What causes INFLAMMATION? Top ANTI-INFLAMMATORY FOODS
Summary
TLDRThis video by Nirupama explains inflammation, distinguishing between acute and chronic forms. Acute inflammation is the body's natural, short-term response to injury or infection, while chronic inflammation can persist for months or years and lead to health issues. Chronic inflammation is linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor diet, smoking, and stress. The video highlights anti-inflammatory strategies, including a nutritious diet (with turmeric, omega-3s, and green leafy vegetables), exercise, and reducing alcohol and smoking. It also discusses foods to avoid, like processed foods and trans fats, to reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Inflammation occurs when the immune system releases white blood cells and inflammatory substances in response to invaders or injury.
- 🛡️ Acute inflammation is short-lived and helps the body heal from infections or injuries, showing symptoms like pain, redness, and swelling.
- ⚠️ Chronic inflammation, unlike acute inflammation, is long-lasting and can persist without external threats, leading to potential health problems.
- 🏥 Chronic inflammation is linked to conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, Alzheimer's, asthma, obesity, and type 2 diabetes.
- 🍔 Unhealthy lifestyle factors like obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, poor diet, and stress can trigger chronic inflammation.
- 📋 Common symptoms of chronic inflammation include joint pain, fatigue, digestive issues, mental health disorders, and sudden weight gain.
- 🔬 Chronic inflammation can be detected by measuring markers like C-reactive protein and fibrinogen, though there’s no perfect test for it.
- 🍵 Anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric (curcumin), green tea (EGCG), omega-3 fatty acids, walnuts, and green leafy vegetables can help reduce inflammation.
- 🚫 Foods to avoid include processed foods, trans fats, refined carbohydrates, and products with excessive sugar or hydrogenated oils.
- 🏃 Regular physical exercise, reduced alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and managing stress are effective ways to naturally reduce inflammation.
Q & A
What is inflammation, and why does it occur?
-Inflammation is the body's immune response to harmful stimuli, such as bacteria, viruses, toxins, or injury. It occurs when the immune system releases white blood cells and other inflammatory substances into the blood to trap invaders or heal injured tissue.
What are the two types of inflammation?
-The two types of inflammation are acute and chronic inflammation. Acute inflammation is short-lived and helps the body heal from infections or injuries, while chronic inflammation is long-lasting and can occur without an external threat, potentially leading to health problems.
Is inflammation good or bad for the body?
-Acute inflammation is generally good for the body as it aids in healing and protecting against infections or injuries. Chronic inflammation, however, can be harmful, as it persists over time and can lead to various health issues.
What are the signs and symptoms of acute inflammation?
-Signs of acute inflammation include pain, redness, tenderness, and swelling at the site of infection or injury. These symptoms are typically short-lived, lasting from a few hours to a few days.
What are the signs and symptoms of chronic inflammation?
-Chronic inflammation symptoms can be vague and may include abdominal pain, joint pain, fatigue, fever, insulin resistance, gastrointestinal issues, stiffness in the lower back, and mental health issues such as stress or anxiety.
What lifestyle factors contribute to chronic inflammation?
-Several lifestyle factors contribute to chronic inflammation, including obesity, excess visceral fat, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, high stress, diets rich in saturated and trans fats, processed foods, and irregular sleep patterns.
How is chronic inflammation detected?
-There is no perfect test for chronic inflammation, but doctors often use blood tests to measure markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and fibrinogen, especially when inflammation is linked to another medical condition.
What foods have anti-inflammatory properties?
-Anti-inflammatory foods include turmeric (containing curcumin), green tea (containing EGCG), green leafy vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish, walnuts, flax seeds, green moong beans, and sesame seeds.
What foods should be avoided to prevent or reduce inflammation?
-Processed foods, refined carbohydrates, excess sugar, and trans fats should be avoided. Examples of trans fats include hydrogenated oils found in products like vanaspati, cakes, cookies, chips, and popcorn.
What other anti-inflammatory measures can be taken aside from diet?
-Aside from diet, engaging in regular physical exercise, reducing alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and managing stress are effective strategies to reduce inflammation and its associated risks.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

INFLAMASI PADA AUTOIMUN - dr. Sarah Akbari, MARS, ABAARM, FAARM, FINEM
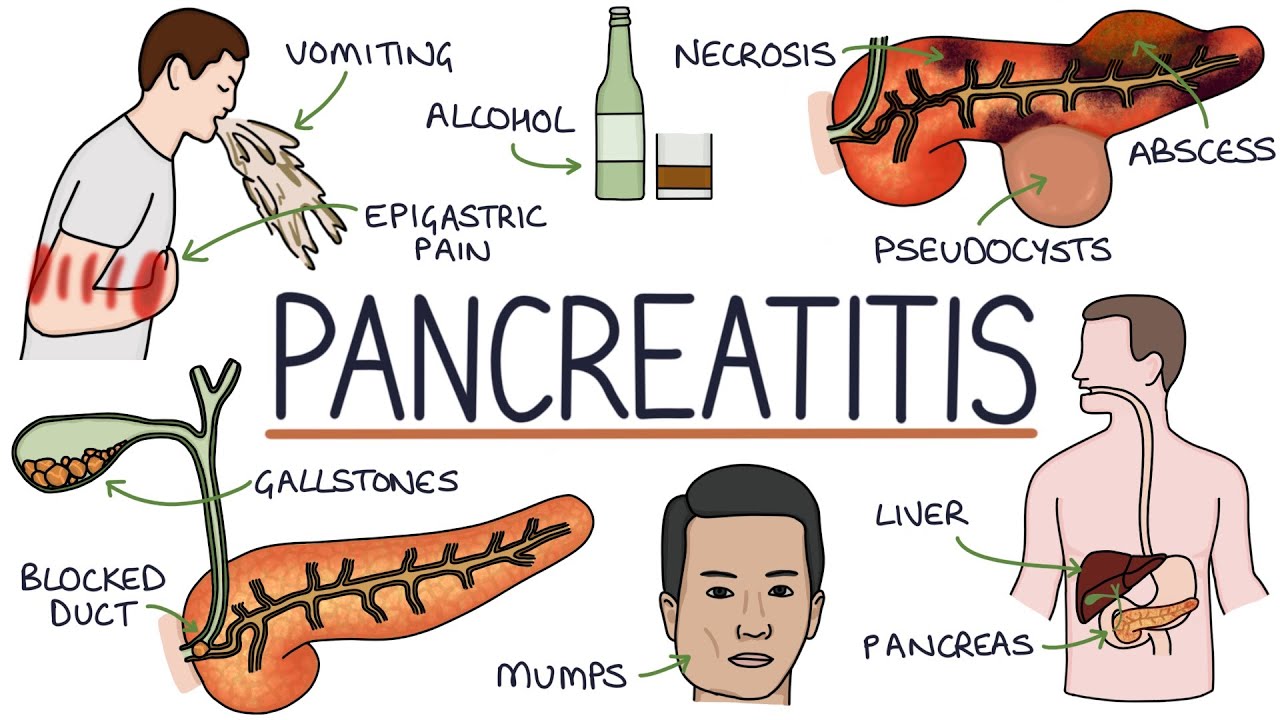
Understanding Pancreatitis
Radang (Inflamasi) Akut, Kronis, Granuloma | Patologi Anatomi 101

Gastritis | Pathology of gastritis | treatment of gastritis | USMLE step 1

Video Edukasi Pencegahan Gagal Ginjal Kronik

Inflamação Aguda - Aula completa - Patologia Geral
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
