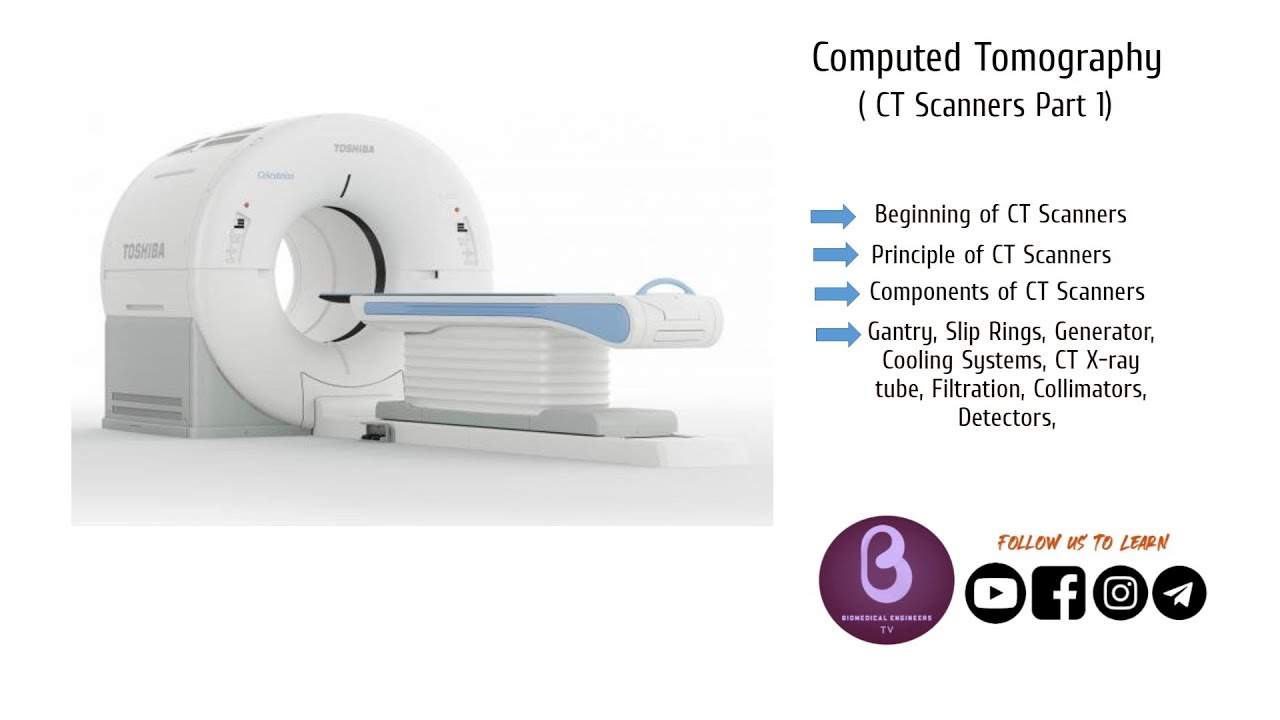
Overview of the X-Ray Tube and Components
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful introduction to x-ray tubes, essential components in various radiology modalities like radiography and computed tomography. It explains the functions of the cathode, anode, glass envelope, and tube housing, emphasizing their roles in x-ray production and safety. The cathode generates electrons through thermionic emission, while the anode absorbs these electrons to create x-rays. The video also discusses dual focus tubes, the significance of the focusing cup for spatial resolution, and the differences between stationary and rotating anodes, highlighting their heat capacity and applications in medical imaging.
Takeaways
- 😀 X-ray tubes are vital in various radiology modalities such as radiography, fluoroscopy, mammography, and computed tomography.
- 🧪 The cathode generates free electrons through thermionic emission and is negatively charged, serving as the source of these electrons.
- ⚡ The anode absorbs electrons from the cathode and produces x-rays; it is positively charged to attract the negatively charged electrons.
- 🛡️ The glass envelope creates a vacuum around the cathode and anode, preventing oxidation and ensuring optimal operation.
- 🔒 Tube housing prevents x-rays from leaking into the exam room, allowing only those directed at the patient to pass through.
- 🔄 There are two types of anodes: stationary and rotating. Rotating anodes are preferred for general radiography due to their higher heat capacity.
- 🔥 The cathode consists of tungsten filaments that create a cloud of free electrons, known as the space charge, when heated.
- 📏 Dual focus tubes feature two cathode filaments (small and large), allowing for different exposure settings and image quality.
- 🏋️ The induction motor spins the rotating anode without contact, using stators, a rotor, and bearings for smooth operation.
- 🎯 Good spatial resolution in x-ray imaging is achieved through the focusing cup, which directs the electron beam for clearer images.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the x-ray tube?
-The primary function of the x-ray tube is to generate x-rays for various radiological modalities, including radiography, fluoroscopy, mammography, and computed tomography.
What is the role of the cathode in an x-ray tube?
-The cathode is the negatively charged component that creates free electrons through thermionic emission, serving as the source of these electrons for x-ray production.
How does the anode function in the x-ray tube?
-The anode, which is positively charged, absorbs electrons emitted from the cathode and converts them into x-rays.
What is thermionic emission?
-Thermionic emission is the process by which the cathode is heated to create free electrons, forming a cloud of electrons known as the space charge.
What is the significance of the glass envelope in an x-ray tube?
-The glass envelope creates an air-free vacuum around the cathode and anode, protecting the tube from oxidation and corrosion, which is essential for maintaining its functionality.
Why is the tube housing important in x-ray tubes?
-The tube housing prevents x-rays from being emitted throughout the examination room and ensures safety by limiting leakage radiation to a maximum of 0.88 milligray per hour.
What are dual focus tubes and their advantages?
-Dual focus tubes have two cathode filaments—a small one for low mA and a large one for high mA. The small filament allows for high spatial resolution, while the large filament is suited for imaging larger body parts.
How does the focusing cup enhance x-ray image quality?
-The focusing cup, which is negatively charged, helps to concentrate the electron beam by repelling the electrons, resulting in a tightly aligned x-ray beam that improves spatial resolution.
What is the difference between stationary and rotating anodes?
-Stationary anodes have a simple design with low heat capacity, suitable for low exposures, while rotating anodes distribute heat over a larger area, allowing for higher exposures essential for general radiography.
What components make up the induction motor in a rotating anode system?
-The induction motor consists of stators (electromagnets), a rotor (attached to the anode disk), and bearings that facilitate the smooth rotation of the rotor, enabling the anode to spin without contact.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)