Maslow In Ten Minutes
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses Abraham Maslow's ideas, particularly his hierarchy of needs, which explains human motivation from basic physical needs to self-actualization. Maslow divides self-actualization into two types: Theory Z (with peak experiences) and Theory Y (without). He also distinguishes between deficiency motivations (D-motivations) and being motivations (B-motivations). The 'Jonah Complex' explains why people fear fulfilling their potential. Maslow connects self-actualization with creativity, social engagement, and education, stressing the importance of seeing life as sacred to achieve fulfillment. Ultimately, Maslow’s view is open-ended, emphasizing continuous growth and self-transformation.
Takeaways
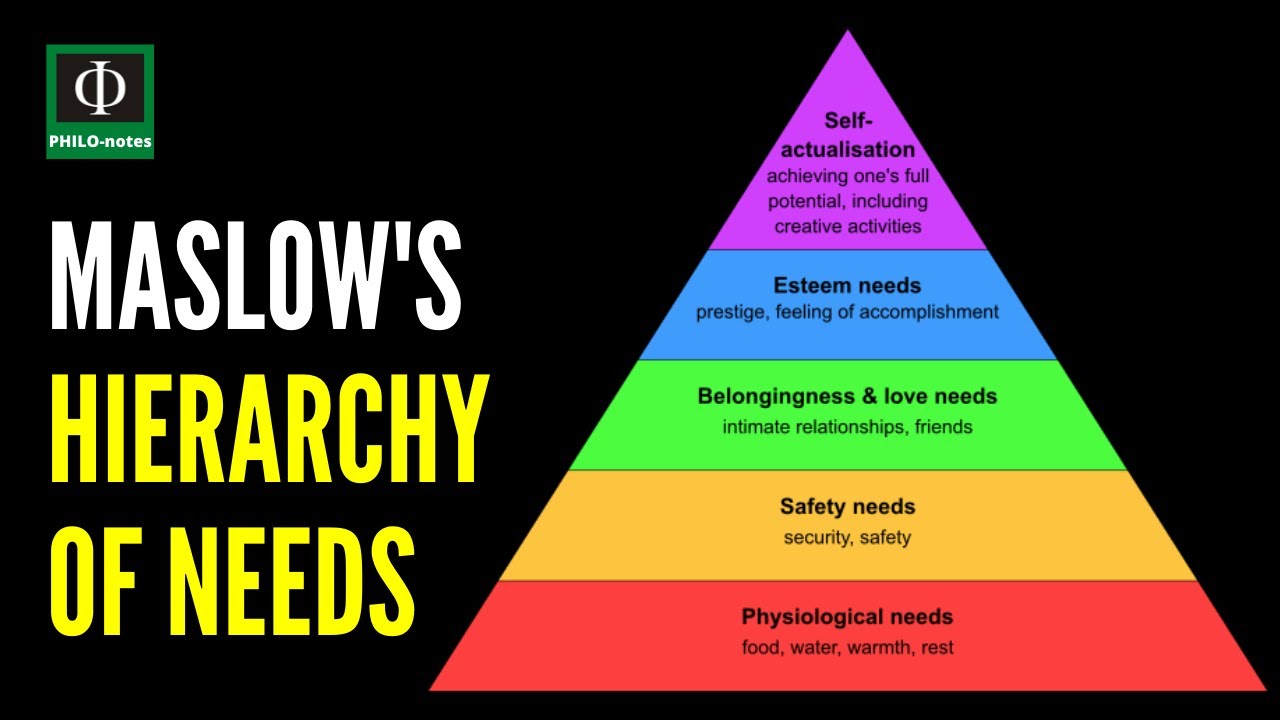
- 📚 Maslow's hierarchy of needs starts with basic physical needs like food and safety, then moves up to psychological needs such as belonging and esteem, and finally reaches self-actualization.
- 🔺 Self-actualization represents the fulfillment of one’s deepest potential, divided into Theory Z (which includes peak and plateau experiences) and Theory Y (without such experiences).
- 🌟 Peak experiences are intense, often spiritual moments of unity with the cosmos, while plateau experiences are calmer and more enduring.
- 🧠 Maslow introduced the concepts of 'deficiency motivation' (D-motivation) and 'being motivation' (B-motivation), where the former is driven by lack and the latter by the desire to fulfill potential.
- 🔄 The Jonah complex explains why people often avoid fulfilling their potential due to fear of responsibility, fear of social consequences, or fear of personal transformation.
- 🙌 Maslow emphasized that self-actualization is not selfish, as those who achieve it are deeply engaged in causes beyond themselves.
- 🎨 Creativity is a vital pathway to self-actualization, divided into 'primary creativeness' (inspiration) and 'secondary creativeness' (refinement).
- 🎭 Maslow critiqued modern society for becoming desacralized, losing its sense of sacredness and thus reducing opportunities for self-actualization.
- 🌀 Self-actualization is an ongoing process; as people achieve their potential, their potential itself evolves, meaning there is no final destination.
- 🏆 Ultimately, Maslow’s ideas encourage recognizing human potential and striving toward self-fulfillment, blending psychological understanding with social critique.
Q & A
What is Maslow's most famous idea?
-Maslow's most famous idea is his hierarchy of needs, which outlines how human beings are motivated to satisfy their basic physical, psychological, and self-actualization needs.
How is Maslow's hierarchy of needs typically represented?
-Maslow's hierarchy of needs is almost always presented in the form of a triangular pyramid.
What are the basic categories of needs in Maslow's hierarchy?
-The basic categories are physical needs (like food, shelter, and safety), psychological needs (such as belonging and esteem), and self-actualization needs.
What is the difference between Theory Z and Theory Y in Maslow's framework?
-Theory Z includes self-actualization experiences that involve peak or plateau experiences, while Theory Y focuses on self-actualization without such experiences.
What is a peak experience according to Maslow?
-A peak experience is a brief, intense, often spiritual experience of ecstasy, unity with life, or oneness with the cosmos.
What does Maslow call motivations driven by deficiencies in life?
-Maslow refers to these motivations as deficiency motivation or 'D motivation'.
What is 'B motivation' in Maslow's theory?
-'B motivation' refers to motivations that are driven by the desire to fulfill the deepest possibilities of one's being, aligned with self-actualization.
What is the Jonah complex in Maslow's theory?
-The Jonah complex refers to the fear of fulfilling one's deepest potential, leading individuals to turn away from self-actualization due to fear of responsibility, social consequences, or existential change.
How does Maslow describe the self in self-actualization?
-Maslow describes the self of self-actualization as a kind of selflessness, where the usual egoistic sense of self disappears, allowing individuals to be fully immersed in the moment.
What role does creativity play in Maslow's view of self-actualization?
-Creativity is a primary way to move toward self-actualization, often involving peak experiences. Maslow divides creativity into two phases: primary creativeness (inspiration) and secondary creativeness (refinement of the inspiration).
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)