Hukum Coulomb Tentang Muatan Listrik
Summary
TLDRThis educational lesson on Coulomb's law explores the fundamental principles of electric charges, highlighting how like charges repel and unlike charges attract. It explains Coulomb's law mathematically, emphasizing the relationship between charge, distance, and force. The lesson includes discussions on electroscopes, the process of charge induction, and the significance of electric fields and potential differences. Additionally, it touches on natural phenomena like lightning, linking these concepts to real-world applications. Overall, the session aims to deepen students' understanding of electrostatics and encourage curiosity in the study of electricity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Coulomb's Law explains the relationship between electric charge and the force between charged objects.
- 😀 Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract, as demonstrated with examples of glass and rubber.
- 😀 The strength of the force increases as the distance between two charged objects decreases.
- 😀 The mathematical expression of Coulomb's Law involves the product of the magnitudes of the charges and the inverse square of the distance between them.
- 😀 The formula for calculating the force is F = k * (Q1 * Q2) / r^2, where k is Coulomb's constant.
- 😀 The unit of electric force is Newton (N), and distances must be converted to meters for calculations.
- 😀 An electroscope is used to detect electric charge and demonstrates the principles of charge induction.
- 😀 Electric fields are regions around charged objects that exert forces on other charges placed within them.
- 😀 Potential difference (voltage) is defined as the energy per unit charge, measured in Joules per Coulomb.
- 😀 Thunderstorms and lightning result from electrical charges building up in clouds due to differences in potential, leading to the discharge of electrons.
Q & A
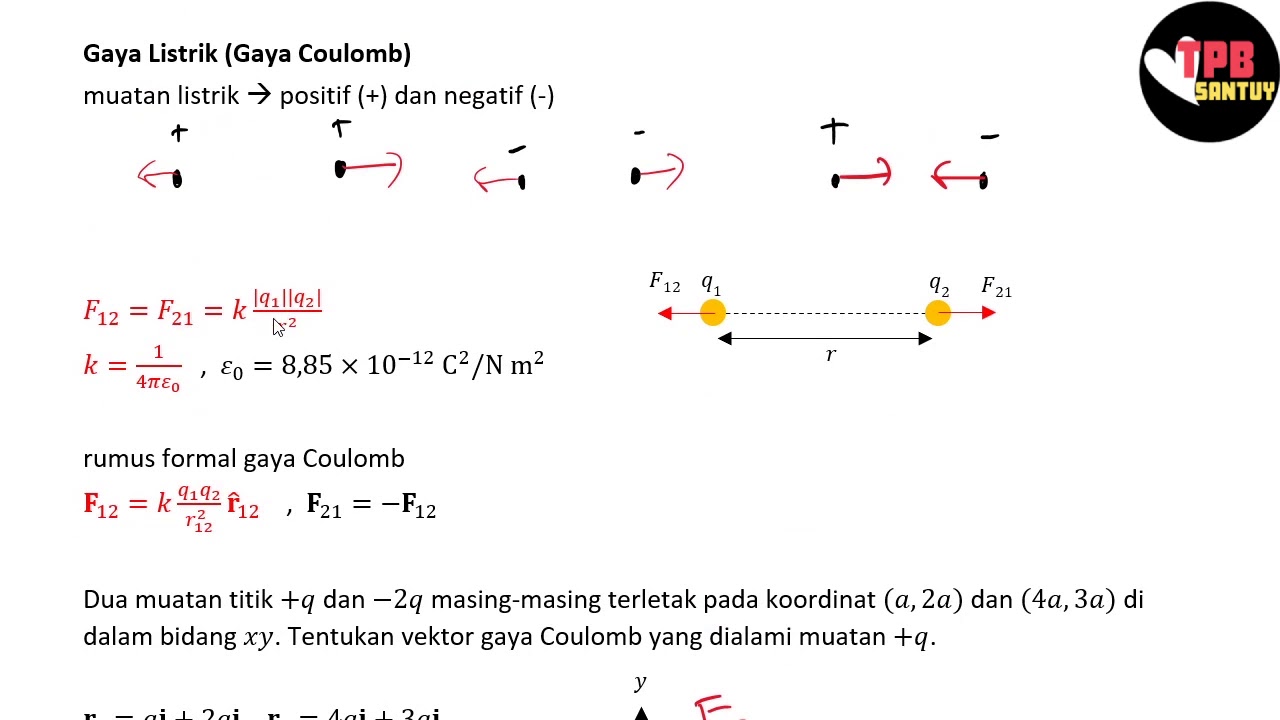
What is Coulomb's Law?
-Coulomb's Law describes the force between two charged objects. It states that the electric force between two charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
How does distance affect the electric force between two charged objects?
-As the distance between two charged objects increases, the electric force between them decreases. Specifically, the force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance.
What happens when like charges are brought close together?
-When like charges (both positive or both negative) are brought close together, they repel each other.
What occurs when unlike charges are brought close together?
-Unlike charges (one positive and one negative) attract each other when brought close together.
What is the formula for Coulomb's Law?
-The formula for Coulomb's Law is F = k * (|Q1 * Q2|) / r^2, where F is the force, k is Coulomb's constant (approximately 9 x 10^9 N m²/C²), Q1 and Q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, and r is the distance between the centers of the two charges.
What is an electroscope and how does it work?
-An electroscope is a device used to detect electric charge. It operates by allowing a charged object to induce a charge in the electroscope, causing the leaves to separate due to like charges repelling each other.
What is the concept of induction in electricity?
-Induction is the process where a charged object causes the separation of charges within a neutral object without direct contact. For instance, bringing a positively charged object near a neutral object will cause the negative charges in the neutral object to move toward the charged object.
What is meant by electric field?
-An electric field is a region around a charged object where other charged objects experience a force. It represents the influence that a charged object exerts on other charges in its vicinity.
How is electrical potential defined?
-Electrical potential is defined as the amount of electric potential energy per unit charge at a specific point in an electric field. It is given by the formula V = U/Q, where V is the electric potential, U is the potential energy, and Q is the charge.
What natural phenomenon is caused by electrical charges in the atmosphere?
-Lightning is caused by the discharge of electrical charges in the atmosphere. It occurs due to the buildup of static electricity in clouds, leading to a significant difference in electric potential between the clouds and the ground.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

FISIKA Kelas 12 - Hukum Coulomb & Medan Listrik | GIA Academy

2 Listrik Statis gaya listrik
Gaya Coulomb | Gaya dan Medan Listrik | Part 1 | Fisika Dasar

FORÇA ELÉTRICA: o que é, fórmula, Lei de Coulomb | Resumo de Física Enem. Professor Otávio Bocheco

LISTRIK STATIS PART 2 | HUKUM COLOUMB

Universo Mecánico 28 Electricidad Estática
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
