What is the Difference Between a Microprocessor, Microcontroller and a Microcomputer?
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the significance of microcontrollers in modern technology and how they differ from microprocessors. It highlights the growing importance of miniaturized electronics in personal devices and explores the key components of microcontrollers, such as the CPU, memory, clocking function, and peripherals. The video compares microcontrollers to personal computers and microprocessors, emphasizing that while both are powerful, microcontrollers are designed for specialized tasks, integrating the entire system onto one chip. It provides an overview of how microcontrollers are used in everyday devices like smartphones and home appliances.
Takeaways
- 😀 Microtechnology plays a crucial role in the development of smaller, more powerful electronic devices.
- 😀 Advances in microtechnology are necessary to integrate increasingly powerful systems into everyday personal devices.
- 😀 Microcontrollers are compact, self-contained systems that function as mini-computers, often embedded into devices like smartphones, automobiles, and home appliances.
- 😀 Unlike PCs, microcontrollers are typically designed for a single task, whereas PCs can perform multiple tasks simultaneously.
- 😀 Both microcontrollers and PCs have a Central Processing Unit (CPU) that performs calculations and logic operations.
- 😀 Microcontrollers have memory similar to a PC’s RAM and hard drive, storing commands and data needed for specific functions.
- 😀 Microcontrollers use a clocking function, regulated by an oscillator, to control the speed at which operations are carried out.
- 😀 PCs have peripherals like a mouse or keyboard for input and a monitor for output, while microcontrollers use attached pins for similar input and output functions.
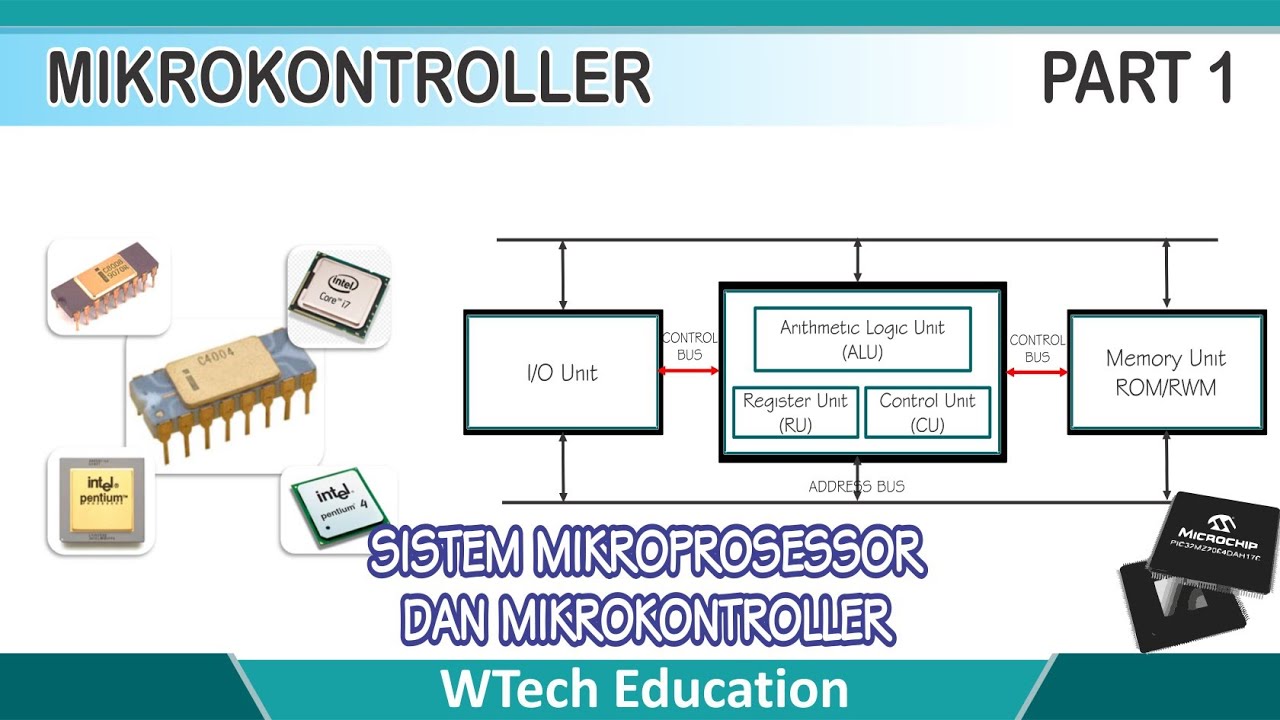
- 😀 Microcontrollers should not be confused with microprocessors, as microprocessors only integrate the CPU, lacking the full system capabilities of a microcontroller.
- 😀 Microcontrollers are generally used for specialized tasks in embedded systems, whereas microprocessors handle broader computing operations in more complex systems.
Q & A
What is the significance of miniaturized electronic components in modern manufacturing?
-Miniaturized electronic components are crucial because they allow for the development of increasingly powerful integrated systems that can be incorporated into everyday personal devices, driving the advancement of modern technology.
How does micro technology differ from traditional computing devices?
-Micro technology focuses on reducing the size of computing components, enabling them to be embedded in small, portable devices like smartphones and home appliances, whereas traditional devices are often larger and less specialized.
What is a microcontroller, and how does it function?
-A microcontroller is a self-contained integrated circuit that functions as a powerful, compact computer. It is typically dedicated to a single task and is embedded in electronic systems like automobiles, smartphones, and home appliances.
What are the main components of a microcontroller?
-A microcontroller includes a central processing unit (CPU), memory (similar to RAM and a hard drive), a clocking function to control speed, and peripherals for input and output tasks.
How does the CPU of a microcontroller compare to a PC’s CPU?
-Both the CPU of a microcontroller and a PC's CPU perform calculations and logic operations, but a microcontroller's CPU is typically dedicated to a specific task, while a PC's CPU handles a variety of tasks simultaneously.
What role does memory play in a microcontroller?
-Memory in a microcontroller stores commands and data that are used to perform specific tasks, similar to how RAM and hard drives function in a PC.
What is the purpose of the clocking function in a microcontroller?
-The clocking function in a microcontroller, typically controlled by an oscillator, regulates the speed at which processing occurs, impacting the microcontroller's performance in different operational modes.
What is the difference between a microcontroller and a microprocessor?
-A microcontroller integrates the entire computer system, including the CPU, memory, and peripherals, into a single chip. In contrast, a microprocessor only includes the CPU and requires additional components to function, typically used for more general-purpose computing.
How are microcontrollers used in everyday devices?
-Microcontrollers are used in devices like smartphones, tablets, and automobiles to perform specialized tasks, such as controlling functions in a home appliance or managing specific system operations in a car.
Why is a microcontroller considered a 'mini-computer'?
-A microcontroller is called a 'mini-computer' because it incorporates many components of a computer, such as a CPU, memory, and input/output peripherals, into a compact form, but it is typically dedicated to a specific task rather than performing general computing functions.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)