Endocrine Emergencies - Thyroid & Pituitary Disorders
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Professor Adam Thompson discusses endocrine disorders, focusing on growth hormone pathology, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and their various causes and symptoms. He covers conditions like gigantism, dwarfism, and thyroid diseases, including Graves' disease and Hashimoto's disease. The video also addresses emergencies like myxedema coma and thyroid storm, emphasizing the importance of recognizing and managing these life-threatening situations. Additionally, the professor touches on hyperparathyroidism, panhypopituitarism, and disorders of fluid regulation like diabetes insipidus and SIADH, providing a comprehensive overview of endocrine emergencies.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Growth hormone pathology involves over or under secretion from the anterior pituitary gland, leading to conditions like gigantism or dwarfism.
- 🔍 Over secretion of growth hormone results in acromegaly, typically diagnosed in young adulthood, while under secretion can lead to dwarfism.
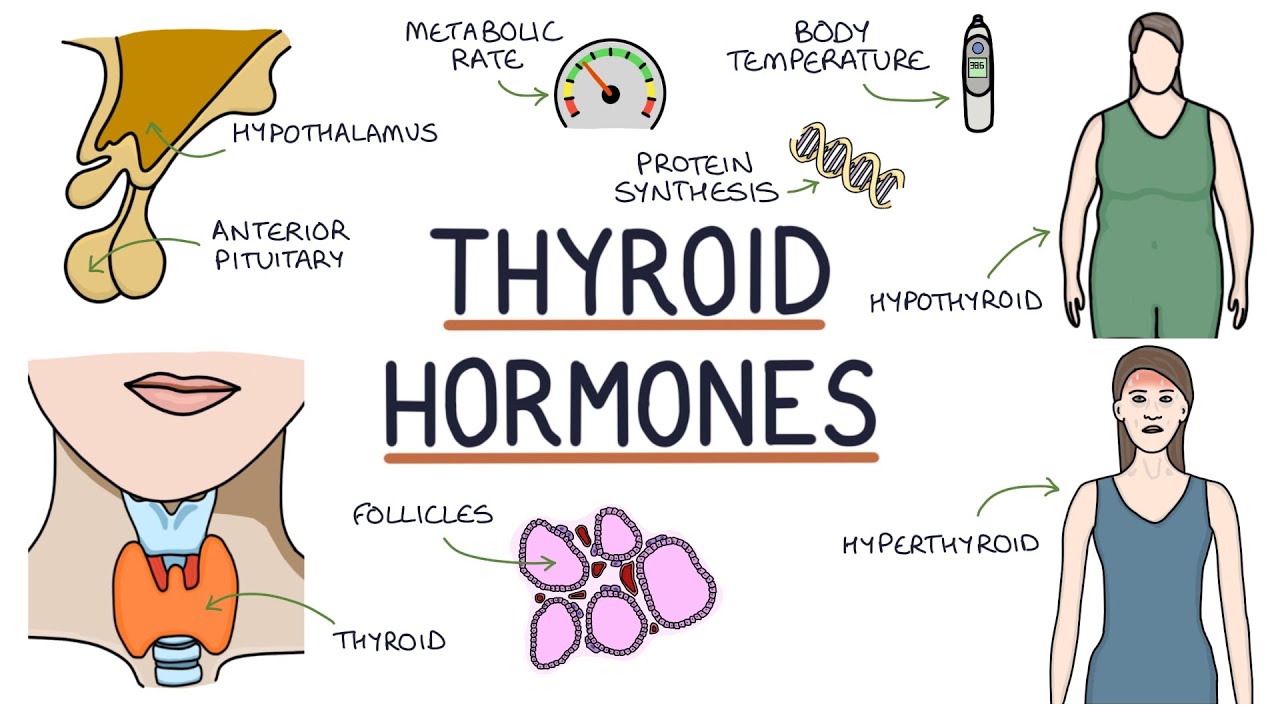
- 👤 Hypothyroidism is characterized by a decrease in metabolism, whereas hyperthyroidism leads to an increase in metabolism.
- 🚺 Graves disease is the most common type of hyperthyroidism, predominantly affecting women and can lead to a hypermetabolic state.
- 🏥 Untreated hyperthyroidism can be fatal, presenting symptoms like increased appetite, weight loss, and heart issues.
- 🧬 Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disorder causing hyperthyroidism and is more common in women.
- 🌡 Myxedema coma is a severe form of hypothyroidism, often triggered by cold exposure, infection, or surgery, and is marked by a slowing metabolic process.
- 💊 Treatment for endocrine emergencies like myxedema coma requires supportive care, including managing airway, breathing, and circulation.
- 🩺 Hyperparathyroidism is indicated by an increase in parathyroid hormone, leading to high blood calcium levels and potential kidney stones or bone thinning.
- 💧 Diabetes insipidus and SIADH are endocrine disorders involving the regulation of body fluids, with diabetes insipidus being caused by a lack of ADH and SIADH by an excess.
- 📊 The management of diabetes insipidus may include synthetic ADH, while SIADH may require loop diuretics and hypertonic fluids.
Q & A
What are the two main problems associated with growth hormone secretion?
-The two main problems associated with growth hormone secretion are over secretion and under secretion. Over secretion can lead to gigantism, while under secretion can result in dwarfism.
What is acromegaly and how is it diagnosed?
-Acromegaly is a condition resulting from over secretion of growth hormone, usually diagnosed in young adulthood. It presents with abnormally large hands and facial features.
What is the most common type of hyperthyroidism and how does it affect the body?
-Graves disease is the most common type of hyperthyroidism. It increases metabolism, leading to a hypermetabolic state, and can cause symptoms such as weight loss despite increased appetite, polydipsia, exophthalmos, and pretibial myxedema.
What are the potential complications of untreated hyperthyroidism?
-Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to heart failure due to the increased stress on the heart from the hypermetabolic state, along with tachycardia and increased blood pressure.
How does Hashimoto's disease differ from Graves disease?
-Hashimoto's disease is another cause of hypothyroidism, not hyperthyroidism, and it results in the infiltration of T lymphocytes and plasma cells, leading to a decrease in thyroid function.
What is myxedema coma and what are its common triggers?
-Myxedema coma is a life-threatening condition characterized by a severe decline in mental status due to hypothyroidism. It is often triggered by factors such as infection, exposure to cold, trauma, surgery, or certain medications.
What is the typical demographic for myxedema coma and when does it usually occur?
-Myxedema coma typically occurs in women over the age of 60, usually during the winter season, due to the extreme cold.
What are the treatment considerations for a patient in myxedema coma?
-Treatment for myxedema coma includes supportive care such as monitoring and managing airway, breathing, and circulation, treating hypothermia with passive rewarming, and avoiding sedatives, narcotics, and anesthetics if possible.
What is the difference between diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus?
-While both conditions involve increased urination, diabetes insipidus is caused by a lack of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) leading to increased diuresis, whereas diabetes mellitus is a pancreatic pathology with high glucose levels in the urine.
What are the potential risks associated with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)?
-SIADH can cause fluid retention, leading to hypertension, tachycardia, hyponatremia, seizures, and confusion due to an excess of ADH.
How does hyperparathyroidism affect blood calcium levels and what are its common symptoms?
-Hyperparathyroidism is marked by an increase in parathyroid hormone, leading to hypercalcemia (increased blood calcium levels) and decreased phosphate levels. Symptoms can include fatigue, weakness, nausea, vomiting, confusion, and pathologic fractures.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)