Understanding the OSI Model - CompTIA Network+ N10-009 - 1.1
Summary
TLDRThe video introduces the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, a conceptual framework for understanding how data travels across networks. It outlines the seven OSI layers, from the physical layer (Layer 1) to the application layer (Layer 7), explaining their roles in network communication. Each layer has specific functions, such as data transmission, routing, and application interaction. The video also emphasizes the importance of the OSI model for IT professionals to communicate effectively and troubleshoot network issues by referencing specific layers.
Takeaways
- 📚 The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework used to describe how data moves through a network, not a protocol suite itself.
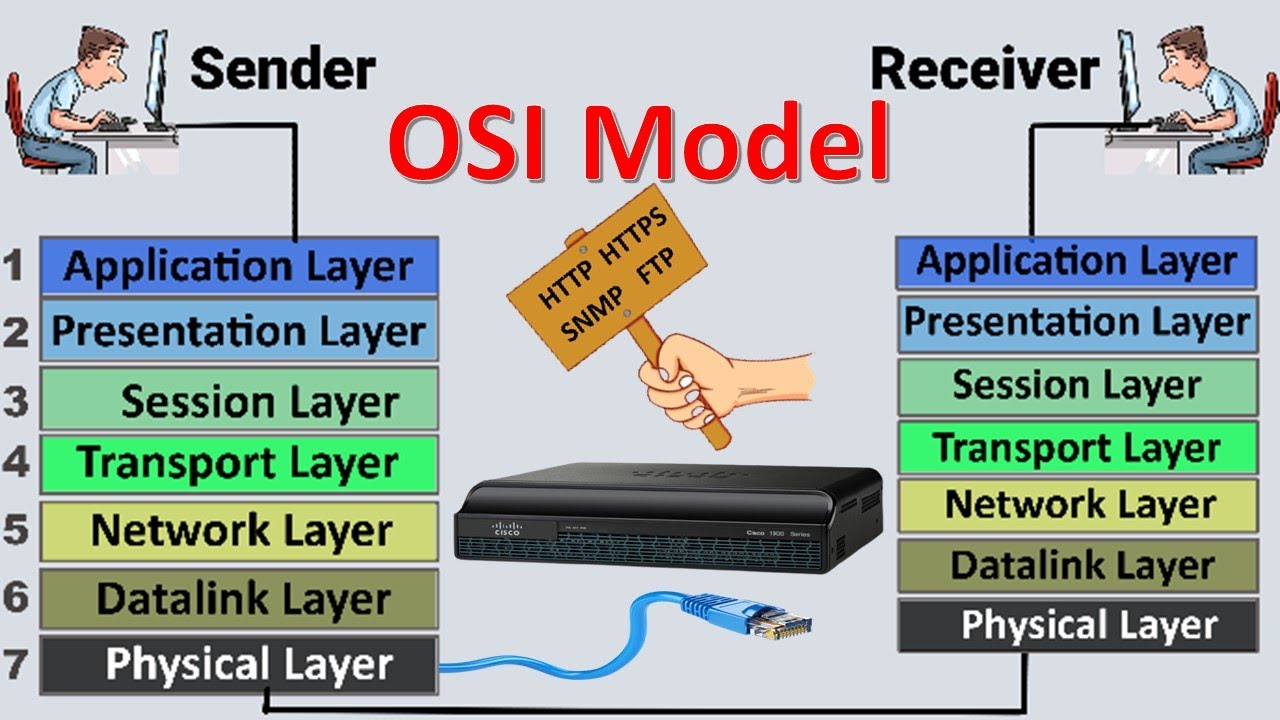
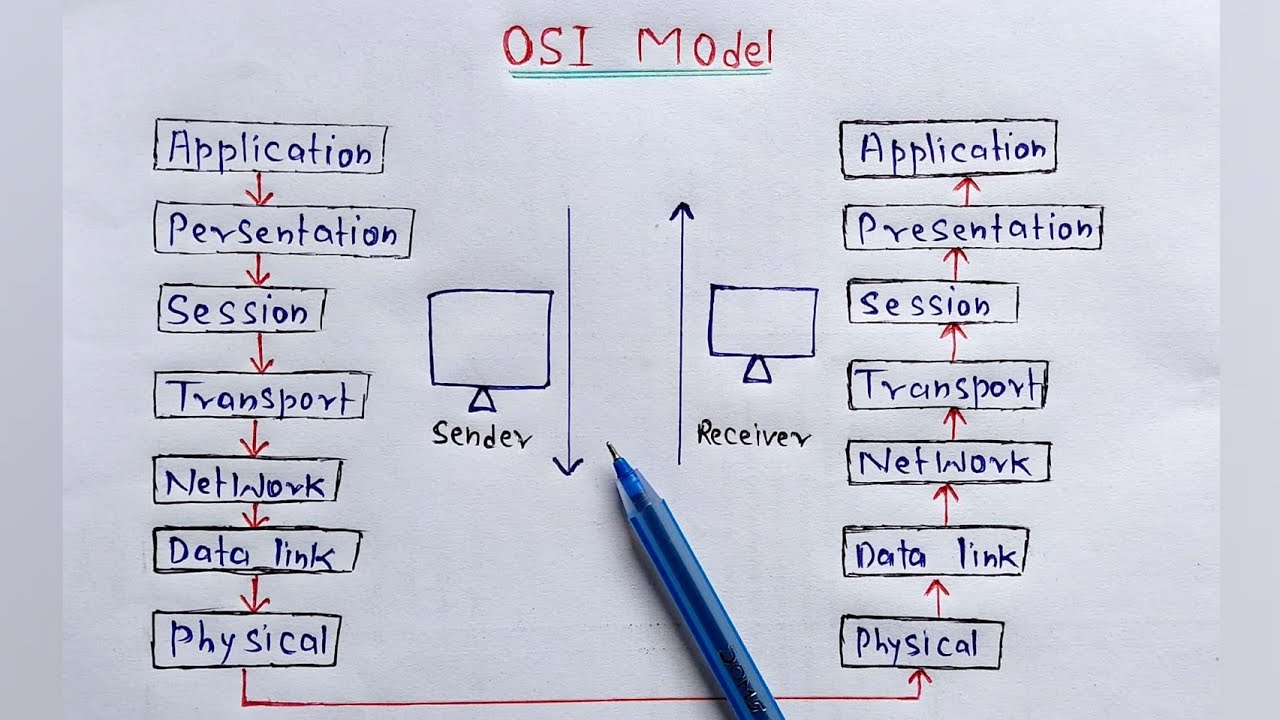
- 🌐 The OSI model has seven layers: Application (7), Presentation (6), Session (5), Transport (4), Network (3), Data Link (2), and Physical (1).
- 🔄 The OSI model helps IT professionals communicate effectively, as it provides a common language for understanding data transmission across networks.
- 🔌 OSI Layer 1 (Physical) deals with the physical transmission of signals, such as cables, fibers, or wireless connections.
- 🖧 OSI Layer 2 (Data Link) is often referred to as the MAC address layer and is responsible for communication between devices on a network, like switches.
- 📡 OSI Layer 3 (Network) handles routing and forwarding traffic using IP addresses. It's where routers operate and data fragmentation occurs.
- 📦 OSI Layer 4 (Transport) deals with transporting data between devices, using protocols like TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
- 🔗 OSI Layer 5 (Session) manages communication sessions between devices, including starting, stopping, or tunneling sessions.
- 🔐 OSI Layer 6 (Presentation) handles data formatting, encryption, and decryption, ensuring information is readable and secure.
- 💻 OSI Layer 7 (Application) is the top layer where users interact with applications, such as HTTP, DNS, and other network-based services.
Q & A
What is the OSI model and what is its purpose?
-The OSI model, or Open Systems Interconnection Reference model, is a conceptual framework used to describe the process data takes as it traverses networks. It provides a broad overview of how data moves through systems but is not a protocol suite itself.
How does the OSI model relate to the TCP/IP protocol suite?
-The OSI model can be applied to many different protocols, including TCP/IP. While most protocols used today are based on TCP/IP, the OSI model is useful for describing how various protocols operate within a network.
What is the significance of understanding the OSI model in IT communications?
-Understanding the OSI model allows IT professionals to communicate clearly about network operations. Terms like 'OSI Layer 7' or 'OSI Layer 4' are universally understood in the industry, regardless of the specific organization.
What is the role of Layer 1 in the OSI model?
-Layer 1, or the physical layer, deals with the physical transmission of signals over network cables, fibers, or wireless connections. Issues at this layer often involve problems with cables, fibers, or wireless interference.
What is the function of Layer 2, the data link layer?
-Layer 2, the data link layer, facilitates communication between two devices on a network. It is associated with MAC addresses, which are physical addresses on network adapters. This layer is often referred to as the 'switching layer' due to the role switches play in forwarding traffic based on MAC addresses.
How does Layer 3, the network layer, function?
-Layer 3, the network layer, is responsible for routing and IP addressing. Routers use this layer to forward traffic based on destination IP addresses, and this is also where fragmentation of data packets occurs to fit different network frames.
What are the key responsibilities of Layer 4, the transport layer?
-Layer 4, the transport layer, is responsible for ensuring the reliable transmission of data across the network. Common protocols at this layer include TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol), which manage the segmentation and reassembly of data.
What happens at Layer 5, the session layer?
-Layer 5, the session layer, manages communication sessions between devices. It is responsible for establishing, maintaining, and terminating connections or sessions between devices.
What is the role of Layer 6, the presentation layer?
-Layer 6, the presentation layer, ensures that data is presented in a usable format. This layer handles tasks such as character encoding and encryption/decryption, making data readable for applications.
What protocols operate at Layer 7, the application layer?
-Layer 7, the application layer, is where users interact with applications. Common protocols operating at this layer include HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, FTP, and POP3. This is the layer where network applications like web browsers and email clients operate.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Animasi Alur Kerja OSI Layer
OSI Model | OSI Model Explained | OSI Animation | OSI Model in easiest Way | OSI 7 Layers

OSI Model animated, What is osi model in networking? 7 OSI layers explained

Understanding the OSI Model - CompTIA Network+ N10-007 - 1.2
What is OSI Model? full Explanation | Networking

Model Jaringan Komputer - Jaringan Komputer dan Internet | Informatika XI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
