Cytoskeleton Structure and Function
Summary
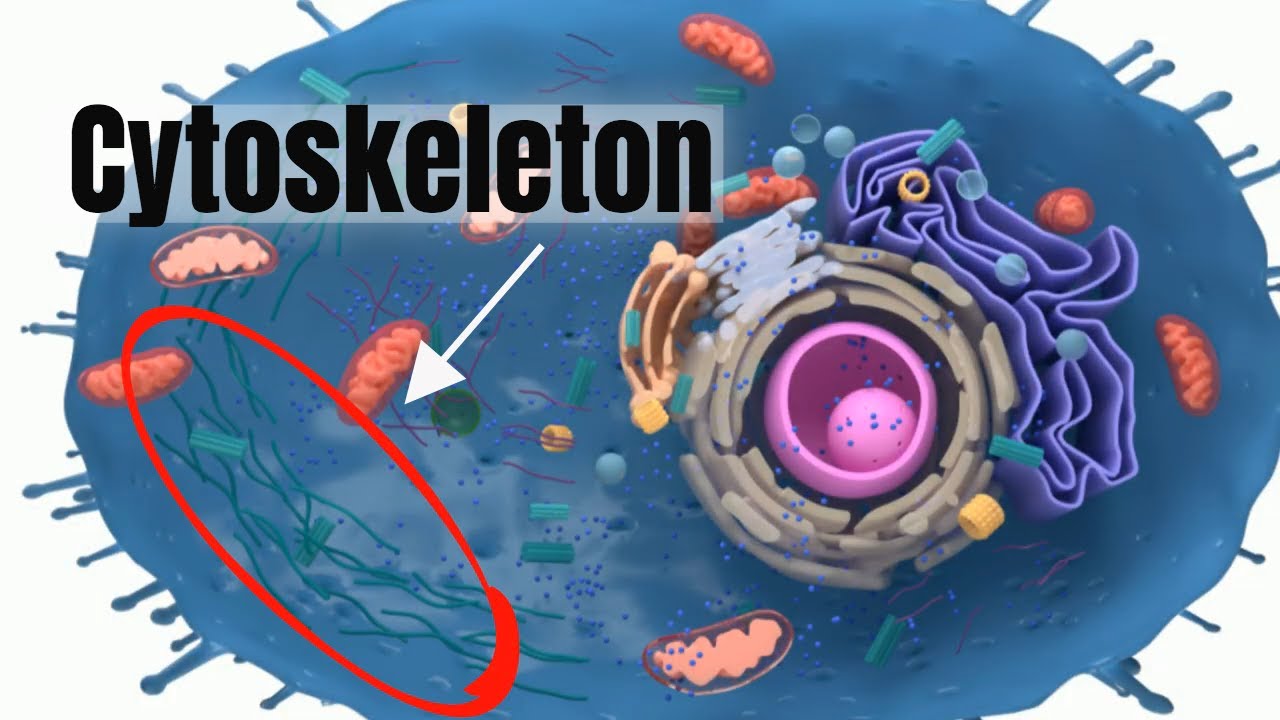
TLDRThis video delves into the cytoskeleton's critical role in cell function, highlighting its three main components: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. Microtubules, the largest, maintain cell shape and facilitate intracellular transport and cell division. Microfilaments, composed of actin, are crucial for cell movement and muscle contraction. Intermediate filaments, with their unique protein composition, provide stability and anchor organelles. Together, these elements ensure cell integrity and mobility across various eukaryotic cells.
Takeaways
- 🌀 The cytoskeleton is crucial for cell function, providing shape, movement, and anchorage.
- 🔬 Microtubules are the largest cytoskeletal structures, composed of alpha- and beta-tubulin, forming a strong, hollow tube that resists compression.
- 🚚 Microtubules act as a transport system within cells, guiding the movement of organelles and vesicles via motor proteins.
- 🔴 Microtubules play a critical role in cell division, helping to separate chromosomes and ensuring proper cell division.
- 🏃 Cilia and flagella, which are composed of microtubules, enable cell motility and are essential for various bodily functions.
- 🧬 Microfilaments, composed of actin polymers, maintain cell shape and are key to changing cell shape through interaction with myosin filaments.
- 🏋️♂️ Microfilaments facilitate cell movement by extending and deforming the cell, as seen in amoebas using pseudopodia for locomotion.
- 🌱 In plants, microfilaments enable cytoplasmic streaming, which aids in the movement of chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
- 🔗 Intermediate filaments, with a diameter intermediate between microtubules and microfilaments, provide stability and anchor organelles within the cell.
- 🛡️ The nuclear lamina, made of intermediate filaments called lamins, offers structural support and regulates nuclear activities.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the cytoskeleton in cells?
-The cytoskeleton provides shape, movement, and anchorage for cells, and it is essential to their function.
What are the three types of cytoskeletal elements mentioned in the script?
-The three types of cytoskeletal elements are microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments.
What are microtubules composed of, and what is their role in maintaining cell shape?
-Microtubules are composed of pairs of tubulin protein molecules, alpha-tubulin and beta-tubulin. They maintain the overall shape of the cell, acting like steel beams in a building to prevent collapse.
How do microtubules function as a transport system within the cell?
-Microtubules form a network that allows organelles and vesicles to move around the cell via motor proteins that travel along the microtubules, similar to a railroad track.
What role do microtubules play during cell division?
-Microtubules anchor to kinetochores on chromosomes and shorten to pull chromosome pairs apart during cell division.
How are cilia and flagella related to microtubules, and what are their functions?
-Cilia and flagella are short and long bundles of microtubules, respectively. They can beat in a wave-like motion to move cells or fluid around cells, and in the case of flagella, they can propel or pull cells in one direction.
What are microfilaments made of, and how do they contribute to cell shape and movement?
-Microfilaments are made of two intertwined strands of actin polymers. They help maintain cell shape and are key to changing cell shape, allowing for cell motility through mechanisms like the extension of pseudopodia in amoebas.
How do microfilaments assist in cell division?
-After mitosis, actin filaments form a ring around the center of the cell, which constricts to pinch the cell into two new cells.
What is unique about the composition of intermediate filaments?
-Intermediate filaments are not defined by a single monomer composition but by their size, which is intermediate between that of microtubules and microfilaments. They are composed of various types of proteins.
What is the primary function of intermediate filaments in terms of cell stability?
-Intermediate filaments provide stability to the cell and are excellent anchors for organelles that do not need to move. They also form the nuclear lamina, providing structural support and regulating nuclear activities.
How do the cytoskeletal elements collectively contribute to eukaryotic cells?
-The cytoskeletal elements, including microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, provide structure and mobility for eukaryotic cells, maintaining cell shape, facilitating cell division, and anchoring organelles.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)