Soil Profile and Soil Horizons
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the essential role of soil in supporting life, highlighting its composition of 45% minerals, 5% organic matter, 25% water, and 25% air. It explores the soil profile, which includes distinct layers known as horizons: O (litter), A (topsoil), E (eluviation), B (subsoil), C (parent material), and R (bedrock). Each layer has unique properties, contributing to soil's fertility and health. The video emphasizes the importance of decomposers in creating nutrient-rich humus and how soil layers interact with water movement. It invites viewers to learn more through additional resources on soil.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Soil is essential for plant growth, supporting grass and trees, and is the foundation for food production.
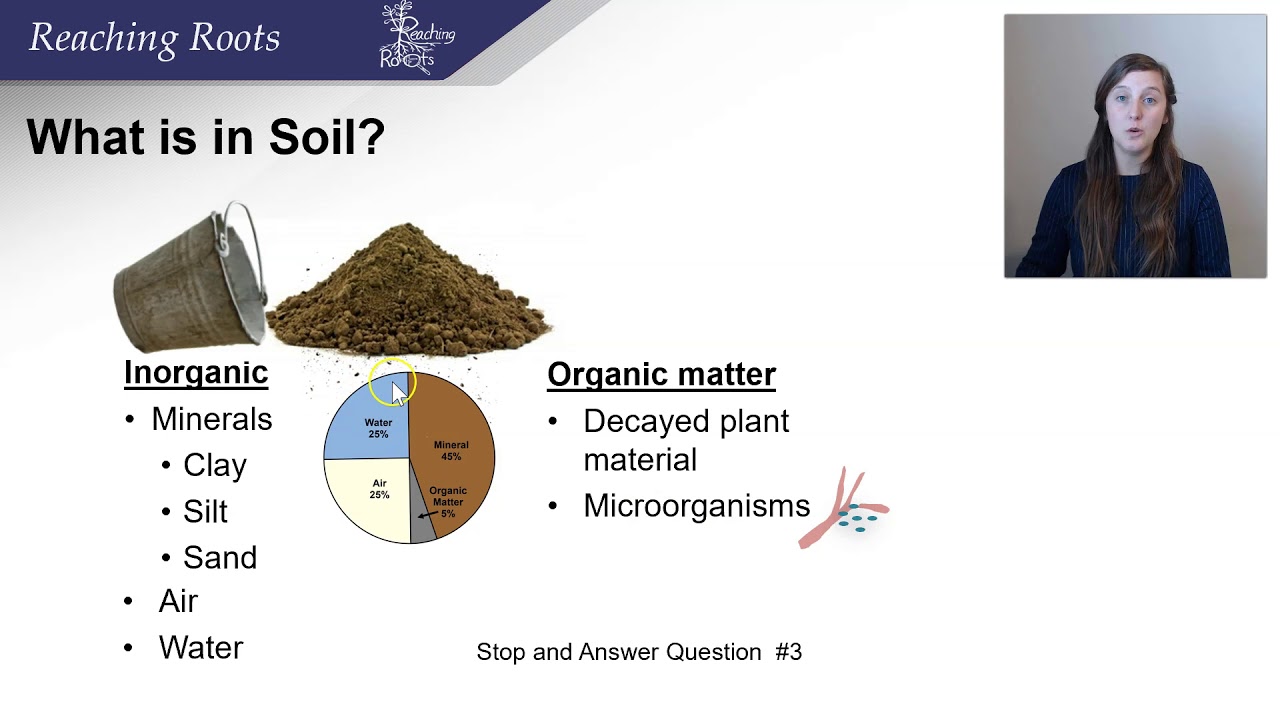
- 🔬 Soil composition consists of approximately 45% minerals, 5% organic matter, 25% water, and 25% air.
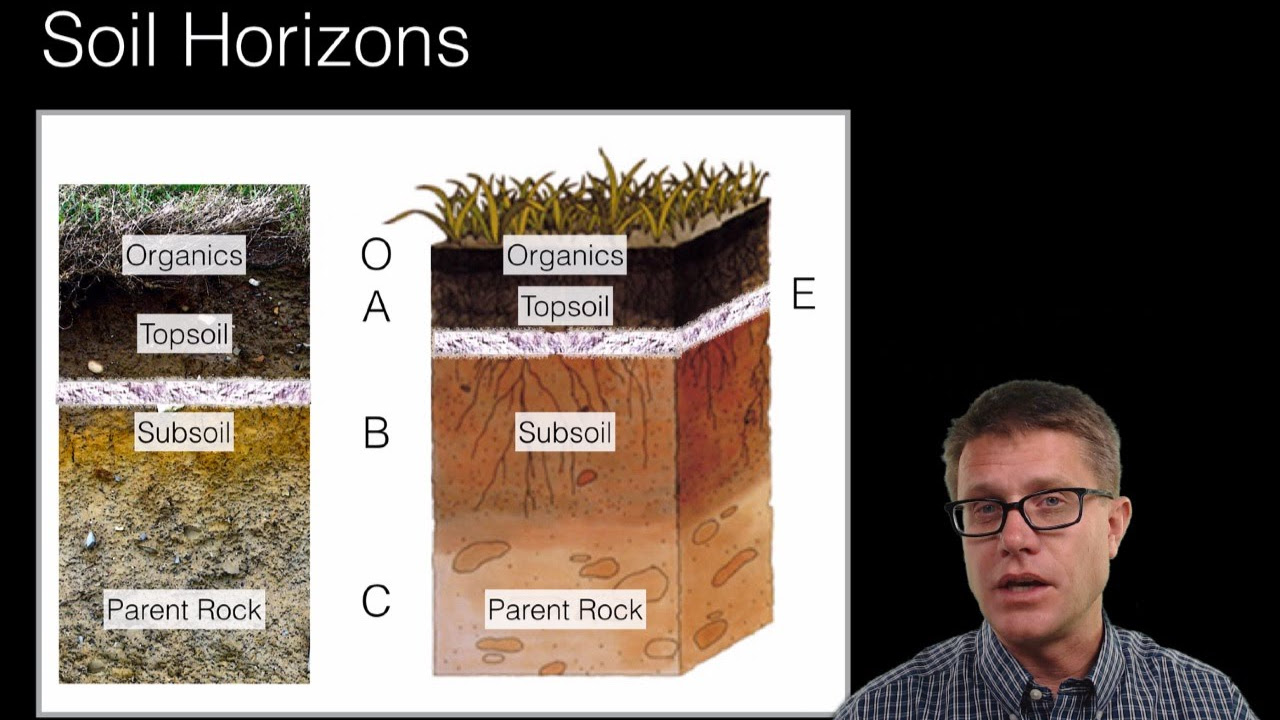
- 📏 A soil profile displays vertical layers of soil, which are referred to as soil horizons.
- 📖 The O horizon, or litter layer, contains dead organic material such as leaves and fallen trees.
- 🌍 The A horizon, or topsoil, is rich in organic matter and is where decomposers break down plants and animals.
- 💧 The E horizon, or eluviation layer, is characterized by the leaching of minerals and can result in sand and silt concentration.
- 🏗️ Horizon B, or subsoil, is often lighter in color and serves as a zone of accumulation for clay and other materials.
- 🪨 The C horizon consists of parent material, which includes rock fragments that break down to form soil.
- 🪨 Horizon R is the bedrock, comprising solid rock such as granite or limestone, forming the base material for soil.
- 📺 For more information on soil, additional educational resources are available through the playlist provided.
Q & A
What is the composition of soil?
-Soil is composed of 45% minerals, 5% organic matter, 25% water, and 25% air.
What does the soil profile represent?
-The soil profile is a vertical layer of soil that shows all the different layers, similar to a profile on social media.
What are the main layers of soil, known as horizons?
-The main layers are O, A, E, B, C, and R horizons.
What is the O horizon, and what does it contain?
-The O horizon, also called the litter layer, contains dead leaves, twigs, sticks, and fallen trees.
What is the A horizon and its significance?
-The A horizon, or topsoil, contains rich organic matter and minerals and is home to decomposers that break down plants and animals.
What happens in the E horizon?
-In the E horizon, water moves down and removes substances, leading to a concentration of sand and silt particles.
What characterizes the B horizon?
-The B horizon, or subsoil, is lighter in color, often reddish or brown, and acts as a zone of accumulation for materials like clay.
What is the composition of the C horizon?
-The C horizon consists of parent material, containing rock fragments that weather into smaller pieces.
What does the R horizon represent?
-The R horizon is the bedrock, which can be made of various types of rock, including granite, basalt, and sandstone.
How do decomposers contribute to soil health?
-Decomposers break down dead plants and animals, creating humus, a dark organic material that enriches the soil.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)