BAC Sciences_SVT_04 Comparaison entre l'ovogenèse et la spermatogenèse
Summary
TLDRThis transcript compares spermatogenesis and oogenesis, highlighting their distinct processes of gamete formation in males and females. Spermatogenesis occurs continuously from puberty to death, producing numerous sperm cells, while oogenesis begins before birth, pauses during childhood, and results in a single ovum per cycle, with lengthy maturation periods. The processes differ in cell division, growth phases, and the number of gametes produced, showcasing the efficiency of spermatogenesis against the complexity of oogenesis. Understanding these differences is crucial in reproductive biology, illustrating the unique roles each gamete plays in fertilization.
Takeaways
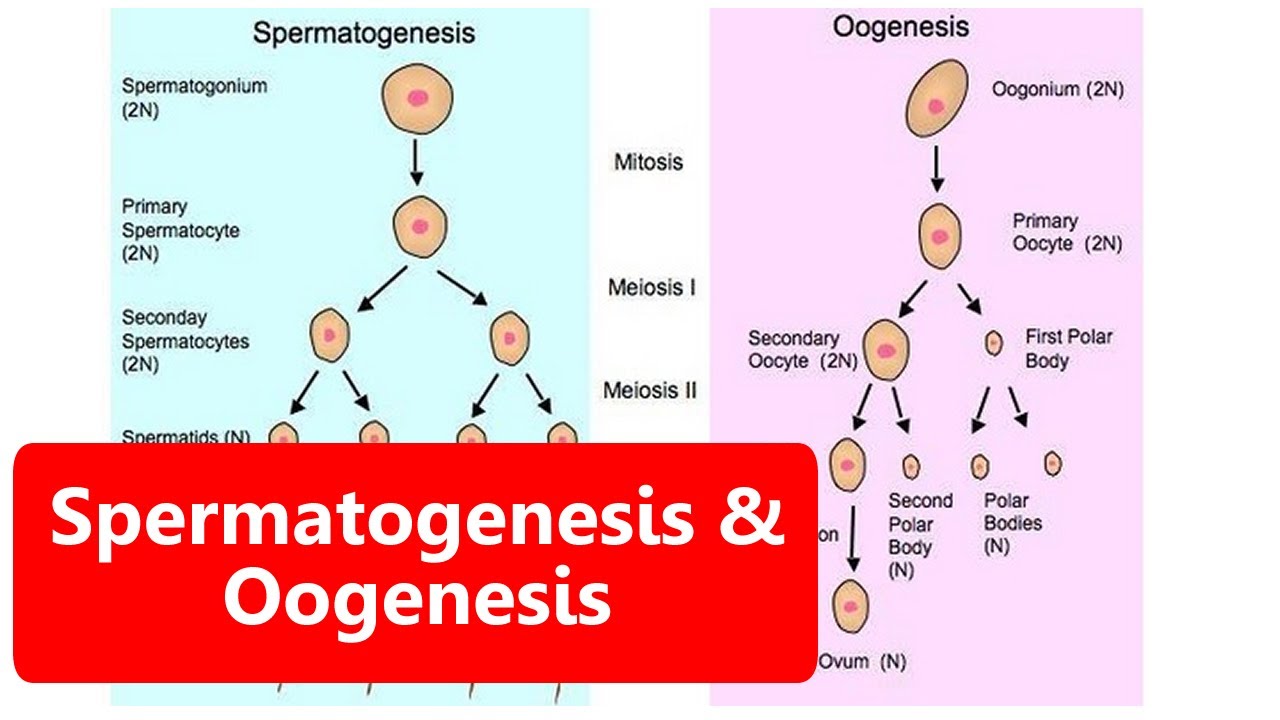
- 😀 Spermatogenesis begins at puberty and is a continuous process throughout a man's life.
- 😀 Oogenesis starts before birth, pauses during childhood, and resumes until menopause, making it a discontinuous process.
- 😀 The duration of spermatogenesis is approximately 74 days from spermatogonia to spermatozoa.
- 😀 Oocytes can remain dormant for years before maturing, resulting in a lengthy overall process.
- 😀 Both spermatogenesis and oogenesis involve mitosis during the multiplication phase, producing diploid cells.
- 😀 Each spermatocyte produces four spermatozoa, while each oocyte produces only one ovum.
- 😀 Spermatogenesis features equal cytoplasmic division, resulting in identical-sized sperm cells.
- 😀 Oogenesis involves unequal cytoplasmic division, leading to one large ovum and smaller polar bodies.
- 😀 Significant growth occurs in oogenesis across various follicular stages, while spermatogenesis involves only slight increases in size.
- 😀 The maturation phase of spermatogenesis includes substantial transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa, while oogenesis has minimal change from secondary oocyte to ovum.
Q & A
What is the main difference in the timing of spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
-Spermatogenesis begins at puberty and continues throughout a man's life, making it a continuous process. In contrast, oogenesis starts before birth, pauses during childhood, resumes at puberty, and continues until menopause, making it a discontinuous process.
How long does spermatogenesis take from start to finish?
-Spermatogenesis lasts approximately 74 days from spermatogonia to mature spermatozoa.
Why can oogenesis take several years before maturation?
-Oogenesis can take years because oocytes can remain in a dormant state for extended periods before resuming development and potentially being fertilized.
What is the significance of the number of gametes produced in spermatogenesis compared to oogenesis?
-In spermatogenesis, each primary spermatocyte produces four spermatozoa, resulting in a large number of gametes. In contrast, each primary oocyte only yields one viable ovum, leading to a much smaller number of gametes in females.
What occurs during the growth phase of spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
-During the growth phase of spermatogenesis, there is slight growth leading to primary spermatocytes. In oogenesis, there is significant growth of oocytes within various follicle stages, resulting in the accumulation of cytoplasmic reserves.
Describe the maturation process in spermatogenesis.
-In spermatogenesis, each primary spermatocyte undergoes meiotic division to produce four haploid spermatozoa. This process is continuous and occurs in the testes.
How does the differentiation phase differ between spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
-In spermatogenesis, each spermatid undergoes significant transformations to become a mature spermatozoon. In oogenesis, the transformation from the secondary oocyte to the ovum is minimal, with the focus on producing one functional gamete.
What types of cells are produced during the multiplication phase in both processes?
-In both spermatogenesis and oogenesis, the multiplication phase involves mitosis, resulting in diploid cells, which will then undergo further development.
What is the outcome of the division process during oogenesis?
-During oogenesis, each primary oocyte divides unevenly, resulting in one functional ovum and polar bodies, which typically degenerate.
What does the term 'cytoplasmic division' refer to in the context of spermatogenesis?
-In spermatogenesis, 'cytoplasmic division' refers to the equal division of cytoplasm during the meiotic divisions, resulting in sperm cells of equal size, unlike in oogenesis where the divisions are unequal.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

GAMETOGENESIS #videopembelajaranipa @nova_scienceart9251

Gamet Structure part 1

Oogenesis and Spermatogenesis | Reproductive

Gametogenesis pada Manusia/Hewan : Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis
SPERMATOGENESIS DAN OOGENESIS - Sistem Reproduksi Pada Manusia | Belajar IPA Kelas 9 SMP/ MTS

Sistem Reproduksi: Regulasi Reproduksi Pria | Alternatifa
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
