Akuntansi Pemerintah SMK Kelas XI - Pencatatan Keuangan Pemerintah Daerah
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the instructor discusses government accounting principles, focusing on local government finance and the key concepts of revenue, expenditures, financing, obligations, and equity. The lesson begins by introducing basic terms such as autonomy, administrative areas, and government obligations, followed by an in-depth exploration of financial management in local governments. Topics include tax collection, budget management, revenue types, operational costs, and financial recording methods, such as cash and accrual bases. The session also emphasizes the importance of financial transparency, responsibility, and system integration within local governance, providing a foundational understanding of financial recordkeeping in government settings.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson focuses on government accounting, specifically for local governments, and covers topics such as revenue, expenditure, financing, and equity recording.
- 😀 The goal of the lesson is to help students understand and analyze local government financial transactions, including income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity.
- 😀 It introduces the concept of 'autonomous regions,' where local governments have the authority to manage their own affairs in Indonesia under the national framework of the Republic of Indonesia.
- 😀 Key concepts include the distinction between mandatory and optional government services, with mandatory services required for all regions and optional ones tailored to each area's needs.
- 😀 The importance of basic services and minimum service standards is highlighted, ensuring that all citizens have access to essential services such as education and healthcare.
- 😀 Local government finances are regulated by various laws, including the right to collect local taxes and fees, manage assets, and handle financial transactions like loans.
- 😀 The financial management process involves planning, execution, recording, reporting, accountability, and auditing, ensuring compliance and effective use of public funds.
- 😀 Two basic principles govern local government finance: financial management must be orderly and efficient, and it must be integrated within the annual regional budget (APBD).
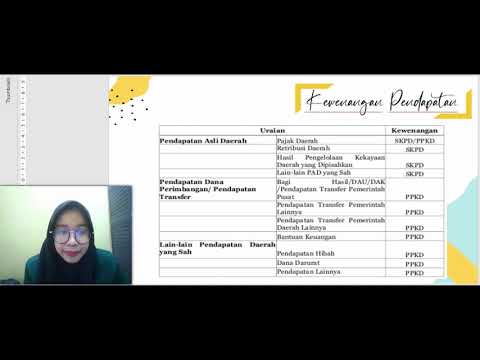
- 😀 There are two main types of local revenue: 'Pendapatan-LRA' (Revenue in the General Budget Report) and 'Pendapatan-LO' (Revenue in the Operational Report), with different recording methods.
- 😀 The script explains different types of local revenue, such as original local revenue, transfer funds from the central government, and other legal sources like grants and social assistance.
- 😀 Expenditures are categorized as operational expenses (e.g., salaries, goods), capital expenditures (e.g., infrastructure), and unexpected expenses, with clear distinctions between expenditures and liabilities in the accounting system.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the lesson in this video?
-The main focus of the lesson is on the financial recording and management of regional government finances, particularly in local government accounting.
What are the key learning objectives for this topic?
-The learning objectives include explaining regional income, spending, financing, liabilities, and equity, as well as demonstrating and analyzing transactions related to these financial elements.
What does 'autonomous region' mean in the context of local government?
-'Autonomous region' refers to the rights, authorities, and responsibilities granted to local governments to manage and regulate their own governance, in line with national principles.
How is the scope of local government finance defined according to Government Regulation No. 58/2005?
-The scope of local government finance includes the right to collect taxes and fees, manage local wealth, receive and expend funds, and handle financial obligations such as loans and government transfers.
What is the difference between 'belanja' (expenditure) and 'beban' (expenses) in government accounting?
-'Belanja' refers to actual expenditures that reduce the local budget surplus and are not reimbursed, while 'beban' refers to the economic cost incurred by the government, which reduces its net worth and is recorded on an accrual basis.
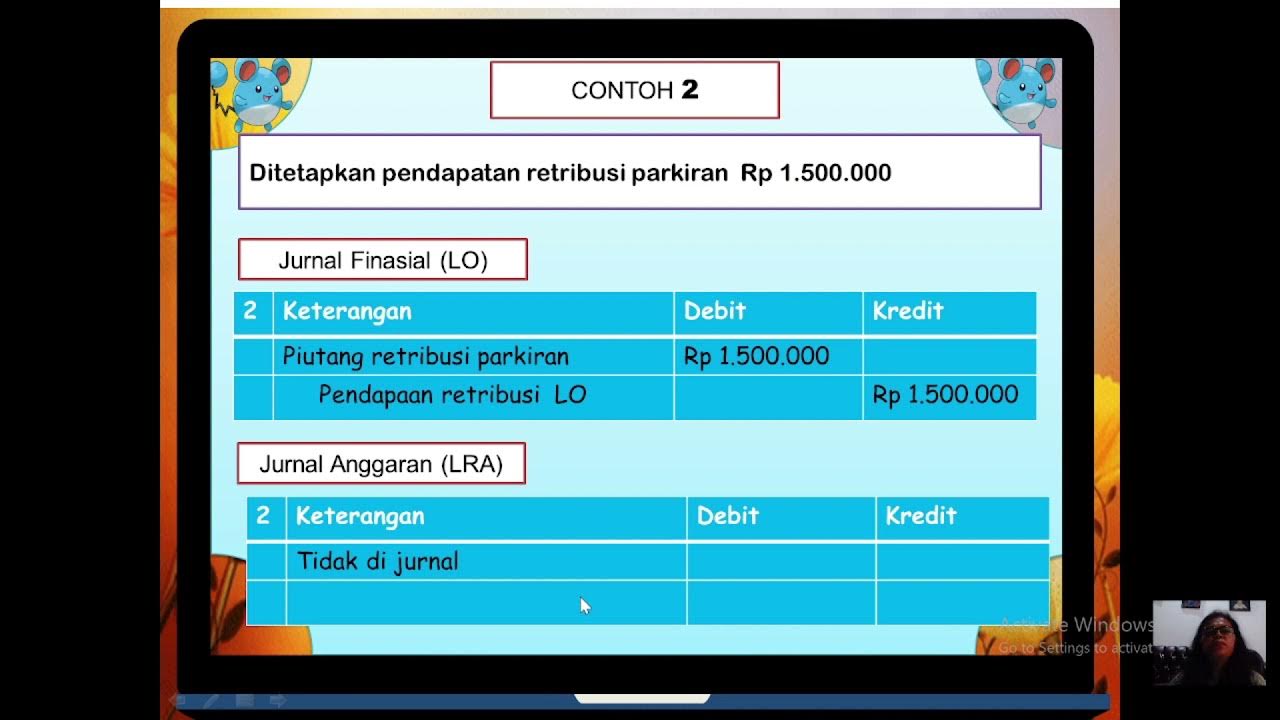
Can you explain the difference between 'pendapatan LRA' (LRA income) and 'pendapatan LO' (LO income)?
-Pendapatan LRA (LRA income) is recorded based on cash basis, meaning it is recognized when cash is actually received, whereas pendapatan LO (LO income) is recorded on an accrual basis, meaning it is recognized when the income-generating activity occurs, regardless of cash receipt.
What are the different types of regional income in local government accounting?
-The main types of regional income are local income (PAD), transfer funds from the central government (dana perimbangan), other legal income (lain-lain pendapatan yang sah), non-operational surplus, and extraordinary income.
What is meant by 'dana perimbangan' (equitable fund) in local government finances?
-Dana perimbangan refers to funds transferred from the central government to local governments for implementing regional autonomy. This includes revenue-sharing funds, general allocation funds, and special allocation funds.
What is the purpose of the 'pencatatan pembiayaan' (recording of financing) in local government?
-Pencatatan pembiayaan (recording of financing) is crucial for tracking the inflows and outflows of funds related to financial activities such as loans, investments, or the use of surpluses to address budget deficits.
What is the concept of 'surplus non-operasional' (non-operational surplus) and how is it different from a regular surplus?
-A surplus non-operasional refers to income or savings from non-recurring, non-routine activities. Unlike regular surpluses, which occur from everyday operational activities, non-operational surpluses stem from exceptional, unforeseen events or financial gains.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

[MEET 9] AKUNTANSI SEKTOR PUBLIK - AKUNTANSI PEMBIAYAAN
Praktikum Akuntansi Instansi/Lembaga Pemerintah XI AKL (Transaksi Pendapatan dan Belanja Daerah)

KONSEP AKUNTANSI PENDAPATAN - AKUNTANSI INSTANSI PEMERINTAH (Part 1)

Pengantar Akuntansi Pemerintah Kelas XI SMK
JURNAL SKPD AKUNTANSI PEMERINTAHAN

[MEET 6] AKUNTANSI SEKTOR PUBLIK - TRANSAKSI PENDAPATAN LRA DAN LO
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
