Cellule musculaire : organisation - SVT - SANTÉ Term spé #7 - Mathrix
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the structure and function of skeletal muscle cells, detailing the three muscle types, with a focus on striated skeletal muscles. It discusses their properties, such as excitability and contractility, and highlights their crucial roles in body movement, posture, joint stability, and heat production. The video dives into the microscopic structure of muscle fibers, including sarcomeres and myofibrils, and explains the mechanism of muscle contraction through the sliding filament theory, emphasizing the interaction between actin and myosin filaments. Overall, it provides a comprehensive understanding of skeletal muscles in the human body.
Takeaways
- 😀 There are three types of muscles: smooth (involuntary), cardiac, and striated (skeletal), with the latter being the focus of this video.
- 😀 Skeletal muscles are under voluntary control and account for 43% of the adult body's mass, consisting of 639 muscles, 570 of which are striated.
- 😀 Skeletal muscles can be classified into three categories: fusiform, flat, and circular, each with distinct shapes and functions.
- 😀 Key properties of skeletal muscles include excitability, contractility, elasticity, tonicity, and plasticity, which contribute to their functionality.
- 😀 Skeletal muscles serve four primary functions: facilitating body movement, maintaining posture, stabilizing joints, and generating heat.
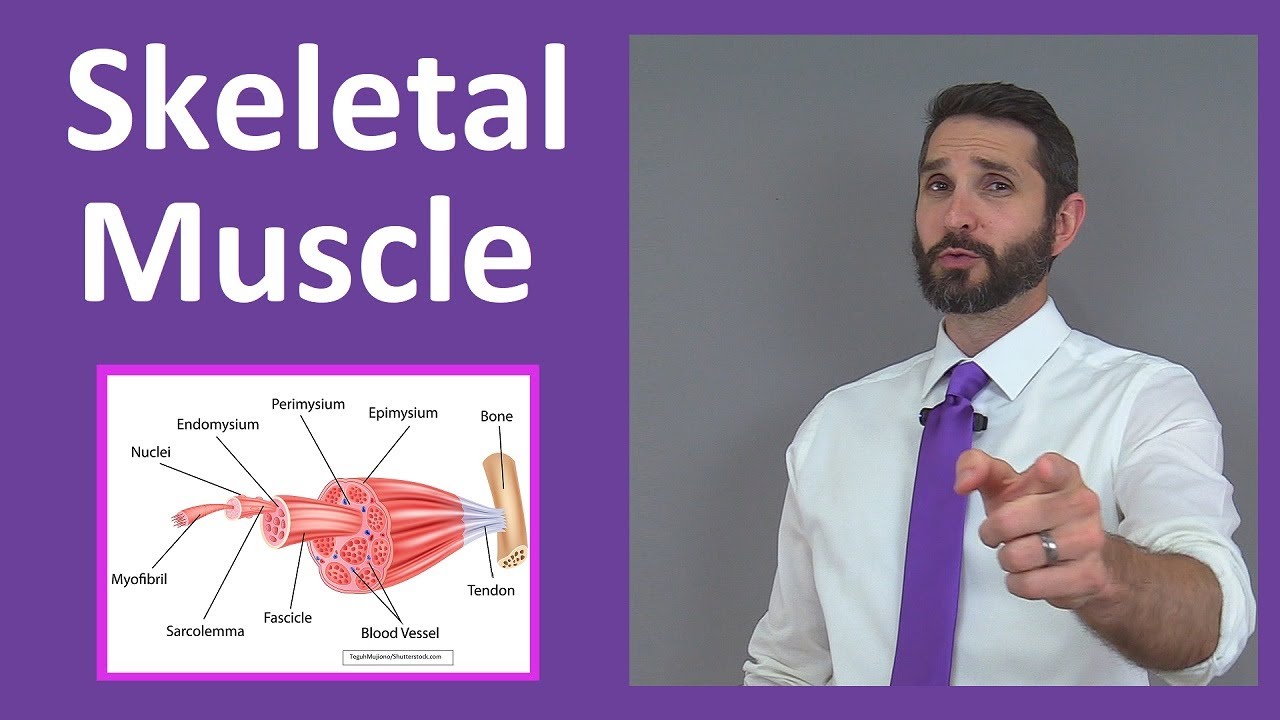
- 😀 The muscle fiber (myofiber) is a specialized cell that can be up to 35 cm long and is surrounded by the sarcolemma, a membrane that aids in cell adhesion.
- 😀 Myofibrils within muscle fibers contain myofilaments (actin and myosin) that play a crucial role in muscle contraction through the sliding filament mechanism.
- 😀 During contraction, the sarcomere shortens by 20-40%, with actin filaments sliding toward the center, while the overall length of the myosin filaments remains unchanged.
- 😀 The contraction process involves repeated cycles of attachment and detachment between myosin heads and actin, which pulls the actin filaments inward.
- 😀 Muscle structure includes connective tissue that supports and protects muscle fibers and contains blood vessels and nerves, facilitating muscle function.
Q & A
What are the main categories of muscles in the human body?
-The main categories of muscles are smooth muscles (involuntary) and striated muscles (which include skeletal and cardiac muscles).
How many muscles does the human body have, and how many are striated?
-The human body has 639 muscles, out of which 570 are striated muscles.
What percentage of body mass do skeletal muscles represent in adults?
-Skeletal muscles represent 43% of body mass in adults.
What are the three shapes of skeletal muscles mentioned in the transcript?
-The three shapes of skeletal muscles are fusiform, flat, and circular.
What are the five essential properties of striated muscles?
-The five essential properties are excitability, contractility, elasticity, tonicity, and plasticity.
What functions do skeletal muscles perform?
-Skeletal muscles are responsible for mobilizing the body, maintaining posture, stabilizing joints, and producing heat.
What is a sarcomere, and what role does it play in muscle contraction?
-A sarcomere is the basic unit of a muscle fiber, defined as the segment between two Z-lines. It shortens during contraction, allowing muscle movement.
What is the significance of myofibrils in muscle fibers?
-Myofibrils are protein structures within muscle fibers that contain the actin and myosin filaments responsible for muscle contraction.
How does the sliding filament theory explain muscle contraction?
-The sliding filament theory explains that during contraction, actin filaments slide over myosin filaments, causing the sarcomere to shorten and the muscle to contract.
What role do mitochondria play in muscle cells?
-Mitochondria provide the energy necessary for muscle contraction by producing ATP through aerobic respiration.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)