What is RDBMS? full Explanation | Learn Coding | #rdbms
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the concept of a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) and how it organizes data in rows and columns. It defines key terms like entity, attribute, record, degree, cardinality, and domain with a practical example of a student table. The speaker demonstrates how to create a table, insert records, and retrieve data using Oracle 11g, with commands like `CREATE TABLE` and `INSERT INTO`. It offers a practical approach to understanding RDBMS and provides a link to a detailed SQL tutorial in the video description.
Takeaways
- 📚 RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System, where data is organized in rows and columns.
- 🔢 In RDBMS, data is stored in a tabular format, with rows representing records and columns representing attributes.
- 📝 Key technical terms in RDBMS include Entity (Table), Attribute (Column), Record (Row), Degree (Number of Columns), Cardinality (Number of Rows), and Domain (Column Values).
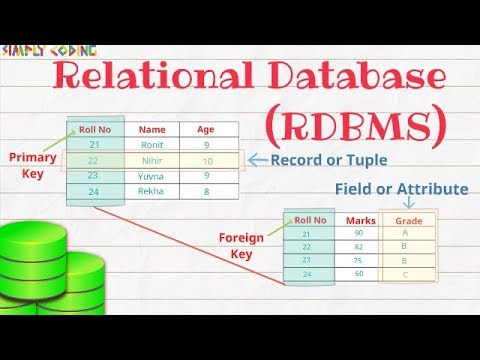
- 🧑🎓 The example used is a 'Student Details' table with rows and columns illustrating how data is stored.
- 📊 The term 'Entity' refers to the table itself, and 'Attribute' refers to the columns within the table.
- 🎓 The degree of a table is the total number of columns, while cardinality is the total number of rows.
- 🔍 The 'Domain' refers to the possible values that a column can hold, like names in a 'Student' table.
- 💻 The practical demonstration included creating a table, defining its structure, and inserting records using SQL commands.
- 👨💻 The example SQL database used was Oracle 11g, but MySQL and PostgreSQL could also be used.
- 📺 For a detailed understanding of SQL and RDBMS, viewers are encouraged to check out the complete playlist linked in the video's description.
Q & A
What is RDBMS?
-RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System, and it organizes data in a tabular format with rows and columns.
How is data stored in an RDBMS?
-Data is stored in a tabular form, meaning it is arranged in rows and columns within tables in the database.
What is an entity in RDBMS?
-An entity in RDBMS refers to a table, such as 'Student Details' which holds data in a structured format.
What are attributes in an RDBMS table?
-Attributes in an RDBMS table are the columns that define the data types and values, such as 'Name' or 'Age' in a 'Student Details' table.
What does 'record' mean in RDBMS terminology?
-A record represents a single row in the table, containing all the corresponding data for a particular entry.
What is the 'degree' of a table?
-The degree of a table refers to the total number of columns present in the table.
What does 'cardinality' mean in the context of RDBMS?
-Cardinality represents the total number of rows in the table.
What is a 'domain' in RDBMS?
-The domain refers to the possible values that an attribute (column) can have. For example, the domain of the 'Name' column might include 'Ankit', 'Ankush', and 'Akhil'.
What is a schema in RDBMS?
-A schema is the structure that defines the organization of data in a table, including the columns, their data types, and relationships.
How do you insert data into an RDBMS table?
-To insert data, SQL insert queries are used. The script demonstrates this by inserting three records into the 'Student' table.
What SQL command is used to view the structure of a table?
-The 'DESC' (describe) command is used to view the structure of a table, showing all its columns and data types.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Introduction to Relational Data Model

Relational Data Model in DBMS in Hindi | Advantages & Disadvantages - Lecture #5

Introduction to Relational Databases

Was ist ein Relationales Datenbankmodell? - einfach erklärt!

Lec-5: What is Schema | How to define Schema | Database management system in Hindi
Relational Database
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
