SAMPAPP SECTION 2 PART 1 NEW SUB
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of plastic production, beginning with crude oil, which is refined and processed into various chemicals used in petrochemical industries. The oil undergoes distillation, separating into components like naphtha and LPG, which are then cracked into simpler elements in a steam cracker. These elements form monomers like ethylene and propylene, which are used to create various chemical products, including plastics, synthetic rubber, and fertilizers. The video highlights how the oil and gas industry plays a key role in manufacturing a wide range of materials beyond fuel.
Takeaways
- 😀 Plastics are made starting with oil, a crucial raw material in the chemical industry.
- 😀 Oil and gas industries produce fuels not only for vehicles and ships but also lighter fuels and gases for chemical manufacturing.
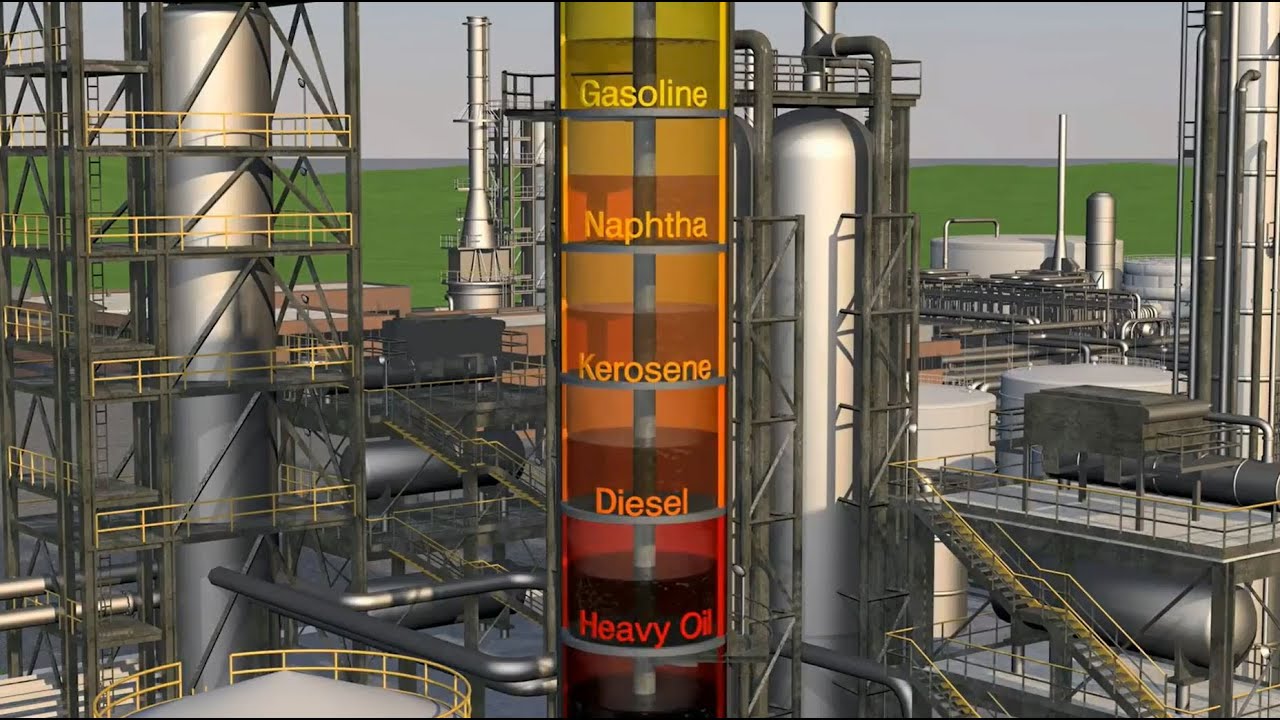
- 😀 The production of plastics begins with crude oil, which is processed in large refineries where it is distilled.
- 😀 The refining process separates crude oil into different components like diesel, kerosene, gasoline, and naphtha.
- 😀 Naphtha and LPG, byproducts from the refining process, are not directly useful, so they are often burned off.
- 😀 Naphtha and LPG undergo further chemical processing in a steam cracker, where they are broken down into simpler elements.
- 😀 The steam cracker is a critical part of the chemical industry, producing basic chemical building blocks for various industries.
- 😀 The elements produced in steam crackers are transformed into monomers like ethylene and propylene, which are key in plastic manufacturing.
- 😀 The chemical industry extends beyond plastics, also producing pharmaceuticals, pesticides, fertilizers, and paints.
- 😀 Plastics are part of a broader category of synthetic materials, including rubber and other compounds.
- 😀 The entire process of plastic production is deeply interconnected with the petrochemical industry, which is essential to the global economy.
Q & A
What is the primary starting material in plastic production?
-Plastic production begins with a drop of oil, which is a byproduct of the oil and gas industry. Oil is refined to produce materials that are essential for creating plastics.
How does the oil refining process contribute to plastic production?
-Crude oil undergoes distillation, where it is heated and separated into different components based on their boiling points. The result is products like gasoline, diesel, and nafta, which are further processed for plastic production.
What is the role of Nafta and LPG in the production of plastics?
-Nafta and LPG, which are byproducts of the oil refining process, are not directly useful as fuels. Instead, they are used in the petrochemical industry, where they are broken down to create monomers for plastics.
What is a 'steam cracker' and how does it relate to plastic production?
-A steam cracker is a crucial part of the petrochemical industry, where Nafta and LPG are heated to extremely high temperatures to break them down into simpler elements. These elements are then used to create monomers like ethylene and propylene, which are key building blocks for plastics.
What are monomers, and why are they important in plastic production?
-Monomers, such as ethylene and propylene, are the fundamental chemical units used to create polymers. These monomers undergo chemical reactions to form long chains, which are then processed into various types of plastic.
What are some other products derived from petrochemicals besides plastics?
-Besides plastics, petrochemicals are used to produce a wide range of products, including pharmaceuticals, fertilizers, pesticides, paints, and synthetic rubber.
What industries benefit from the use of petrochemicals?
-Petrochemicals support various industries such as pharmaceuticals (for drugs), agriculture (for pesticides and fertilizers), and manufacturing (for paints, coatings, and synthetic materials).
What happens to the lighter gases produced during oil refining?
-The lighter gases, such as those produced in the early stages of oil refining, are often burned off at the end of the refinery pipe because they are not useful. However, some of these gases are also used to fuel petrochemical plants.
Why is the 'steam cracker' considered the heart of the chemical industry?
-The steam cracker is vital because it transforms raw petrochemical materials, like Nafta and LPG, into essential chemical elements that are the building blocks for numerous industrial products, especially plastics.
What is the relationship between petrochemicals and synthetic rubber?
-Petrochemicals are also used to create synthetic rubber, which is a type of plastic-like material. It is derived from the same petrochemical processes that produce other plastics, such as the cracking of hydrocarbons to form monomers.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)