LISTRIK STATIS PART 2 | HUKUM COLOUMB
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, viewers learn about Coulomb's Law, which explains the forces between electrically charged objects. The law states that like charges repel and opposite charges attract, with the force between them being proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The video covers the key formula for Coulomb's force and important details like the law's application to point charges and the use of Coulomb's constant in a vacuum. The video also encourages viewers to subscribe for more educational content and updates in the field of physics.
Takeaways
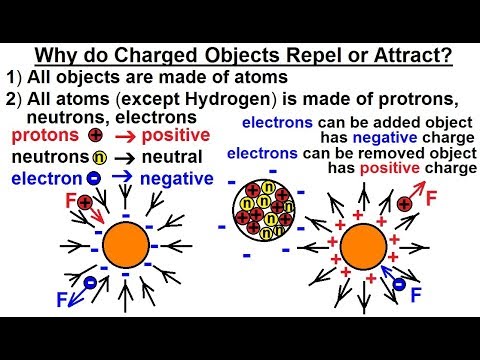
- 😀 Coulomb's law explains the interaction between electric charges, which can either attract or repel depending on the type of charges.
- 😀 Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract each other, as stated in Coulomb's law.
- 😀 Coulomb's law describes the relationship between the magnitude of the force, the charges involved, and the distance between them.
- 😀 The formula for Coulomb's law is F = k * (Q1 * Q2) / R^2, where F is the Coulomb force, k is a constant, Q1 and Q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, and R is the distance between them.
- 😀 The constant k in Coulomb's law is 9 × 10^9 N·m²/C² and is valid for charges in a vacuum or air.
- 😀 Coulomb's law applies to point charges, meaning it doesn't account for the physical size of the charges involved.
- 😀 The force between charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges.
- 😀 The force between charges is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- 😀 If both charges have the same sign (both positive or both negative), the force is repulsive (positive value).
- 😀 If the charges have opposite signs, the force is attractive (negative value).
- 😀 The law is idealized for charges in a vacuum or air, but in other mediums, the constant k would be different.
Q & A
What is Coulomb's Law?
-Coulomb's Law describes the force between two electric charges. It states that like charges repel, and opposite charges attract. The magnitude of this force is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Who discovered Coulomb's Law?
-Coulomb's Law was discovered by French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb through experiments on the forces between charged objects.
What is the formula for Coulomb's Law?
-The formula for Coulomb's Law is F = k * (Q1 * Q2) / R^2, where F is the force between the charges, k is the Coulomb constant, Q1 and Q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, and R is the distance between them.
What does the Coulomb constant (k) represent and what is its value?
-The Coulomb constant (k) is a proportionality constant in Coulomb's Law. Its value is approximately 9 × 10^9 N·m²/C², and it represents the strength of the electrostatic force in vacuum or air.
What happens if the charges are of the same type?
-If the charges are of the same type, the force between them will be repulsive. This means that positive charges repel other positive charges, and negative charges repel other negative charges.
What happens if the charges are of opposite types?
-If the charges are of opposite types, the force between them will be attractive. A positive charge will attract a negative charge, and vice versa.
What does it mean for Coulomb's Law to apply to point charges?
-Coulomb's Law applies to point charges, meaning it assumes that the charges are infinitesimally small, and their physical size does not affect the force between them. The law ignores the volume of the charges.
Does Coulomb's Law apply in all mediums?
-Coulomb's Law, with its constant value of 9 × 10^9 N·m²/C², applies specifically in a vacuum or air. For other mediums, the constant may change due to the material's properties.
What does the negative sign in Coulomb's Law indicate?
-The negative sign in Coulomb's Law indicates an attractive force between charges. If the force is negative, the charges are of opposite types, and they will attract each other.
How does the distance between two charges affect the force between them?
-The force between two charges is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This means that as the distance between the charges increases, the force decreases rapidly.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Coulomb's law

Listrik Statis Kelas 9 SMP (Part-2) Gaya Coulomb

Eduscribe : Fisika (Listrik Statis) Part 1

Tema 01 - A Carga Elétrica e o Spin | Experimentos - Lei de Coulomb

LISTRIK STATIS # belajar di rumah
Physics - E&M: Ch 35.1 Coulumb's Law Explained (1 of 28) Why do Charged Objects Repel or Attract?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
