Expt 2. Flexural Strength Test of Concrete Beam
Summary
TLDRThis video demonstrates the flexural strength test of concrete according to IS 516 standards. The test assesses the concrete's ability to resist failure under bending, using a plain concrete beam subjected to two-point loading. It outlines the steps from preparing the concrete mix, curing the specimen, to testing the beam by applying a gradual load. The video explains the two types of beam failures, Type A and Type B, and how the modulus of rupture is calculated based on these failure types. The final flexural strength is expressed as the modulus of rupture.
Takeaways
- 🧪 The flexural strength test evaluates the bending strength of concrete indirectly.
- 🔨 It assesses the ability of an unreinforced concrete beam or slab to resist failure in bending.
- 📏 The test can be conducted using either a third-point load test or a two-point load test.
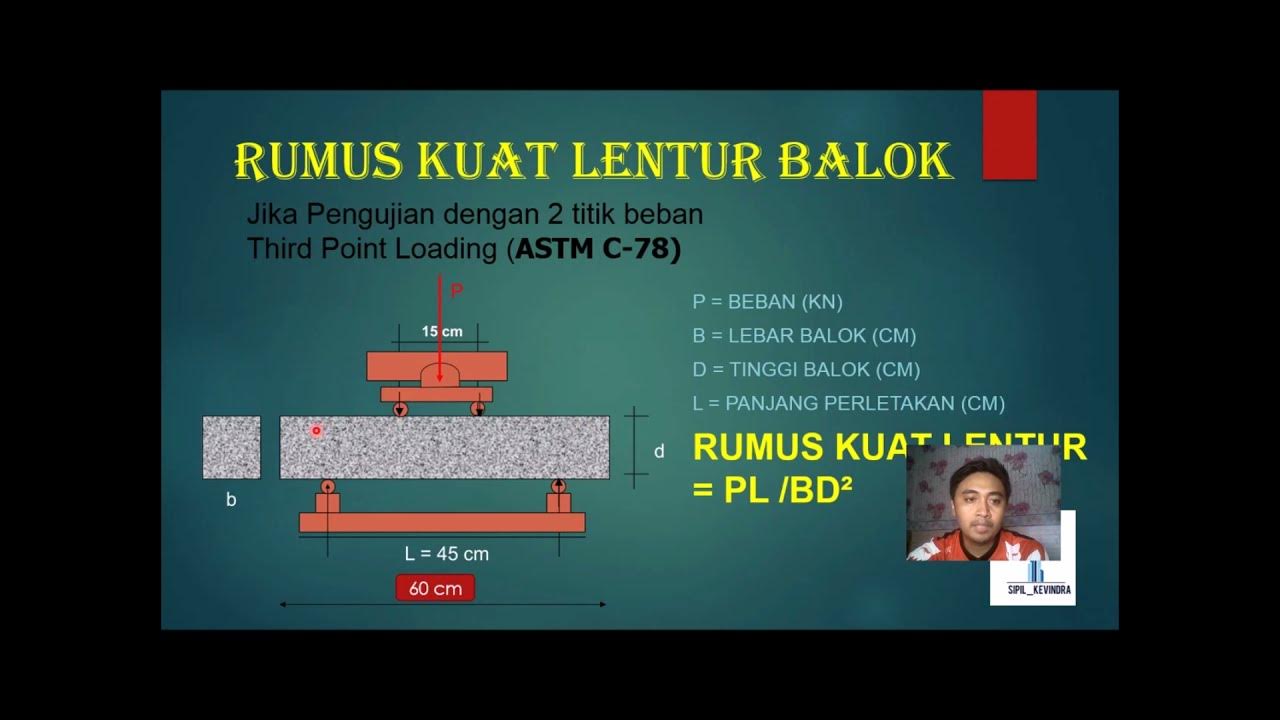
- 🧱 The concrete specimen size for testing is standardized: 150mm width, 150mm depth, and a span of 700mm, or 100mm width, 100mm depth, and a span of 500mm.
- 🔧 For sample preparation, mix cement, sand, aggregate, fly ash, and water by hand or with a mixing machine.
- 🛠️ The fresh concrete is poured into molds, compacted in three layers, and cured at 27°C for 24 hours.
- 🕒 After curing, the specimen is moist-cured at the same temperature until the testing time.
- 📊 During the test, the specimen is placed correctly, and the load is applied continuously at a constant rate until the beam fractures.
- ⚠️ Two types of failure are noted: Type A failure (fracture in the middle third of the span) and Type B failure (fracture outside the middle third but within 5% of the span).
- 🧮 The modulus of rupture is calculated using different formulas depending on the failure type, as per IS 516 standards.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the flexural strength test on concrete?
-The flexural strength test evaluates the tensile strength of concrete indirectly by testing the ability of an unreinforced concrete beam or slab to withstand failure in bending.
Which two methods can be used to conduct a flexural strength test on concrete?
-The flexural test on concrete can be conducted using either the third-point load test or the two-point load test.
What are the dimensions of the concrete specimen used in this test according to Indian Standard IS 516?
-According to IS 516, the dimensions of the concrete specimen are either 150 mm width, 150 mm depth, and 700 mm span, or 100 mm width, 100 mm depth, and 500 mm span. In this test, a 100 mm x 100 mm x 500 mm plain concrete beam is used.
What materials are used to prepare the concrete mix for the test?
-The materials used for the concrete mix include cement, sand, aggregate, fly ash, and water.
What steps should be followed after preparing the concrete mix before testing?
-Once the concrete mix is prepared, it should be poured into lubricated molds in three layers, each layer compacted on a vibrating table. After compaction, the molds should be left undisturbed for 24 hours at 27°C, followed by moist curing of the specimen at the same temperature until testing.
How is the specimen positioned in the machine for testing?
-The test specimen should be placed in the machine correctly, centered with the longitudinal axis of the specimen at a right angle to the longitudinal axis of the upper and lower rollers.
What is the rate of loading applied during the flexural test?
-The load should be applied without shock and increased continuously at a constant rate. For a smaller beam, the rate is 30 Newtons per minute, and for a larger beam, it is 67 Newtons per minute.
What are the types of failure observed in flexural strength testing?
-The two types of failure are: Type A, where the fracture initiates in the tension surface within the middle third of the span between the loading points, and Type B, where the fracture initiates in the tension surface outside the middle third of the span but within 5% of the span length.
How is the modulus of rupture calculated in case of Type A and Type B failure?
-In Type A failure, the modulus of rupture (fcr) is calculated using the formula: fcr = PL / BD², where P is the failure load, L is the span length, B is the width, and D is the depth. In Type B failure, the formula accounts for the distance from the fracture line to the nearest support.
What should be done if the fracture occurs outside the acceptable range?
-If the fracture initiates outside the middle third of the span length by more than 5% of the span length (unsatisfactory failure), the test results should be discarded.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
PENGUJIAN TES KUAT LENTUR BETON

CIVE1265 Concrete lab Part 2

Pemeriksaan Kuat Lentur Kayu

LAB IN YOUR GRASP - KARAKTERISASI MATERIAL BETON : 17 PENGUJIAN KUAT TEKAN BETON

KEREN BANGET NIH !!!!! TUTORIAL PEMBUATAN BETON , PROGRAM STUDI TENIK SIPIL UNIVERSITAS KADIRI 😊🤩

Example-Timber Design-Flexural Member
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
