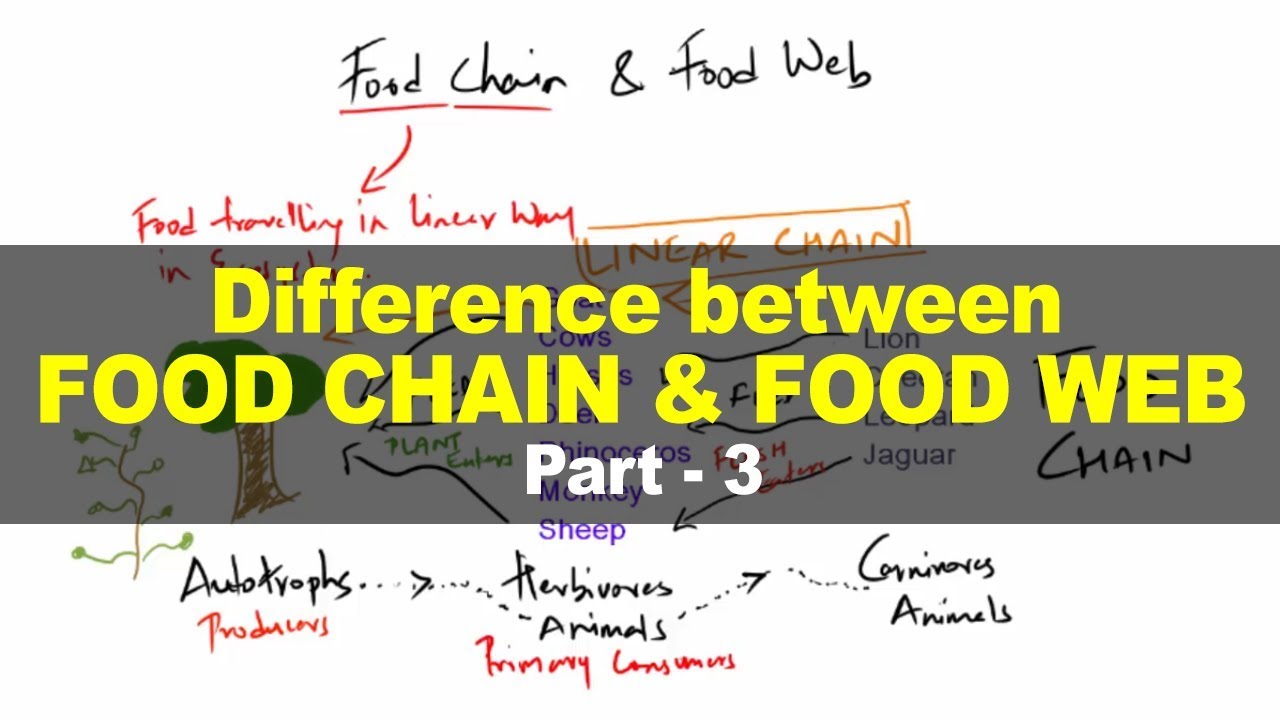
Food Chains vs Food Webs
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the differences between food chains and food webs in ecosystems. It highlights how food chains represent simple, linear pathways of energy transfer, consisting of producers, consumers, and decomposers. In contrast, food webs are more complex, showing interconnected food chains and illustrating the multiple feeding relationships among organisms. The video emphasizes that food webs provide a more comprehensive view of energy flow and ecosystem interactions, while food chains are useful for understanding basic energy transfer. Ultimately, food webs reflect the intricate interdependence of species in nature.
Takeaways
- 😀 A food chain is a simple, linear sequence showing how energy and nutrients flow from one organism to another in an ecosystem.
- 😀 The three main components of a food chain are producers, consumers, and decomposers.
- 😀 Producers, like plants, make their own food through photosynthesis using sunlight.
- 😀 Consumers are organisms that obtain energy by eating other organisms, and are classified as herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores.
- 😀 Herbivores eat plants, carnivores eat meat, and omnivores eat both plants and animals.
- 😀 Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down dead plant and animal matter, recycling nutrients in the ecosystem.
- 😀 Food webs are more complex than food chains and represent multiple interconnected food chains within an ecosystem.
- 😀 Food webs account for the fact that most organisms have multiple food sources and can be part of different food chains simultaneously.
- 😀 A food web shows the flow of energy and matter in a more comprehensive and realistic way than a food chain.
- 😀 Food chains are useful for illustrating a single pathway of energy transfer, focusing on the linear relationship between organisms.
- 😀 Food webs provide a broader picture of the intricate connections and interdependence among species in an ecosystem.
Q & A
What is a food chain?
-A food chain is a simple sequence that shows how energy and nutrients are transferred from one organism to another in an ecosystem. It typically includes producers, consumers, and decomposers.
What are producers in a food chain?
-Producers are organisms, like plants, that make their own food using sunlight through the process of photosynthesis. They form the base of the food chain.
What is the role of consumers in a food chain?
-Consumers are organisms that eat other organisms to obtain energy. They can be herbivores (plant eaters), carnivores (meat eaters), or omnivores (eaters of both plants and animals).
What are decomposers and why are they important in a food chain?
-Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down dead plant and animal matter into simpler substances, returning essential nutrients to the soil. This process helps recycle nutrients and maintain ecosystem health.
How do food chains and food webs differ?
-Food chains are linear and show a single pathway of energy transfer between organisms, while food webs are more complex and consist of interconnected food chains, reflecting the multiple feeding relationships in an ecosystem.
Why are food webs considered more accurate than food chains?
-Food webs are more accurate because they account for the fact that most organisms have multiple food sources and can be part of several food chains simultaneously, providing a more comprehensive view of energy flow in an ecosystem.
Can an organism belong to more than one food chain?
-Yes, many organisms are part of multiple food chains. For example, a bird might eat both plants and small animals, making it a part of both herbivore and carnivore food chains.
What are herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores?
-Herbivores are animals that eat only plants, carnivores eat only meat, and omnivores eat both plants and animals.
How do food webs illustrate the interdependence of species?
-Food webs show the complex and interconnected relationships among species in an ecosystem. When one species is affected, it can ripple through the web, impacting many other organisms due to their interdependent feeding relationships.
What is the significance of decomposers in a food web?
-Decomposers play a crucial role in food webs by breaking down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem, and ensuring that energy flows through the system efficiently.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Difference between Food Chain & Food Web - Environment and Ecology for UPSC IAS Part 3

Jaring-Jaring Makanan

IPA - 4.2 - ALIRAN ENERGI DALAM EKOSISTEM

Rantai Makanan, Jaring-Jaring Makanan, dan Piramida Makanan Pada Ekosistem - Materi Pelajaran IPA

Rantai Makanan, Jaring-jaring Makanan, dan Piramida Ekologi

Food Chains Compilation: Crash Course Kids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
