Sistem Gerak | Rangka Manusia | Biologi Kelas XI
Summary
TLDRThis lesson focuses on the human skeletal system, explaining how bones and muscles work together to allow movement. It details the structure and function of bones, emphasizing their role in support, protection of organs, and production of blood cells. The human skeleton is divided into two parts: the axial skeleton (which includes the skull, spine, and ribcage) and the appendicular skeleton (responsible for limb movement). The lesson highlights the scientific names of key bones and offers a fun song to help students remember them.
Takeaways
- 🦴 Human movement relies on bones and muscles, with bones acting as passive movers.
- 🔢 The adult human skeleton consists of 206 bones, each varying in size and shape.
- 🛡️ Bones protect soft organs like the brain, lungs, and heart.
- 💪 Bones provide attachment points for skeletal muscles to allow movement.
- 🩸 The skeleton is a site for blood cell production (red, white blood cells, and platelets) and stores minerals and fat.
- 🏗️ The human skeleton is divided into two parts: axial skeleton (80 bones) and appendicular skeleton (126 bones).
- 💀 The axial skeleton includes the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum, providing structure and protection for vital organs.
- 🧠 The skull is made up of cranial bones and facial bones, including the frontal, parietal, and occipital bones.
- 📊 The appendicular skeleton includes the limbs, shoulder girdle, and pelvis, crucial for movement and support.
- 🦿 The lower limb bones like the femur, tibia, and fibula are essential for standing and walking.
Q & A
What allows the human body to stand upright?
-The human body can stand upright because the skeleton supports it. The bones provide a structure that is moved by muscles, allowing standing and movement.
What is the main function of bones in the human body?
-Bones serve multiple functions: they provide shape and posture to the body, protect soft organs, serve as muscle attachment points, aid in blood cell production, store minerals and fat, and contribute to the immune system.
How many bones are in an adult human skeleton?
-An adult human skeleton consists of 206 bones of various shapes and sizes.
What are the two main divisions of the human skeleton?
-The human skeleton is divided into the axial skeleton (consisting of 80 bones) and the appendicular skeleton (consisting of 126 bones).
What bones are part of the axial skeleton?
-The axial skeleton includes the skull, inner ear bones, hyoid bone, vertebral column (spine), rib cage, and sternum (breastbone).
What bones make up the skull?
-The skull consists of cranial bones (such as the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal bones) and facial bones (such as the maxilla, zygomatic, nasal, and mandible).
What are the three types of ribs in the human body?
-The human body has three types of ribs: true ribs (7 pairs), false ribs (3 pairs), and floating ribs (2 pairs).
What is the function of the hyoid bone?
-The hyoid bone, located between the larynx and the mandible, serves as an attachment point for muscles of the mouth and tongue, aiding in swallowing.
What bones are part of the appendicular skeleton?
-The appendicular skeleton includes bones of the pectoral girdle (scapula and clavicle), upper limbs (humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges), pelvic girdle (ilium, pubis, and ischium), and lower limbs (femur, tibia, fibula, patella, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges).
What is the difference between the radius and ulna bones?
-The radius is the bone in the forearm that is aligned with the thumb, while the ulna is aligned with the little finger.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Sistem Gerak Bagian 1_ SISTEM RANGKA MANUSIA

Rangkuman IPAS KELAS 6 BAB 1: Bagaimana Tubuh Kita Bergerak?. Topik A: Rangka, sendi, dan otot

"How the Human Musculoskeletal System Works | Bones, Muscles & Movement Explained"

PATHFIT 1: Movement Capacity Training- Module 4: Lesson1: The Skeletal System

Sistem Gerak Bagian 2_ SISTEM OTOT MANUSIA
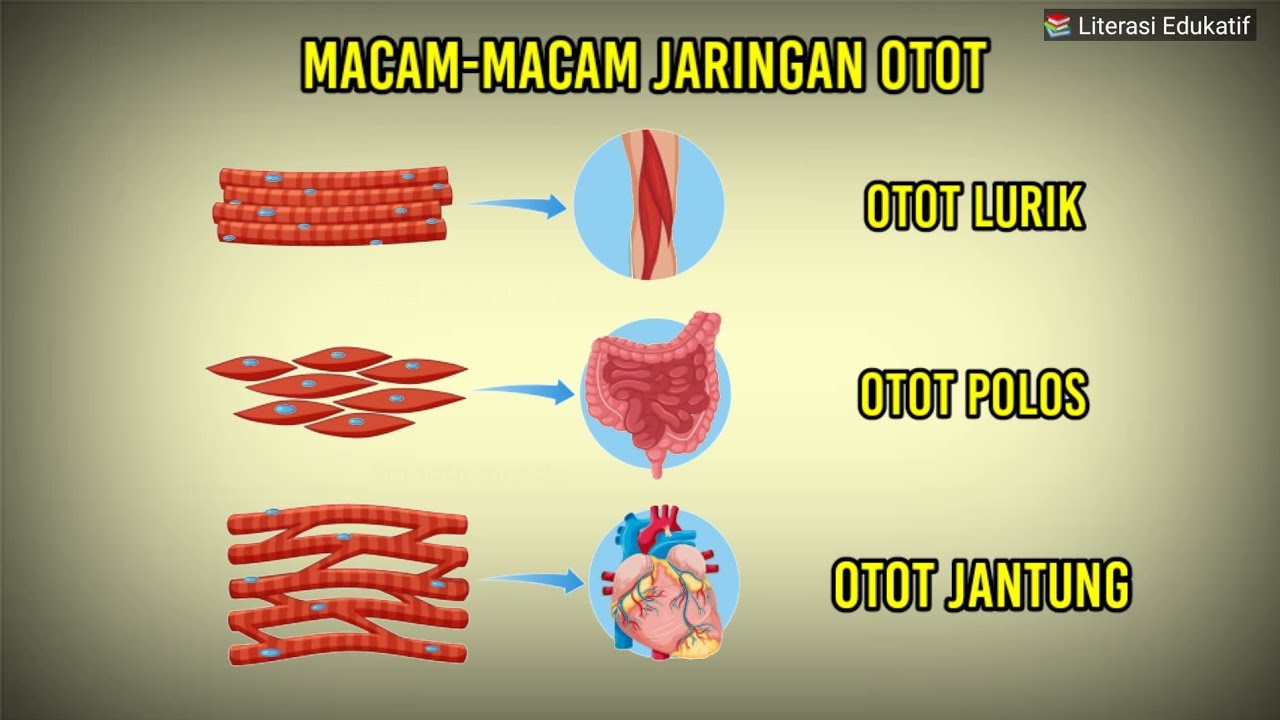
APA BEDANYA OTOT LURIK OTOT POLOS DAN OTOT JANTUNG?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
