Hukum Ohm Ilustrasi dan Contoh Praktis
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces Ohm's Law, explaining the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in electronic circuits. It illustrates how voltage acts as the driving force for electric flow, likening it to water pressure in pipes. The concepts are clarified with a simple example involving a resistor and a voltage source, calculating the current flow using the formula: current equals voltage divided by resistance. This engaging overview not only demystifies basic electrical principles but also emphasizes the practical application of Ohm's Law in everyday calculations.
Takeaways
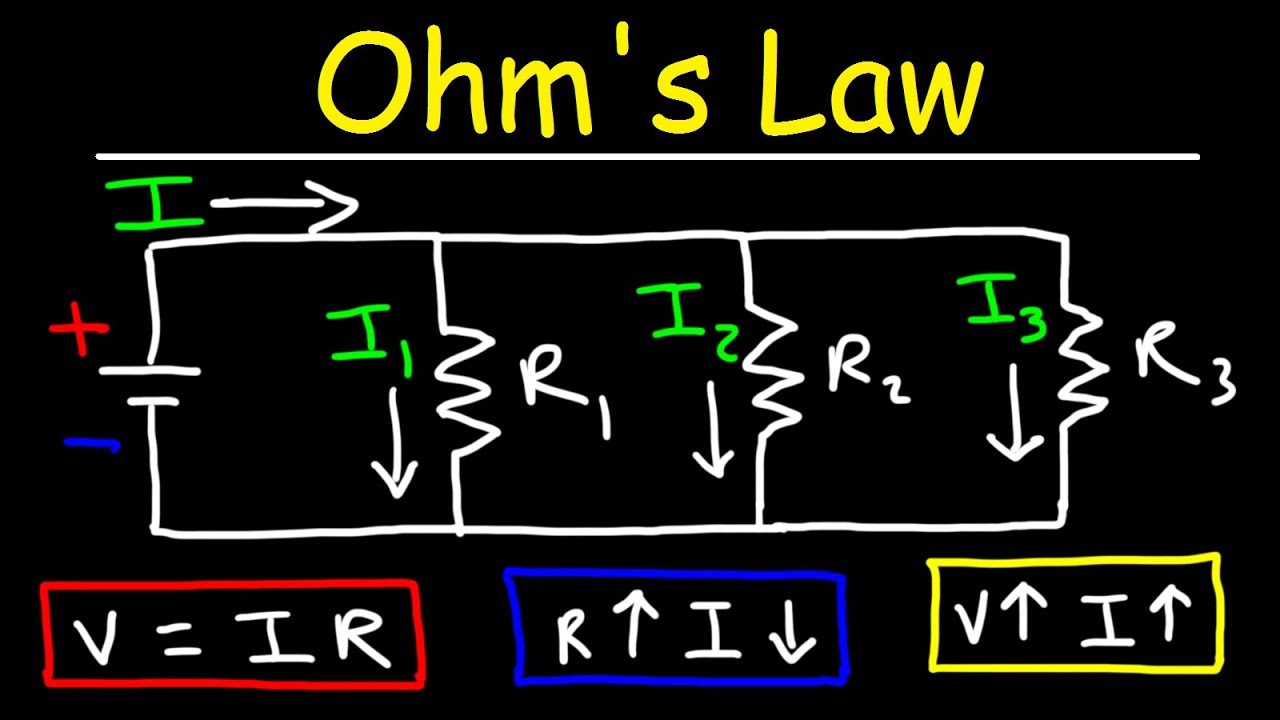
- 😀 Ohm's Law explains the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
- 🔋 Voltage is the force that drives electric current through a circuit.
- 💡 Current is the flow of electric charge, measured in Amperes (AMP).
- 🧲 Resistance is the opposition to the flow of current, measured in Ohms.
- 🚰 Voltage can be likened to water pressure pushing water through pipes.
- 📏 Current is similar to the volume of water flowing through a hose.
- 🔍 Resistance can be compared to the friction that slows down water flow.
- 💡 The formula for Ohm's Law is V = I × R (Voltage = Current × Resistance).
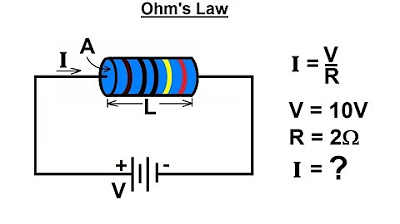
- 📊 A practical example: A 10 Ohm resistor connected to a 20 Volt source produces a current of 2 AMP.
- 👋 Understanding these concepts is crucial for applying Ohm's Law in electrical calculations.
Q & A
What is Ohm's Law?
-Ohm's Law explains the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit.
What are the three key elements in Ohm's Law?
-The three key elements are voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R).
How is voltage defined in the context of electricity?
-Voltage is defined as the force that pushes electric current through a circuit, measured in volts.
What is the formula for calculating current?
-Current can be calculated using the formula: current (I) = voltage (V) / resistance (R), measured in amperes.
What is resistance and how is it measured?
-Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current, measured in ohms.
Can you provide an analogy for understanding voltage?
-Voltage can be likened to water pressure that pushes water through a pipe.
If a resistor has a resistance of 10 ohms and is connected to a 20-volt source, what is the current flowing through the circuit?
-The current flowing through the circuit is 2 amperes, calculated using the formula I = V / R.
What happens to current if the resistance in a circuit increases while the voltage remains constant?
-If resistance increases with constant voltage, the current will decrease according to Ohm's Law.
What is the significance of understanding Ohm's Law in electronics?
-Understanding Ohm's Law is crucial for designing and troubleshooting electrical circuits.
How does the flow of electric current relate to water flow in a hose?
-Electric current is similar to water flow; the current represents the volume of electricity flowing, analogous to the volume of water flowing through a hose.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)