Teoria da Relatividade Especial ou Restrita - Brasil Escola
Summary
TLDRIn this video, a physics professor explains Einstein's theory of relativity, focusing on the groundbreaking concepts of time dilation, length contraction, and mass increase at high speeds. The professor describes how these effects are only noticeable at speeds close to the speed of light. Through simple equations and engaging examples, the video breaks down the theory's implications, including the famous equation E = mc², which shows the equivalence of mass and energy. The theory, which was experimentally confirmed, revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and energy.
Takeaways
- 😀 Einstein's theory of relativity revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and mass, proposing that space and time are elastic and interconnected.
- 😀 Before Einstein, scientists believed that electromagnetic waves needed a material medium (ether) to travel through, similar to mechanical waves. Einstein's theory dismissed this notion.
- 😀 The theory of relativity is based on two fundamental postulates: 1) The laws of physics are the same in all inertial reference frames, and 2) The speed of light in a vacuum is constant and the same for all observers.
- 😀 Time is relative. The faster you move, the slower time passes for you compared to someone who is at rest or moving at slower speeds. This phenomenon is known as time dilation.
- 😀 The time dilation effect becomes noticeable only at speeds close to the speed of light (300,000 km/s). At everyday speeds, relativistic effects are negligible.
- 😀 The 'Twin Paradox' is an example of time dilation, where twins travel at high speeds, and upon reuniting, they find that one has aged less than the other.
- 😀 Space is also relative. Objects moving at high speeds experience length contraction in the direction of motion, making them appear shorter to an outside observer.
- 😀 The mass of an object increases as it approaches the speed of light. This concept is known as relativistic mass.
- 😀 The theory of relativity establishes the famous equation E = mc², showing the equivalence between matter and energy. This means mass can be converted into energy and vice versa.
- 😀 The theory of relativity has been experimentally tested, and in 2005, an experiment with atomic clocks on airplanes confirmed that time does indeed pass more slowly at higher speeds, validating Einstein's predictions.
Q & A
What is the main concept proposed by Einstein in the theory of relativity?
-Einstein's theory of relativity proposes that space and time are elastic, meaning they can stretch and contract depending on the speed of an object relative to the speed of light. This challenges traditional views of a fixed space-time continuum.
What did scientists initially believe about electromagnetic waves before Einstein's theory?
-Before Einstein's theory, scientists believed that electromagnetic waves, like light, required a medium called 'ether' to travel through, similar to mechanical waves that travel through air or water.
What is the key result of the Michelson-Morley experiment, and how does it relate to Einstein's theory?
-The Michelson-Morley experiment, which sought to detect the Earth's motion through the 'ether,' failed to observe any change in the speed of light. This outcome was crucial for Einstein’s development of the theory of relativity, as it showed that light travels at the same speed regardless of the observer's motion.
What are the two main postulates of Einstein's theory of special relativity?
-The two main postulates are: 1) The laws of physics are the same in all inertial reference frames, meaning they apply the same in all non-accelerating systems. 2) The speed of light in a vacuum is constant for all observers, regardless of their relative motion.
What does the theory of relativity imply about the nature of time?
-The theory of relativity suggests that time is relative; it can pass at different rates depending on the observer’s speed. This is known as time dilation, where time moves slower for objects moving at speeds close to the speed of light.
How is time dilation demonstrated in the example of 'twin paradox'?
-In the twin paradox, one twin travels on a spaceship at near-light speed while the other stays on Earth. Upon returning, the traveling twin is younger because time passed more slowly for them due to their high speed, demonstrating time dilation.
What does the theory of relativity say about the length of objects moving at high speeds?
-The theory of relativity states that objects moving at high speeds contract in length along the direction of motion. This is called length contraction, and it becomes noticeable only at speeds approaching the speed of light.
How is relativistic mass different from rest mass?
-Relativistic mass refers to the increased mass of an object as it approaches the speed of light. Unlike rest mass, which is the object's mass when it is at rest, relativistic mass increases as the object's velocity increases, making it harder to accelerate further.
What is the famous equation from the theory of relativity, and what does it represent?
-The famous equation is E = mc², which represents the equivalence of energy (E) and mass (m). This means that mass can be converted into energy and vice versa, with the speed of light (c) squared as the conversion factor.
How have modern experiments tested Einstein’s theory of relativity?
-Modern experiments, such as using atomic clocks in high-speed planes, have tested relativity by showing that time indeed passes more slowly for objects in motion relative to those at rest, confirming the predictions made by Einstein over a century ago.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
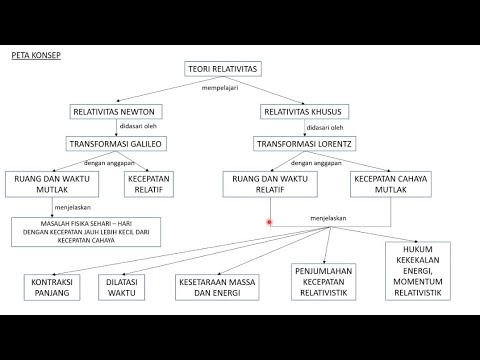
Teori Relativitas Khusus: 1. Pendahuluan

Relativitas Einstein (Materi Fisika Kelas XII Semester 2)

Engineering Physics Variation of Mass With Velocity | AKTU Digital Education

Albert Einstein's Theory of Relativity

Special Theory of Relativity | Explained in Malayalam | Einstein

#AghamUnite: Relativity and the Big Bang
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
