17. Inheritance (Part 1) (Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023, 2024 and 2025)
Summary
TLDRThis IGCSE study video explores the concept of inheritance, explaining how genetic information is passed via DNA in chromosomes. It covers gene functions, alleles, and sex determination. The video also delves into protein synthesis via DNA transcription and mRNA translation. It distinguishes between haploid and diploid cells, outlines mitosis for growth and repair, and contrasts it with meiosis for gamete production, emphasizing their roles in cell division and genetic diversity.
Takeaways
- 🧬 **Inheritance Defined**: Inheritance is the process by which genetic information is passed from parents to offspring through DNA.
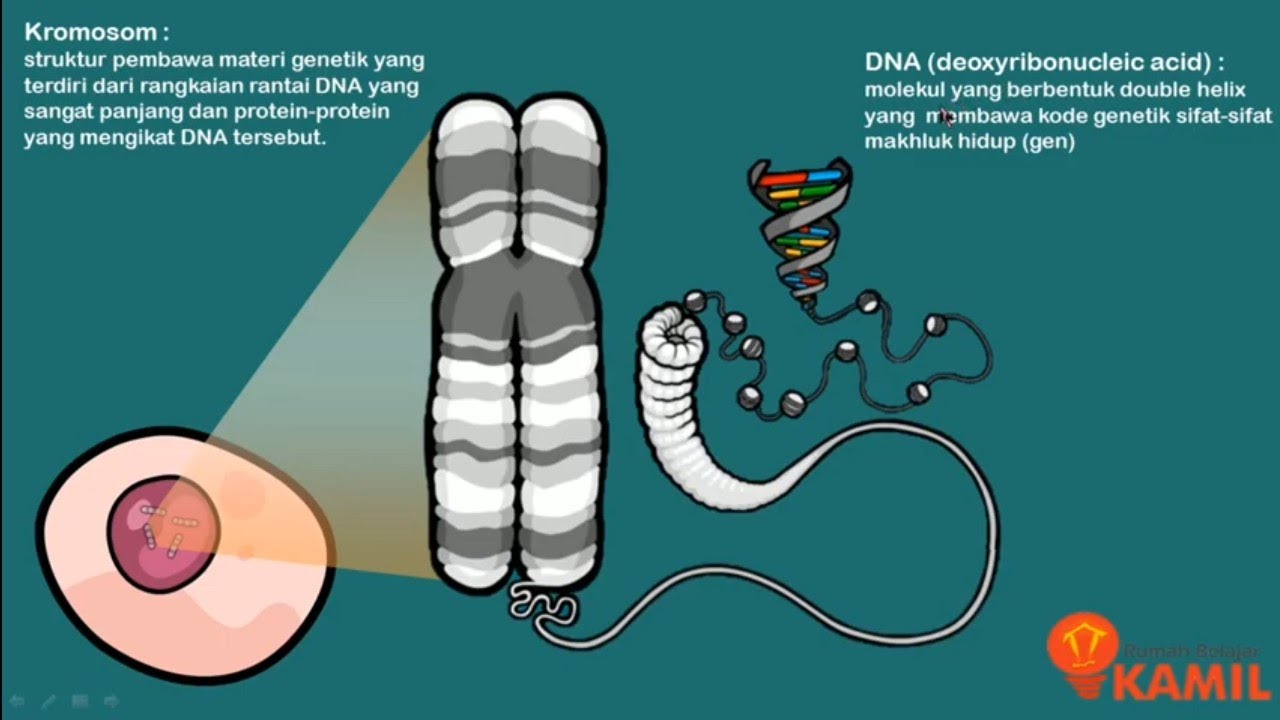
- 🧬 **DNA and Chromosomes**: DNA, carrying genetic information in genes, is located in the cell's chromosomes within the nucleus.
- 🧬 **Genes and Alleles**: Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins and specific traits. Alleles are different versions of the same gene leading to trait variations.
- 🧬 **Sex Determination**: Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes; the sex chromosomes (XX for females and XY for males) determine an individual's sex.
- 🧬 **Punnett Square**: A genetic diagram used to demonstrate inheritance, particularly sex inheritance, by showing possible outcomes of X and Y chromosome combinations.
- 🧬 **Protein Synthesis**: DNA provides instructions for making proteins, which are essential for various cell functions.
- 🧬 **Transcription and Translation**: The process of converting DNA sequences into proteins involves transcription (mRNA creation) and translation (amino acid assembly into proteins).
- 🧬 **Gene Expression**: Not all genes in a cell are expressed; cells produce only the proteins they need, switching genes on or off accordingly.
- 🧬 **Haploid and Diploid**: Haploid cells contain one set of chromosomes, while diploid cells have two sets, with humans having 23 pairs in diploid cells.
- 🧬 **Mitosis and Meiosis**: Mitosis is for growth and repair, producing genetically identical cells, while meiosis produces genetically different gametes with half the chromosome number.
Q & A
What is inheritance in the context of biology?
-Inheritance is the process by which genetic information is passed from parents to offspring.
How is genetic information carried from parents to offspring?
-Genetic information is carried in the form of DNA, which is located in the chromosomes of the cell.
What are chromosomes and where are they found?
-Chromosomes are structures made of DNA that contain genetic information. They are found in the nucleus of a cell.
What is a gene and what does it control?
-A gene is a length of DNA that codes for a protein. It contains instructions for specific traits or characteristics such as eye color or height.
What are alleles and how do they relate to traits?
-Alleles are different versions of the same gene that can lead to variations in the trait that the gene controls.
How does the inheritance of sex in humans work?
-Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, and one pair determines sex. Males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY), while females have two X chromosomes (XX).
What determines the sex of a baby?
-The sex of a baby depends on whether the sperm cell that fertilizes the egg contains an X or a Y chromosome.
What is the role of DNA in controlling cell function?
-DNA controls cell function by controlling the production of proteins, including enzymes, membrane carriers, and receptors for neurotransmitters.
How is a protein made according to the script?
-Proteins are made through a process involving transcription and translation. The gene is transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated into a protein by ribosomes.
What is the difference between haploid and diploid cells?
-A haploid cell contains a single set of chromosomes, while a diploid cell contains two sets of chromosomes.
What is mitosis and what is its role in growth and repair?
-Mitosis is a type of nuclear division that produces genetically identical cells. It plays a role in growth by increasing the size of organisms through cell production and in repair by promoting healing of damaged tissues.
How does meiosis differ from mitosis?
-Meiosis is a reduction division that halves the chromosome number from diploid to haploid, resulting in genetically different cells. It is involved in the production of gametes. Unlike mitosis, which produces two identical daughter cells, meiosis produces four genetically different haploid cells.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

BAB 6 PEWARISAN SIFAT DAN BIOTEKNOLOGI Part 1 (IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka)
IPA Kelas 9 : Pewarisan Sifat I (Materi Genetik : Kromosom, DNA dan RNA)

Introduction to Genetics and Shared Genes (Intro Psych Tutorial #37)

🧬 El ADN y el GENOMA | Explicación científica en 10 minutos 🧬

🧬 Kenapa Kita Mirip Orangtua Kita?

2 hubungan gen dna kromosom
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
