Traversing a Single Linked List (Counting the Nodes)
Summary
TLDRThis presentation teaches how to traverse a single linked list and count its nodes. It explains that traversal involves visiting each node until the end is reached. The script provides a step-by-step explanation of a program that uses a 'count_of_nodes' function to calculate the total number of nodes by iterating through the list using a pointer. It emphasizes the importance of creating the linked list before calling the function and concludes by hinting at an alternative method to be discussed in a future lecture.
Takeaways
- 🔍 **Traversing a Single Linked List**: Visiting each node of the list until the end node is reached.
- 📈 **Application of Traversal**: Counting the number of nodes in the list is a practical application of traversal.
- 💡 **Understanding the Concept**: Traversing means reaching every node using the head pointer until the end.
- 📝 **Program Structure**: The program includes necessary header files and a struct node, along with a main function.
- 🔧 **Function Usage**: The `count_of_nodes` function is used to count nodes by traversing the list.
- 🔑 **Head Pointer**: The head pointer is crucial as it points to the first node and is passed to the counting function.
- 🌐 **LinkedList Creation**: Before traversing, a single linked list must be created.
- 🔄 **Traversal Process**: The traversal loop continues until the pointer (`ptr`) becomes NULL, incrementing the count for each node visited.
- 📊 **Counting Mechanism**: A counter variable is used to keep track of the number of nodes visited.
- 📖 **Code Simplification**: There's mention of an alternative way to write the traversal code, to be discussed in a subsequent lecture.
Q & A
What does traversing a single linked list mean?
-Traversing a single linked list means visiting each node of the list until the end node is reached.
What is the purpose of traversing a linked list in the context of the presentation?
-The purpose of traversing a linked list in the presentation is to count the total number of nodes in the list.
What are the header files required for the program mentioned in the script?
-The header files required for the program are stdio.h and stdlib.h.
What is the significance of the 'head' pointer in the context of the script?
-The 'head' pointer is significant because it points to the first node of the linked list.
What does the 'count_of_nodes' function do?
-The 'count_of_nodes' function counts the number of nodes in the linked list by traversing it.
How is the 'count' variable used in the 'count_of_nodes' function?
-The 'count' variable is used to keep track of the number of nodes visited during the traversal of the linked list.
What does the condition 'if head is equal to NULL' imply in the script?
-The condition 'if head is equal to NULL' implies that the linked list is empty and has no nodes.
What is the role of the 'ptr' pointer in the traversal process?
-The 'ptr' pointer is used to traverse the list by pointing to each node and moving to the next node until it reaches the end of the list.
How does the while loop contribute to the traversal of the linked list?
-The while loop runs until 'ptr' becomes NULL, which means it continues to traverse the list until the end node is reached.
What is the output of the program when the linked list contains three nodes?
-The output of the program when the linked list contains three nodes is 'three', indicating that three nodes have been counted.
Is there an alternative way to write the code for counting nodes in a linked list as suggested in the script?
-Yes, the script suggests that there is another way to write the code for counting nodes in a linked list, which will be discussed in the next lecture.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
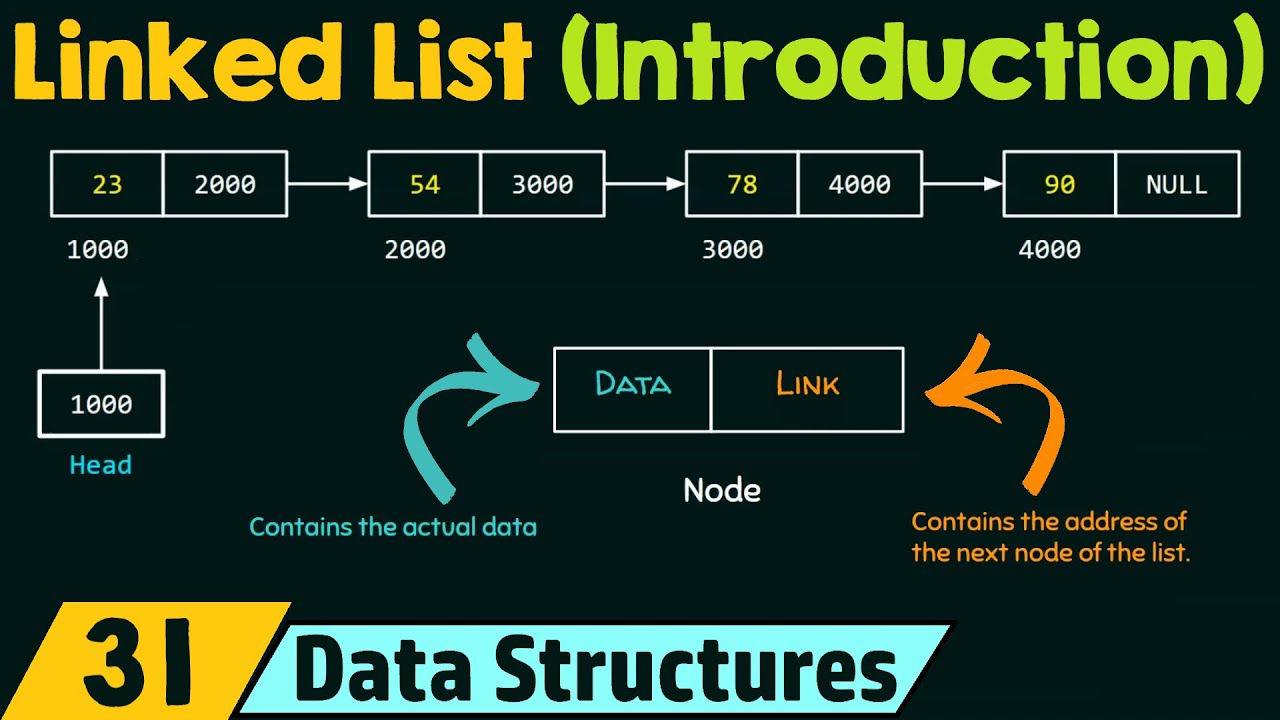
Introduction to Linked List
2- düğüm oluşturma , değer atama, düğümleri birbirine bağlama

10. INF-ED | Lista doblemente enlazada: explicación de la estructura de datos.

Introduction to Linked List | C++ Placement Course | Lecture 22
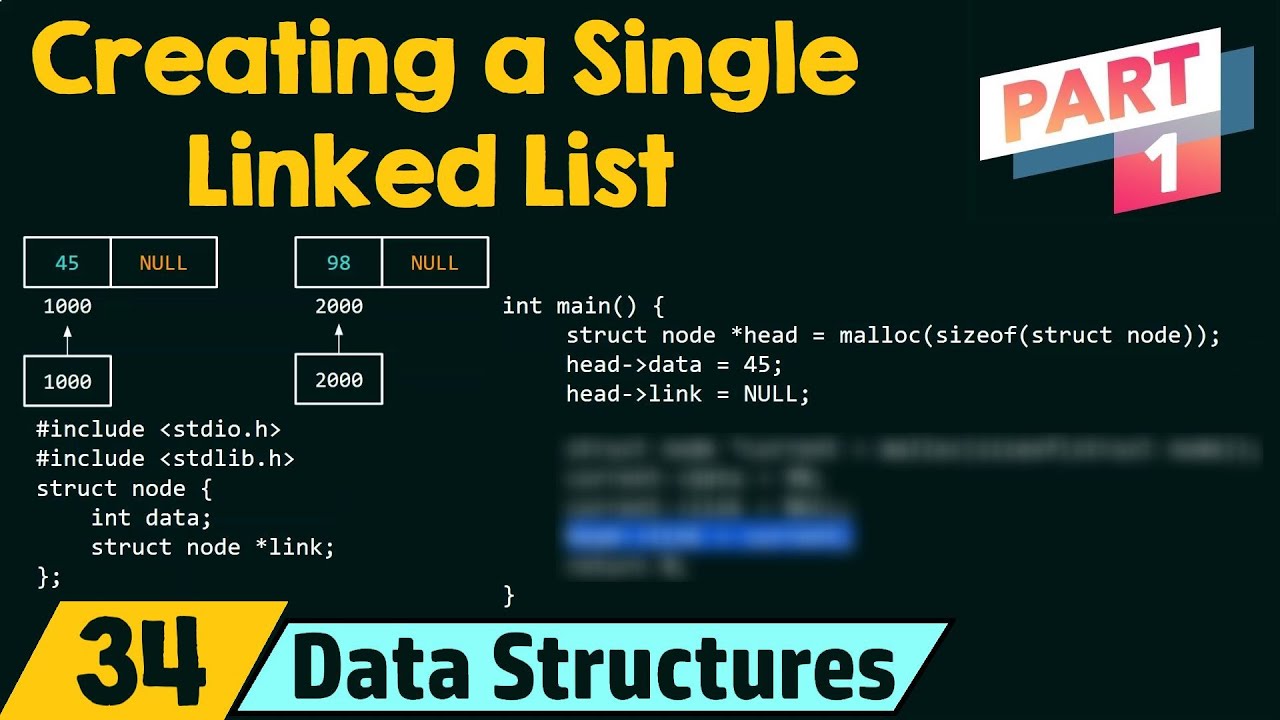
Creating a Single Linked List (Part 1)
Data Structures in Python: Doubly Linked Lists -- Add Node Before/After
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
