Gravimetric Analysis Video
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful introduction to gravimetric analysis, focusing on the precipitation method. It explains the fundamental concepts of isolating unknown substances through mass measurements and the importance of heating samples to constant mass for accurate results. The video details a practical example involving lead(II) sulfate precipitation and offers step-by-step guidance on stoichiometry calculations to determine the mass of a solid product. Additionally, viewers are presented with practice problems to reinforce their understanding of percentage by mass and precipitation calculations, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of gravimetric analysis principles.
Takeaways
- 😀 Importance of proper nutrition for optimal athletic performance.
- 💪 Consistency in training leads to significant muscle gains.
- 🏆 Mental toughness is as crucial as physical strength in competitions.
- 📅 Establishing a well-structured training schedule is essential for success.
- 🏋️♂️ Variety in workouts helps prevent plateaus in strength and endurance.
- 🛌 Recovery time is vital for muscle repair and growth.
- 📈 Tracking progress through measurements and performance metrics enhances motivation.
- 🤝 Support from coaches and peers can greatly influence an athlete's journey.
- 🧠 Mindset plays a crucial role in overcoming challenges and setbacks.
- 🌟 Setting realistic and achievable goals is key to sustained improvement.
Q & A
What is gravimetric analysis?
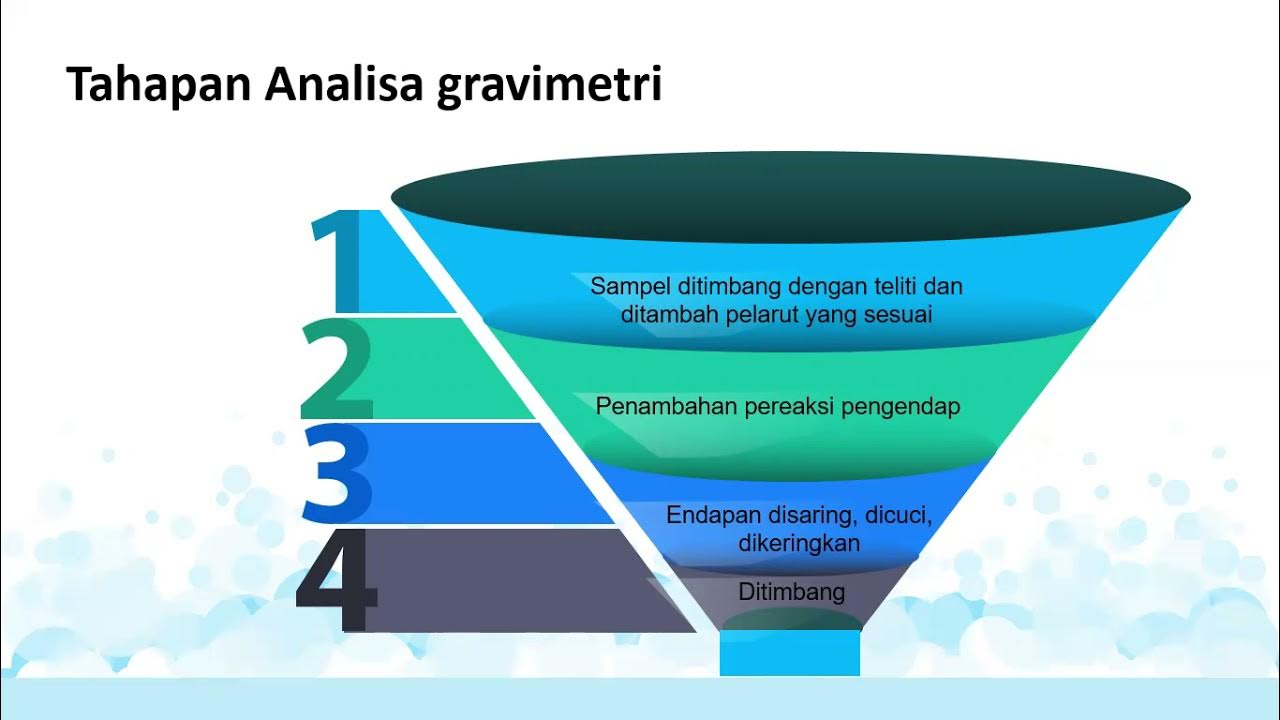
-Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative analytical method that relies on measuring the mass of a substance to determine its quantity.
What is the most common type of gravimetric analysis?
-The precipitation method is the most common type of gravimetric analysis.
How does the precipitation method work?
-In the precipitation method, an unknown substance is isolated by adding a reagent that reacts with specific ions to form an insoluble precipitate, which is then filtered and weighed.
What is the purpose of heating to constant mass in gravimetric analysis?
-Heating to constant mass ensures that all moisture is removed from the sample, allowing for an accurate measurement of the dry solid mass.
Can you describe a specific example of gravimetric analysis involving lead ions?
-In the example, lead 2+ ions are precipitated by adding a sulfate solution, resulting in the formation of solid lead 2 sulfate, which is then filtered, dried, and weighed.
What steps are involved in performing stoichiometric calculations in gravimetric analysis?
-The steps include writing a balanced chemical equation, determining the limiting reactant, and calculating the mass of the solid product formed.
What was the balanced equation provided in the example using NaOH and MgCl2?
-The balanced equation is: 2 NaOH + MgCl2 → 2 NaCl + Mg(OH)2.
How do you determine the limiting reactant in a reaction?
-The limiting reactant is determined by calculating the number of moles of each reactant and comparing them based on the stoichiometry of the balanced equation.
What mass of magnesium hydroxide was calculated in the provided example?
-The mass of magnesium hydroxide calculated from the reaction was approximately 12 grams.
What percentage by mass of calcium was found in the limestone sample?
-The percentage by mass of calcium in the limestone sample was determined to be 38.1%.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)