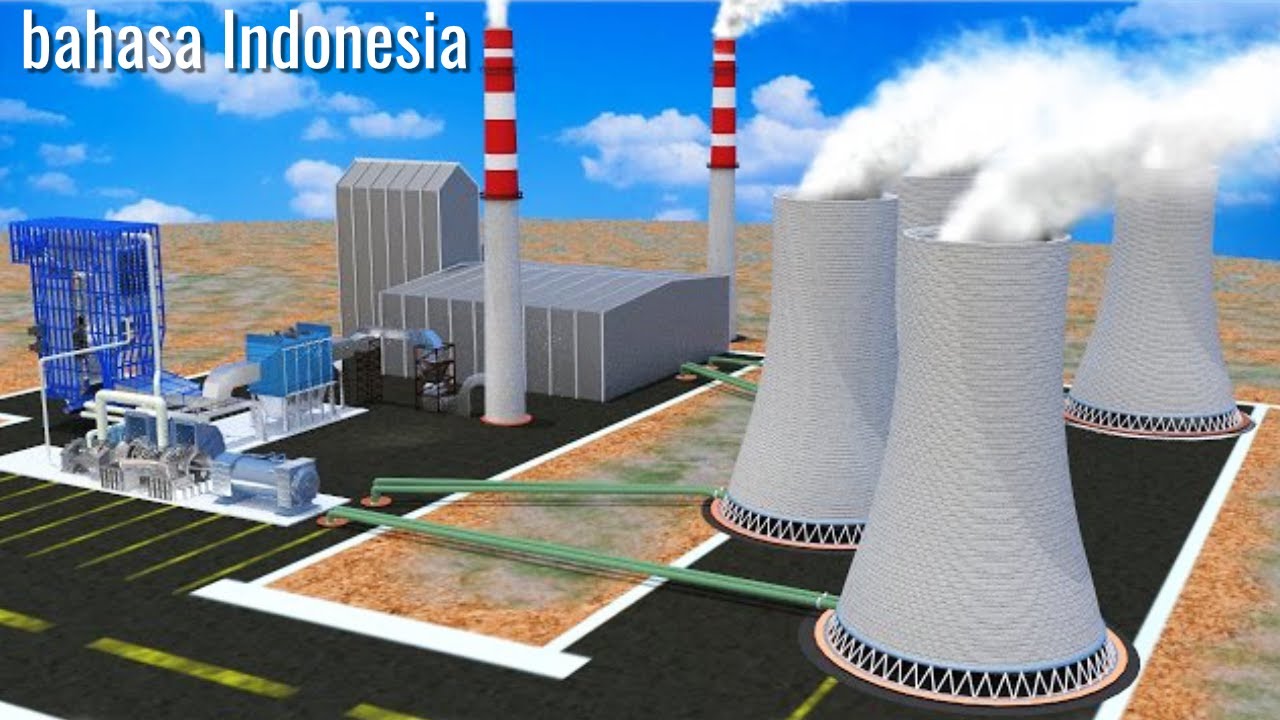

Bagaimana cara kerja pembangkit listrik tenaga termal/uap?

Solar thermal energy | Simply explained | Photovoltaics vs Solar thermal systems

Thermal Power Plant | Boiler | Economizer | Turbine | Khan GS Research Centre
How does a thermal power plant works ? (in Hindi)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
