Medulla Oblongata Anatomy
Summary
TLDRThe medulla oblongata, a crucial part of the brainstem, connects the spinal cord and controls vital functions like heart rate and breathing. It houses nuclei for cranial nerves 9-12, and its anatomy includes the anterior and posterior surfaces with distinct sulci and nuclei. The medulla's internal structure comprises levels of pyramid decussation, medial lemniscus, and olives, with tracts for motor and sensory functions. Understanding its complex vasculature is key to recognizing medullary lesion syndromes.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The medulla oblongata is the lowest part of the brainstem, connecting to the pons above and the spinal cord below.
- 🚀 It serves as a conduit for many essential ascending and descending nerve tracts.
- ❤️ It houses centers that control vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
- 🤖 It contains the nuclei of four cranial nerves: 9, 10, 11, and 12.
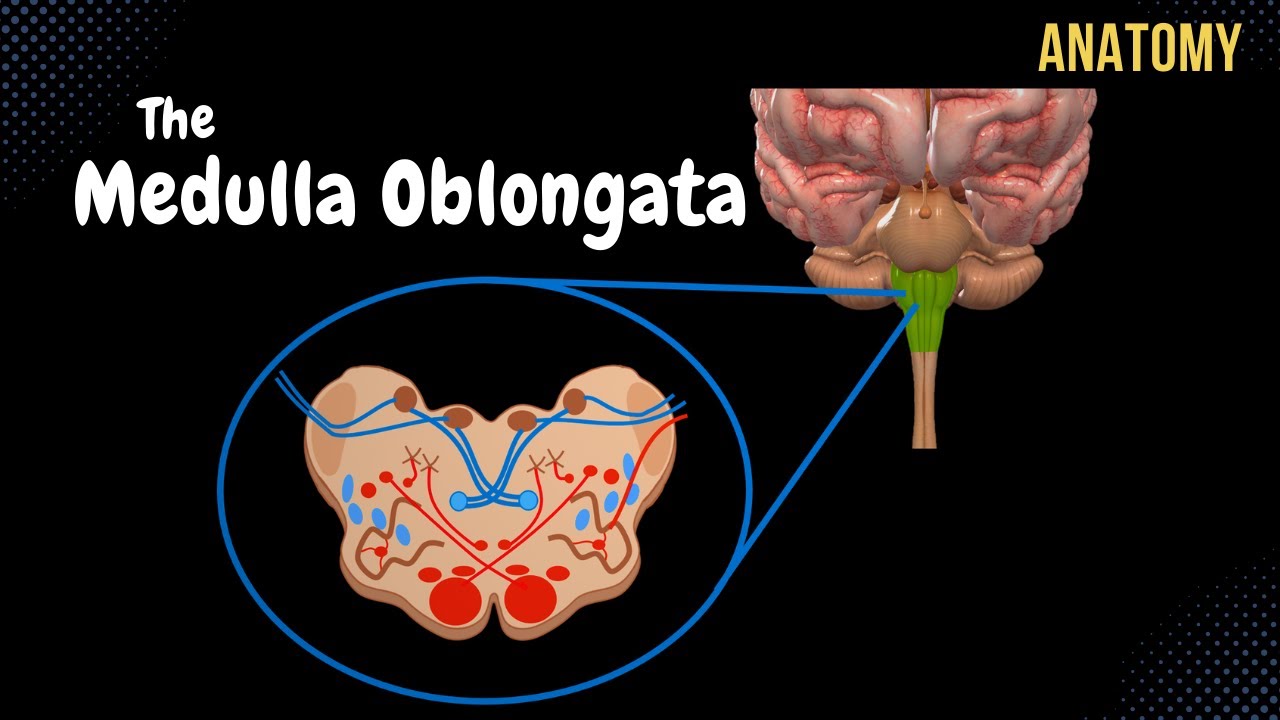
- 🌱 On the anterior surface, the midline features the anterior median fissure, and lateral to it are the ventral and posterolateral sulci.
- 🍇 The pyramids, composed of motor fibers, and the olives, containing the olivary nuclei, are significant lateral structures.
- 🔁 Posteriorly, the medulla has the posterior median sulcus and the gracilis and cuneate tubercles.
- 🧬 Internally, the medulla is divided into levels: pyramid decussation, medial lemniscus decussation, and the level of the olives and inferior cerebellar peduncles.
- 🔄 The decussation of the pyramids is where motor fibers cross from one side of the body to the other.
- 🧲 The decussation of the medial lemniscus is where sensory fibers cross, carrying information like touch and vibration.
- 🩸 The medulla's blood supply comes from the vertebral arteries, posterior spinal artery, anterior spinal artery, and the posterior inferior cerebellar artery.
Q & A
What is the medulla oblongata and its position in the brainstem?
-The medulla oblongata, also known as the medulla, is one of the three sections that make up the brainstem. It is the most inferior part of the brainstem, continuous with the pons above and the spinal cord below.
What are the primary functions of the medulla oblongata?
-The medulla oblongata serves as a conduit for many essential ascending and descending nerve tracts. It houses centers that control vital functions of the body such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure. It also contains the nuclei of four cranial nerves.
What are the key features of the anterior surface of the medulla?
-The anterior surface of the medulla features the anterior median fissure at the midline, which is continuous along the length of the spinal cord. Lateral to the midline are the ventral lateral sulcus and the posterolateral sulcus, where the pyramids are located. The olives, which are swellings containing the olivary nuclei, are found lateral to the pyramids.
What are the cranial nerves associated with the medulla oblongata?
-The medulla oblongata is associated with the last four cranial nerves: cranial nerves 9, 10, 11, and 12.
What is the significance of the posterior surface of the medulla oblongata?
-The posterior surface of the medulla has the posterior median sulcus at the midline, which conveys sensory input from most things below the neck, including the viscera. Lateral to the midline are the gracilis tubercle and the cuneate tubercle, which contain tracts that carry sensory information from the periphery to the brain.
What are the three levels of the medulla oblongata discussed in the script?
-The three levels of the medulla oblongata discussed are: the level of decussation of the pyramids, the level of decussation of the medial lemniscus, and the level of the olives and inferior cerebellar peduncles.
What is the function of the pyramids in the medulla oblongata?
-The pyramids are composed of bundles of motor fibers that make up the corticospinal tract, which carries motor fibers from the brain to the periphery.
What is the role of the olivary nuclei in the medulla oblongata?
-The olivary nuclei, located within the olives, play an important role in movement coordination and movement-related learning.
How does the central canal change at the level of the olives and inferior cerebellar peduncles?
-At the level of the olives and inferior cerebellar peduncles, the central canal expands into the fourth ventricle, making this region the open medulla.
What are the vital functions controlled by the centers located in the medulla oblongata?
-The medulla oblongata contains centers that control vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
What is the blood supply to the medulla oblongata?
-The blood supply to the medulla oblongata includes the vertebral arteries, posterior spinal artery, anterior spinal artery, and the posterior inferior cerebellar artery.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

2-Minute Neuroscience: The Brainstem

SISTEM KOORDINASI PADA MANUSIA - KELAS XI

Neuroscience Basics: Human Brain Anatomy and Lateralization of Brain Function, 3D Animation.

Brain: Parts & functions (Fore, mid & hind) | Control & Coordination | Biology | Khan Academy

Penjelasan Lengkap Bagian-Bagian Otak dan Fungsinya
Medulla Oblongata Anatomy - External & Internal (White & Grey matter) + QUIZ
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
