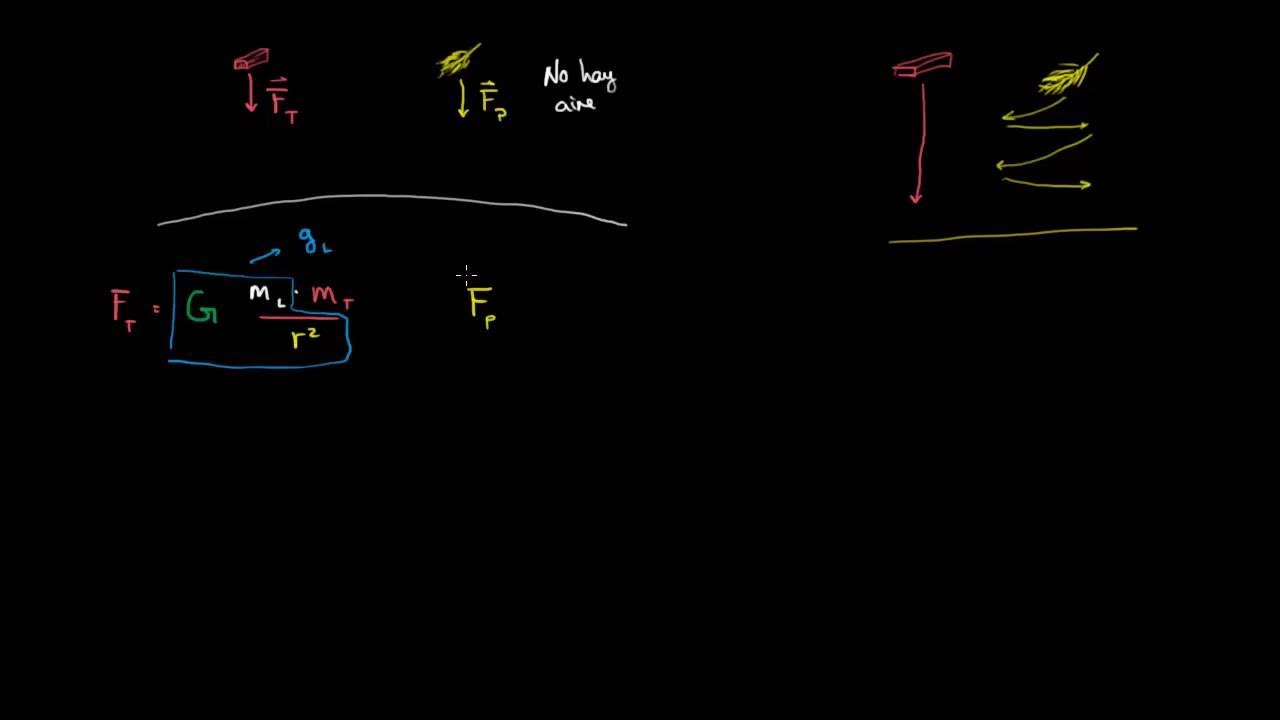
What is Air Resistance?
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, Kaeleigh introduces the concept of air resistance and how it interacts with gravity. The story of Galileo's famous experiment from the Leaning Tower of Pisa demonstrates how gravity affects objects of different masses equally. Students then conduct a hands-on experiment using envelopes to explore the effects of air resistance. The video explains that while gravity pulls objects equally, air resistance (or drag) slows lighter objects more. The lesson concludes with examples of how air resistance is useful, such as in parachutes, and encourages students to experiment with parachute designs.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Galileo proved that objects of different masses fall at the same rate due to gravity, as demonstrated by dropping a cannonball and a musket ball from the Leaning Tower of Pisa.
- 🏛️ The Leaning Tower of Pisa is famous, and Galileo used it for experiments on gravity.
- 📏 Gravity affects all objects equally, regardless of mass, meaning they fall at the same speed when dropped from the same height.
- ✉️ The experiment with envelopes shows that two objects of different masses (one filled and one empty) fall at the same rate when air resistance is minimized.
- 🌬️ Air resistance (drag) opposes the motion of objects and affects how fast they fall, particularly when their shapes are different.
- 🪶 In the case of a feather and a rock, the feather takes longer to fall because it experiences more air resistance, even though gravity affects them the same.
- 🌕 On the moon, where there's no air resistance, objects like a feather and a rock fall at the same speed and hit the ground at the same time.
- 🪂 Parachutes are an example of how air resistance can be useful, slowing down the fall of a person by increasing drag.
- 🖐️ Surface area plays a key role in air resistance—the larger the surface area, the more drag an object experiences, slowing it down.
- 🚗 Speed also affects air resistance: the faster an object moves, the more air resistance it encounters.
Q & A
What did Galileo's experiment at the Leaning Tower of Pisa demonstrate?
-Galileo's experiment showed that gravity affects objects the same way regardless of their mass. He dropped objects with different masses, like a cannonball and a musket ball, and found that they hit the ground at the same time.
Why did Galileo's results surprise people?
-People expected heavier objects to fall faster than lighter ones, but Galileo's experiment showed that, in the absence of air resistance, objects of different masses fall at the same rate.
What is air resistance, and how does it affect falling objects?
-Air resistance, also known as drag, opposes the motion of objects and slows them down as they fall. It affects how quickly objects with different shapes and surface areas reach the ground.
Why does a feather fall more slowly than a rock on Earth?
-On Earth, the feather experiences more air resistance due to its shape and larger surface area, which causes it to fall more slowly than a rock. However, without air resistance, like on the Moon, they would fall at the same rate.
What role does air resistance play in the design of parachutes?
-Parachutes are designed to increase air resistance (drag), which slows down a person's fall, making it safer. Larger parachutes create more air resistance, which reduces the speed of descent.
How does surface area influence air resistance?
-Objects with larger surface areas experience more air resistance because more air pushes against them as they move. This increases drag and slows the object down.
How does the speed of an object affect air resistance?
-The faster an object moves, the more air resistance it encounters. For example, sticking your hand out of a moving car feels different at high speeds than at low speeds due to increased drag.
What did the crumpled envelope experiment teach about air resistance?
-The crumpled envelope experiment showed that the shape and surface area of an object affect how it falls. The crumpled envelope fell faster because it had less surface area and therefore less air resistance compared to the flat envelope.
Why would a rock and feather fall at the same rate on the Moon?
-On the Moon, there is no air, so there is no air resistance (drag). Without air resistance, gravity affects all objects equally, causing them to fall at the same rate, regardless of their mass or shape.
How can you increase the air resistance of an object?
-You can increase air resistance by increasing the object's surface area or by increasing the speed at which the object is moving.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)