IGCSE ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 5 OCEAN AND FISHERIES
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into ocean and fisheries management, highlighting key ocean resources like marine organisms, chemicals, building materials, energy, and tourism. It explains the role of ocean currents in fish distribution, focusing on the impact of warm and cold currents. The El Niño Southern Oscillation's influence on fisheries is explored, detailing how it alters weather patterns and fish populations. The video also addresses the consequences of overfishing, bycatch, and pollution, and discusses sustainable strategies like mariculture, aquaculture, and management practices to conserve marine life.
Takeaways
- 🌊 Oceans are vital resources providing food, chemicals like salt, building materials such as sand, wave and tidal energy for electricity, tourism, and transportation for international trade.
- 🐟 Fisheries are significant for food security, and understanding ocean currents is crucial for predicting fish distribution.
- 📍 Warm and cold ocean currents affect fish distribution; warm currents move away from the equator, while cold currents move towards it.
- 🌡️ The continental shelf is a key area for high fish populations due to factors like shallow depth, more oxygen, sunlight, and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
- 🌐 The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon can reverse normal weather patterns, impacting fish distribution and causing issues like flooding or drought.
- 🔄 Upwelling, the rising of deep ocean currents to the surface, brings nutrients that support high fish populations, especially along coasts with cold currents.
- 🌡️ Cold currents are typically nutrient-rich and support higher fish populations compared to warm currents, which are less nutrient-rich.
- ⚠️ Overfishing leads to a decrease in fish populations and biodiversity, and it can result in the extinction of certain species.
- 🚫 Bycatch, the unintended capture of non-target species, contributes to overfishing and can lead to the decline of marine species populations.
- 🌱 Aquaculture and mariculture can help reduce the pressure on wild fish stocks by cultivating marine organisms for food and other products.
- 🛡️ Strategies for managing marine species include mesh size regulation, fishing quotas, closed seasons, protected areas, and international agreements to prevent overfishing.
Q & A
What are the major resources found within the ocean?
-The major resources found within the ocean include food such as marine organisms, chemicals like salt, building materials such as sand, wave and tidal energy for electricity generation, tourism, and transportation through ships and vessels.
How can ocean water be made suitable for drinking?
-Ocean water can be made suitable for drinking through the process of desalination, which involves the removal of salt content found within the water.
What is the difference between warm and cold ocean currents?
-Warm ocean currents flow from the equator upward, moving away from the equator, while cold ocean currents move towards the equator. Warm currents are typically associated with higher temperatures, higher salinity, and lower nutrient levels, whereas cold currents are denser, have lower temperatures, and are usually rich in nutrients due to upwelling.
Why are continental shelves important for marine life?
-Continental shelves are important for marine life because they are shallow areas with more oxygen, sunlight, and carbon dioxide, which allows for photosynthesis. This results in a higher food supply, supporting a greater population of marine organisms.
How does the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) affect fisheries?
-During an El Niño year, the equatorial trade winds change direction and move eastward, leading to increased rainfall and flooding in South America, and reduced upwelling of nutrient-rich water, which decreases fish populations. Conversely, in a normal year, the warm currents move westward, leading to high rainfall in Australia and high fish populations in South America due to upwelling.
What is overfishing and what are its consequences?
-Overfishing occurs when more fish are caught than the population can replace through natural reproduction, leading to a reduction in biodiversity and potential extinction of some fish species. It can also cause pollution of marine waters due to oil leakages and noise pollution from fishing vessels.
What is bycatch and why is it a problem?
-Bycatch refers to the unintentional capture of non-target species during fishing activities. It is a problem because it can lead to the unnecessary death of marine life that is not intended for consumption or sale, contributing to overfishing and biodiversity loss.
How can mariculture and aquaculture help reduce the impact of overfishing?
-Mariculture and aquaculture involve the cultivation of marine organisms in open ocean enclosures or tanks using ocean water. These practices can help reduce the impact of overfishing by providing an alternative source of fish and other marine species, thus decreasing the pressure on wild fish populations.
What strategies can be used to manage and conserve marine species?
-Strategies to manage and conserve marine species include using appropriate net and mesh sizes to allow for the growth and breeding of fish, implementing fishing quotas, establishing closed seasons, creating protected areas and reserves, enacting legislative and conservation laws, and participating in international agreements to monitor and reduce overfishing.
Why are protected areas and reserves important for marine conservation?
-Protected areas and reserves are important for marine conservation as they provide safe habitats for marine species, allowing them to breed and recover from overfishing. These areas are often chosen for their ecological and cultural significance, and they help maintain biodiversity and ecological balance.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Ruang Laut Indonesia

Pengantar Oseanografi - Biological Oceanography (part 1)

Materi Pembelajaran - GEOGRAFI kls XI Karakteristik Wilayah Daratan dan perairan Indonesia baru

Pemanfaatan Sumber Daya Alam di Indonesia

Pengantar Oseanografi - Marine Ecosystem (part 1)
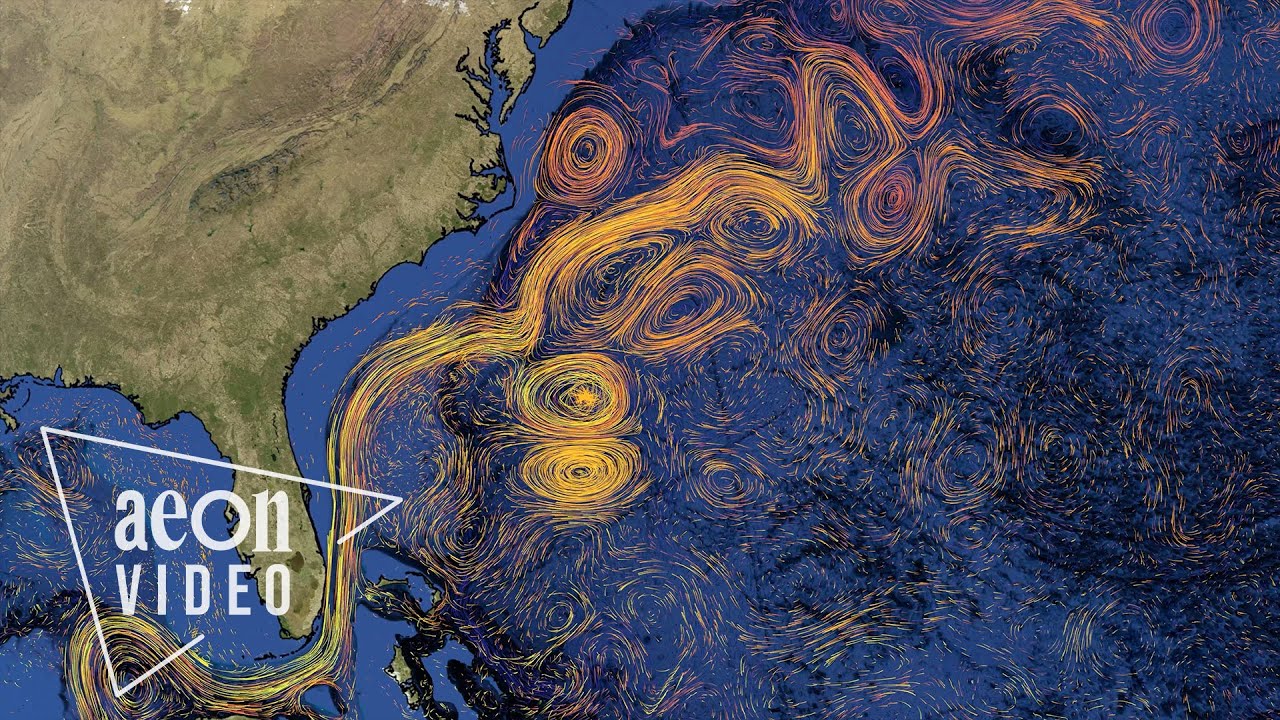
Visualising the intricate circulatory system of our oceans | An Ocean in Motion
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
