Low-pass High-pass Band-pass Band-stop Filter Basics
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive explanation of electronic filters, focusing on their behavior, types, and design principles. Filters alter the amplitude or phase of electrical signals based on frequency, with key categories including low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and band-stop filters. The video also covers filter analysis using tools like frequency response analyzers and oscilloscopes, demonstrating how to evaluate and optimize filter performance. It concludes by highlighting the importance of understanding filter behavior and design to select the right filter for various applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electronic filters modify the amplitude or phase of electrical signals depending on the frequency.
- 😀 Filters can pass, stop, or attenuate signals over specific frequency ranges and shift the phase of the signal.
- 😀 The **passband** is the frequency range where the filter allows the signal to pass with minimal alteration.
- 😀 The **stopband** is the range where the filter significantly attenuates the signal.
- 😀 The **transition band** is where signal attenuation gradually increases between the passband and stopband.
- 😀 Attenuation curves of filters often exhibit ripples and non-uniformities, especially in the passband and stopband.
- 😀 A **frequency response analyzer** like the SF88 measures filter performance by displaying both gain and phase transfer functions.
- 😀 The **cutoff frequency** is typically defined as the point where the filter's gain drops by 3 dB, marking the bandwidth of the filter.
- 😀 Filters rely on components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors, with capacitors' impedance decreasing and inductors' impedance increasing as frequency rises.
- 😀 There are four main types of filters: low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and band-stop (notch), each with different frequency range characteristics.
- 😀 A **low-pass filter** passes low frequencies and attenuates higher ones, while a **high-pass filter** passes high frequencies and blocks lower ones.
- 😀 A **band-pass filter** is formed by combining a low-pass and high-pass filter, passing signals within a specific frequency range.
- 😀 A **band-stop (notch) filter** blocks signals within a certain frequency range by combining low-pass and high-pass filters in parallel.
- 😀 Instruments like a frequency response analyzer or oscilloscope can be used to visualize and verify filter performance across different frequencies.
- 😀 Online filter design tools allow engineers to optimize filters for specific performance requirements, offering complex designs with steep transition regions.
Q & A
What is the primary function of electronic filters?
-The primary function of electronic filters is to alter the amplitude or phase characteristics of electrical signals based on their frequency.
What are the main frequency regions in a filter's frequency response?
-The main frequency regions in a filter's frequency response are the pass band, stop band, and transition band. The pass band allows signals to pass with little or no attenuation, the stop band attenuates signals significantly, and the transition band lies between the pass and stop bands with gradual attenuation.
How is the performance of a filter typically analyzed?
-The performance of a filter is typically analyzed using a frequency response analyzer, such as the SF88, which generates Bode plots for gain and phase, showing the amplitude and phase characteristics of the filter's output relative to its input.
What is the significance of the cut-off frequency in a filter?
-The cut-off frequency defines the point at which the filter's gain falls to 71% of its maximum value, typically corresponding to a -3 dB gain. It marks the boundary between the pass band and the transition band.
What are passive filters, and how do they differ from active filters?
-Passive filters do not use active components like op-amps. They rely on resistors, capacitors, and inductors to control signal frequencies. Active filters, on the other hand, include active components such as operational amplifiers to enhance their performance.
What are the four basic types of passive filters?
-The four basic types of passive filters are low pass, high pass, band pass, and band stop (or notch) filters.
How is a low pass filter typically designed?
-A basic low pass filter is designed using an RC circuit, where a resistor is in series with the input signal and a capacitor is connected to ground. The output is taken across the capacitor, which filters the high-frequency components.
What happens to the impedance of a capacitor at higher frequencies?
-At higher frequencies, the impedance of a capacitor decreases, making it behave more like a short circuit. This characteristic is used in designing filters.
How is a band pass filter created using low pass and high pass filters?
-A band pass filter is created by combining a low pass filter and a high pass filter in series. The low pass filter removes higher frequencies, and the high pass filter eliminates lower frequencies, allowing only mid-range frequencies to pass.
What is the purpose of a band stop (notch) filter?
-A band stop (or notch) filter blocks or attenuates frequencies between two cut-off points. It can be made by combining a low pass and a high pass filter in parallel, effectively attenuating a specific band of frequencies.
How do online filter design tools assist engineers in filter design?
-Online filter design tools help engineers by providing optimized designs for specific filter performance requirements. These tools can generate Bode plots and other analyses to ensure that filters meet the desired specifications.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Electrode Electrolyte Interface - Bio Potentials and their Measurement - Biomedical Instrumentation

Pengolahan Sinyal Digital: 10 Filter IIR dan FIR
Concept of Fugacity || Solution Thermodynamics || Chemical Engineering
cara kerja bahan bakar diesel (Tipe common rail)
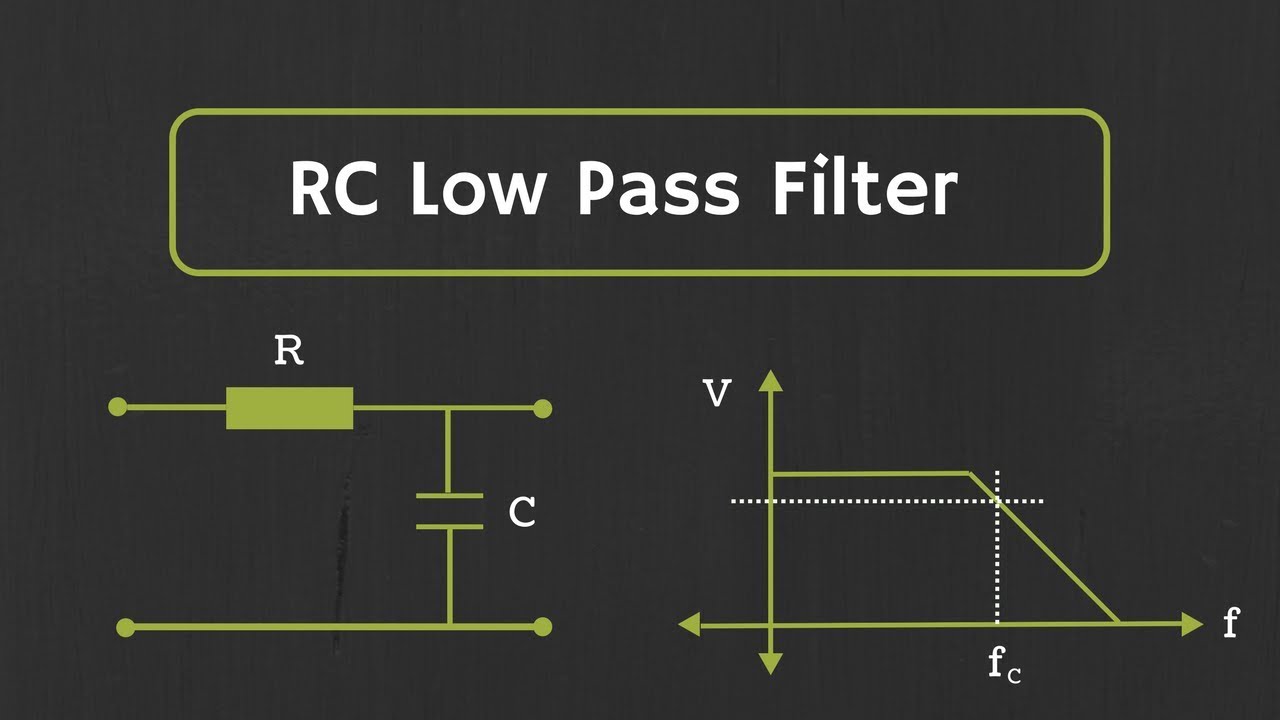
RC Low Pass Filter Explained

Seri Elektronika – 013: Komponen Elektronika Penunjang (Kabel dan Saklar)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
