Polarization of light, linear and circular | Light waves | Physics | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the concept of light polarization, focusing on the behavior of electromagnetic waves, particularly the electric field. It describes how light can be polarized in various directions (vertical, horizontal, or diagonal) and how polarizers filter light based on its orientation. The script covers practical uses of polarization, such as reducing glare with sunglasses and creating 3D movie experiences. It also introduces circular polarization, where the light’s polarization rotates, and explains its advantage in 3D movies for a better viewing experience, even when tilting the head.
Takeaways
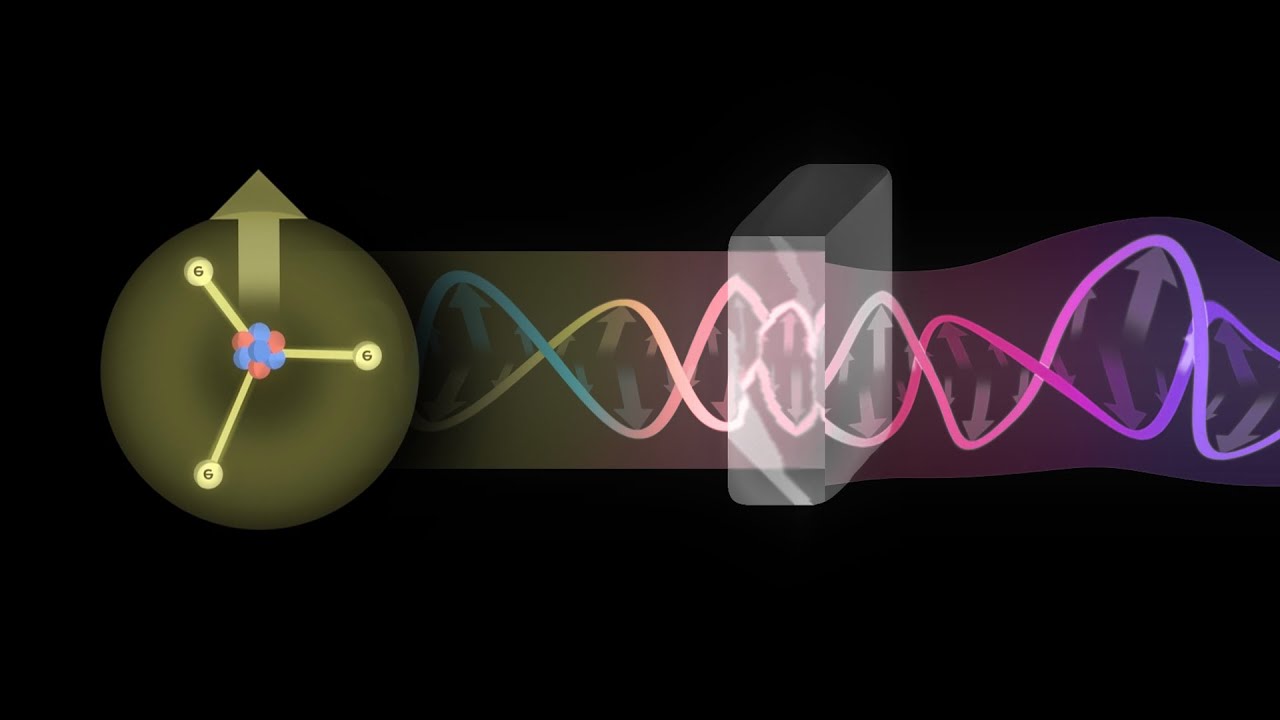
- 🔦 Light waves are electromagnetic waves composed of both electric and magnetic fields, which oscillate perpendicularly to each other.
- ⚡ Polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field in a light wave, where the electric field oscillates in a specific direction.
- 📏 Light can be polarized vertically, horizontally, or diagonally, meaning the electric field oscillates in just one direction.
- 💡 Most natural light, like sunlight or light from a bulb, is unpolarized, meaning the electric field oscillates in random directions.
- 🕶️ Polarizers are materials that allow light with a specific polarization direction to pass through while blocking other orientations.
- 🌞 Polarized sunglasses reduce glare by blocking light that reflects off surfaces like water or snow, which becomes partially polarized during reflection.
- 🎣 Fishermen use polarized sunglasses to block reflected light from water surfaces and enhance visibility under the water.
- 🎬 3D glasses often use polarized lenses to project different images to each eye, allowing the brain to perceive depth and create a 3D effect.
- 🔄 Circular polarization occurs when the electric field rotates in a circular motion as the light wave travels, instead of remaining in one linear direction.
- 🍿 Movie theaters commonly use circular polarized glasses for 3D movies, which work regardless of head tilt, providing a more comfortable viewing experience.
Q & A
What is polarization of light?
-Polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field of a light wave. Polarized light has its electric field oscillating in one direction, such as vertically, horizontally, or diagonally.
How is light typically polarized?
-Light can be polarized through a polarizer, which only allows light waves oscillating in one specific direction to pass through. This filters out light waves in other orientations.
Is sunlight polarized?
-No, sunlight is generally not polarized when it reaches the Earth. The light waves from the sun oscillate in many directions, making the light unpolarized.
What happens when light reflects off a surface like water or snow?
-When light reflects off a surface like water or snow, it becomes at least partially polarized. The reflected light often has its electric field aligned with the surface, typically resulting in horizontal polarization.
How do polarized sunglasses reduce glare?
-Polarized sunglasses use vertical polarizers to block horizontally polarized light, which is the primary component of glare reflected off horizontal surfaces like water or roads.
What is circular polarization?
-Circular polarization occurs when the orientation of the electric field rotates as the light wave moves. The electric field spirals around the direction of propagation, either in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction.
Why is circular polarization used in 3D movies?
-Circular polarization is used in 3D movies because it allows the viewer to tilt their head without losing the 3D effect. Unlike linear polarization, which can cause image distortion if the head is tilted, circular polarization ensures each eye gets the correct image regardless of head orientation.
What is the difference between linear and circular polarization?
-Linear polarization involves the electric field oscillating in a single, fixed direction, like vertical or horizontal. Circular polarization involves the electric field rotating around the direction of travel, creating a spiral pattern.
How does a polarizer work?
-A polarizer works by filtering light so that only waves oscillating in one particular direction are allowed to pass through. It blocks all other orientations of light waves, thereby creating polarized light.
What would happen if you look at a 3D movie without polarized glasses?
-Without polarized glasses, both eyes would receive both images meant for each eye, causing a blurry and distorted view of the 3D movie.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum | Physics | Khan Academy

Part_1(Boundary Conditions_1)

Electromagnetic Waves Problem Solutions

Radiasi Gelombang Elektromagnetik • Part 1: Definisi dan Sifat Gelombang Elektromagnetik

ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES In 20 Minutes || Complete Chapter For JEE Main/Advanced
The origin of Electromagnetic waves, and why they behave as they do
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
