Basics of IP Addressing
Summary
TLDRThis lecture introduces the fundamentals of IP addressing, crucial for identifying devices in computer networks. It explains the difference between IPV4 and IPV6, focusing on IPV4's decimal-based, four-octet structure ranging from 0 to 255. The lecture also demonstrates how to view a device's IP address using the 'ipconfig' command and concludes with an exercise to distinguish between valid and invalid IP addresses, emphasizing the importance of each octet's range and the address's format.
Takeaways
- 🌐 **IP Address Basics**: An IP address is a unique identifier for devices on a computer network, allowing them to communicate over the internet.
- 📚 **Learning Outcomes**: By the end of the session, learners will understand IP addressing basics, how to view an IP address on a device, and how to identify valid and invalid IP addresses.
- 🔍 **IP Address Example**: The script uses an example of a computer with IP address 172.15.150.2 sending data to another with IP address 192.168.150.2 to illustrate the concept.
- 📈 **IP Address Types**: There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6, with the lecture focusing on IPv4 for the time being.
- 🏙️ **Logical Addresses**: IP addresses are considered logical because they can be changed based on the device's location or network.
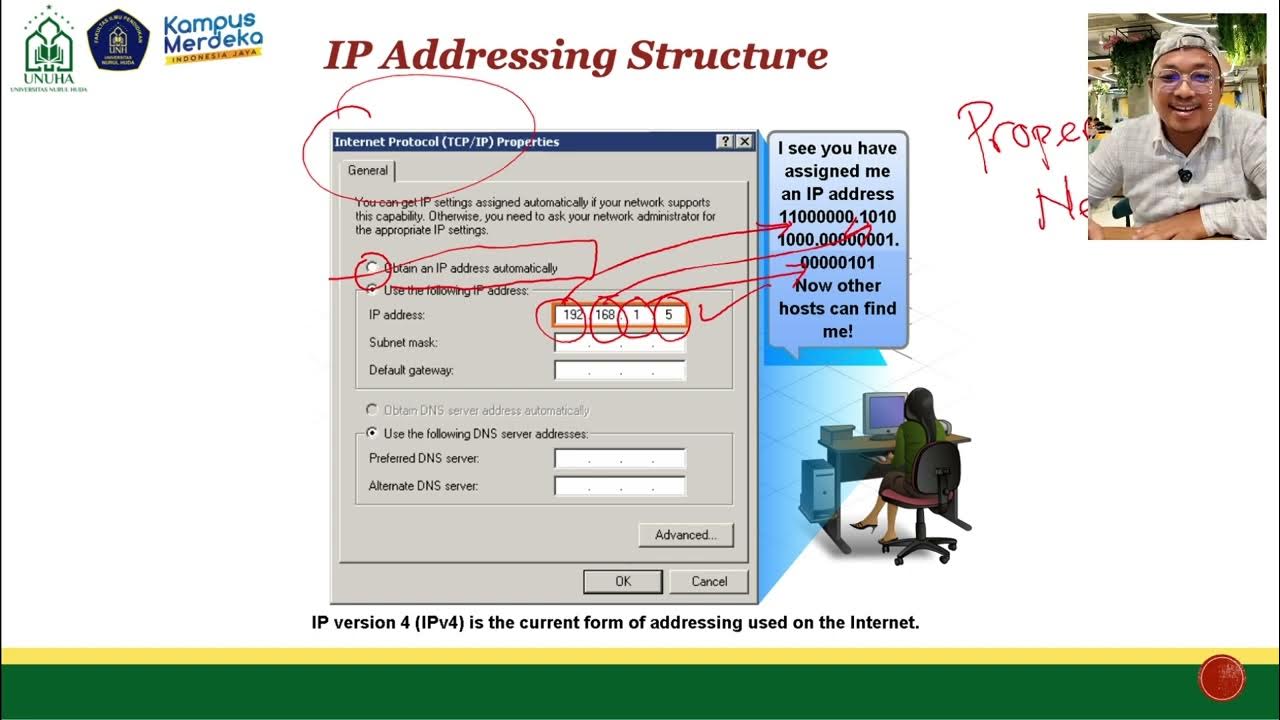
- 🔢 **IPv4 Address Structure**: IPv4 addresses are represented in decimal and consist of four octets (x.x.x.x), each ranging from 0 to 255.
- 💻 **Viewing IP Address**: To view an IP address on a Windows device, open the command prompt by typing 'cmd' in the start menu and then enter 'ipconfig'.
- 📋 **IP Address Identification**: The script provides an activity to identify valid and invalid IP addresses, emphasizing the importance of understanding IP address structure.
- ✅ **Valid IP Address Criteria**: A valid IP address must have four octets, each with a value between 0 and 255.
- ❌ **Invalid IP Address Criteria**: An IP address is invalid if it has more than four octets, any octet value exceeds 255, or if it contains non-decimal characters.
Q & A
What is the main topic of this lecture?
-The main topic of this lecture is the basics of IP addressing in computer networks.
What are the outcomes expected from this session on IP addressing?
-Upon completion, learners will understand the basics of IP addressing, know how to view an IP address on a real device, and be able to identify valid and invalid IP addresses.
What does IP stand for and why is it important?
-IP stands for Internet Protocol. It is important because it is used to identify every node in a computer network.
What are the two variations of IP addresses mentioned in the lecture?
-The two variations of IP addresses mentioned are IPv4 and IPv6.
What is a logical address and why are IP addresses considered logical?
-A logical address is an address that can be changed based on logic or location. IP addresses are considered logical because they can be changed based on the device's location and can be assigned manually or dynamically.
How are IPv4 addresses represented and what is the range of each octet?
-IPv4 addresses are represented in decimal and have four octets, with each octet taking a value between 0 and 255.
How can one view the IP address of their computer?
-To view the IP address of a computer, one can click the start menu, type 'cmd', press enter to open the command prompt, and then type 'ipconfig' to display the IP address.
What is the IPv4 address of the computer shown in the lecture?
-The IPv4 address of the computer shown in the lecture is 192.168.29.173.
What is the difference between a valid and an invalid IP address?
-A valid IP address has four octets, with each octet ranging from 0 to 255. An invalid IP address either has more or less than four octets, or contains values outside the 0 to 255 range.
Why is the IP address with the value '256' considered invalid?
-The IP address with the value '256' is considered invalid because each octet in an IPv4 address must be between 0 and 255, and 256 exceeds this range.
What is the reason why the IP address with '2e' is invalid?
-The IP address with '2e' is invalid because IPv4 addresses must be in decimal format, and 'e' is typically associated with hexadecimal notation, which is not allowed in IPv4 addresses.
How many total bits are there in every IPv4 address?
-There are 32 bits in every IPv4 address.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)