Reference Frames
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the concept of reference frames in physics, crucial for describing an object's motion. It explains that velocity is always relative to something, the reference frame. Using examples of John and Sally, it illustrates how to calculate velocities relative to the ground and to each other. The script also covers scenarios on a moving train, showing how to determine velocities using formulas and a common reference frame, emphasizing the importance of understanding reference frames in motion analysis.
Takeaways
- 📏 Reference frames are essential for discussing an object's motion, as they provide a point of comparison for velocity or movement.
- 🌐 The ground is commonly used as a default reference frame when one is not specified.
- 🚀 An object's velocity is always relative to its chosen reference frame, which could be another moving object.
- 🔄 Velocity can be positive or negative depending on the direction relative to the reference frame.
- 🚶♂️ John's velocity relative to the ground is calculated by adding his walking speed to the train's speed if they are moving in the same direction.
- 🚶♀️ Sally's velocity relative to the ground is found by adding her walking speed to the train's speed, considering her direction is opposite to the train's.
- 🤔 The relative velocity between two objects can be determined by subtracting their velocities with respect to the ground.
- 🧮 The formula for relative velocity is V(AB) = V(A) - V(B), where V(AB) is the velocity of object A relative to object B.
- 🚄 When calculating velocities, it's crucial to consider the direction of movement and whether to add or subtract the values.
- 🔄 Changing reference frames can provide different perspectives on the same motion, but the mathematical relationships remain consistent.
Q & A
Why are reference frames important in discussing motion?
-Reference frames are important because they provide a point of comparison when discussing an object's motion, such as its velocity. They allow us to describe how fast an object is moving relative to something else, which is necessary for understanding motion.
What is the default reference frame when one is not specified?
-When a reference frame is not specified, it is typically assumed to be the ground.
How does the velocity of an object change when described relative to different reference frames?
-The velocity of an object can appear different when described relative to different reference frames. For example, a car moving at 20 meters per second relative to a bus might have a different velocity when described relative to the ground.
What is the relationship between John's velocity and Sally's velocity when both are moving relative to the ground?
-When John is moving at 2 miles per hour and Sally is moving at 3 miles per hour relative to the ground, Sally's velocity relative to John (v_s_j) is 1 mile per hour, as she is moving faster than John.
How can you calculate the velocity of one object relative to another using a formula?
-The velocity of one object relative to another can be calculated using the formula: V_object1_relative_to_object2 = V_object1_relative_to_ground - V_object2_relative_to_ground.
What is the significance of a negative velocity in the context of reference frames?
-A negative velocity indicates that an object is moving in the opposite direction relative to the reference frame. For example, if Sally is moving west while the train is moving east, her velocity relative to the train would be negative.
How does the motion of a train affect the velocities of people walking on it relative to the ground?
-The velocities of people walking on a moving train relative to the ground are the sum of their velocities relative to the train and the train's velocity relative to the ground, depending on whether they are walking in the same or opposite direction as the train.
What is the formula to calculate an object's velocity relative to the ground when it is moving on a vehicle?
-The formula to calculate an object's velocity relative to the ground when it is on a moving vehicle is: V_object_ground = V_object_vehicle + V_vehicle_ground.
Why does the reference frame chosen affect the perceived velocity of an object?
-The reference frame chosen affects the perceived velocity of an object because it determines what the object is being compared against. Different reference frames can yield different velocities for the same object.
How can you determine the velocity of one person relative to another when both are moving on a train?
-To determine the velocity of one person relative to another on a train, you can use the formula: V_person1_relative_to_person2 = V_person1_ground - V_person2_ground, using the ground as a common reference frame.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
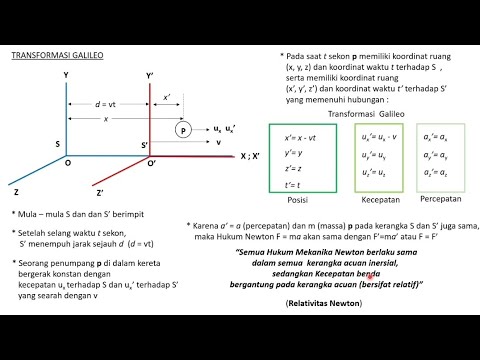
Teori Relativitas Khusus: 2. Transformasi Galileo

Relativity 101a: Introduction to Galilean Relativity

1. Eulerian and Lagrangian Descriptions in Fluid Mechanics
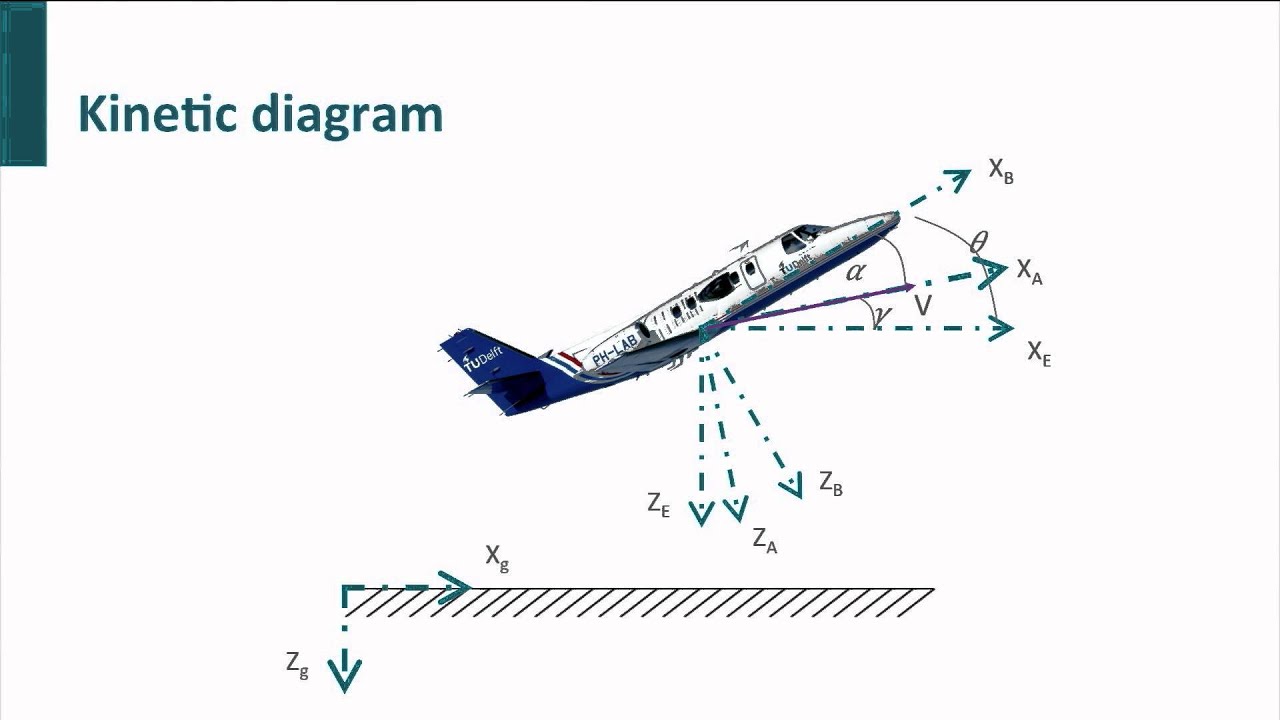
AE1110x - W09_1b - Equations of Motion

Breakthrough Junior Challenge 2017 | Relativity & The Equivalence of Reference Frames

Frames of Reference (1960)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
