Anatomorfofisiologia (...) - u01t01p03
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the anatomy and histological features of the lower gastrointestinal tract, focusing on the pancreas, liver, and intestines. It details the pancreas's dual role as an endocrine and exocrine gland, emphasizing its production of pancreatic juice for digestion. The liver's metabolic functions and bile production are highlighted, crucial for fat digestion. The small intestine, divided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, is essential for enzymatic digestion and nutrient absorption. Finally, the large intestine's structure and functions, including water absorption and fecal storage, are discussed, providing a comprehensive understanding of digestive processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 The digestive process continues in the lower gastrointestinal tract, specifically in the small intestine after the stomach.
- 🍽️ The pancreas is a mixed gland located behind the stomach, with both endocrine and exocrine functions.
- 🔬 The exocrine portion of the pancreas secretes pancreatic juice, which contains digestive enzymes essential for digestion.
- 🩸 The liver is the largest gland in the body and plays a crucial role in metabolism and detoxification.
- 🧪 The liver produces bile, which is important for the digestion of fats and is stored in the gallbladder.
- 🔗 The pancreatic duct and the common bile duct merge to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla, which delivers digestive substances to the duodenum.
- 🧬 The small intestine is divided into three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, each playing specific roles in digestion and nutrient absorption.
- 💧 The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes and compacts intestinal contents into feces.
- 📏 The large intestine is about 1.5 meters long and consists of four parts: the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal.
- 🔍 The inner lining of the large intestine contains epithelial cells responsible for absorption and secretion, although it lacks the structural adaptations seen in the small intestine.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video focuses on the anatomy and histological characteristics of the organs and glands that comprise the lower gastrointestinal tract.
What role does the pancreas play in digestion?
-The pancreas is a mixed gland that produces hormones and secretes pancreatic juice, which contains digestive enzymes necessary for chemical digestion in the small intestine.
How is the pancreas structured?
-The pancreas is made up of clusters of glandular epithelial cells, primarily organized into clusters called acini, which form the exocrine portion that secretes digestive enzymes.
What are the main functions of the liver?
-The liver regulates blood levels of carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids, acts as a reservoir for vitamins, processes drugs and hormones, detoxifies the body, and produces bile to aid in fat digestion.
Where is bile produced and stored?
-Bile is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder before being released into the duodenum to facilitate fat digestion.
What are the three parts of the small intestine?
-The three parts of the small intestine are the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
What occurs in the jejunum?
-The jejunum is primarily responsible for chemical digestion and the absorption of nutrients.
What distinguishes the ileum from the jejunum?
-The ileum is the final segment of the small intestine, continuing the absorption of nutrients and terminating at the ileocecal valve, which controls the flow of materials into the large intestine.
What are the main functions of the large intestine?
-The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes, compacts intestinal contents into feces, stores fecal material before defecation, and absorbs vitamins produced by intestinal bacteria.
How is the large intestine structured?
-The large intestine consists of four parts: cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal, with the cecum receiving chyme from the small intestine and the colon further processing and absorbing water.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Sistema Digestório 1/5: Introdução, Funções, Órgãos e Histologia | Anatomia e etc

Conheça o trato gastrointestinal! | Vida e evolução | Khan Academy

GI A and P review

Development of the gastrointestinal system

Anatomorfofisiologia (...) - u01t01p02
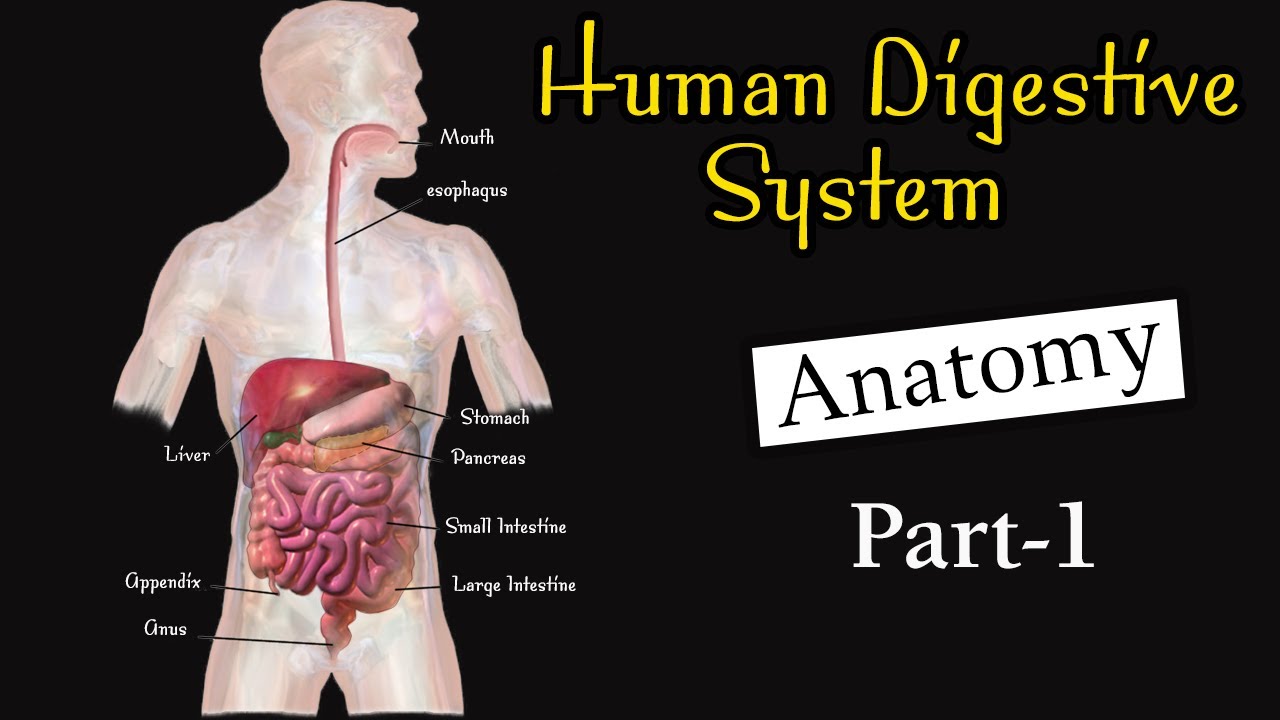
Anatomy of human digestive system I Digestive system I Digestive system class 11
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
